Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) 题解(ABCDE) (二分,dfs序,数据结构)
2017-03-07 19:59
676 查看
A. Andryusha and Socks
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Andryusha is an orderly boy and likes to keep things in their place.
Today he faced a problem to put his socks in the wardrobe. He has n distinct pairs of socks which are initially in a bag. The pairs
are numbered from 1 to n.
Andryusha wants to put paired socks together and put them in the wardrobe. He takes the socks one by one from the bag, and for each sock he looks whether the pair of this sock has been already took out of the bag, or not. If not (that means the pair of this
sock is still in the bag), he puts the current socks on the table in front of him. Otherwise, he puts both socks from the pair to the wardrobe.
Andryusha remembers the order in which he took the socks from the bag. Can you tell him what is the maximum number of socks that were on the table at the same time?
Input
The first line contains the single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) —
the number of sock pairs.
The second line contains 2n integers x1, x2, ..., x2n (1 ≤ xi ≤ n),
which describe the order in which Andryusha took the socks from the bag. More precisely, xi means
that the i-th sock Andryusha took out was from pair xi.
It is guaranteed that Andryusha took exactly two socks of each pair.
Output
Print single integer — the maximum number of socks that were on the table at the same time.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first example Andryusha took a sock from the first pair and put it on the table. Then he took the next sock which is from the first pair as well, so he immediately puts both socks to the wardrobe. Thus, at most one sock was on the table at the same time.
In the second example Andryusha behaved as follows:
Initially the table was empty, he took out a sock from pair 2 and put it on the table.
Sock (2) was on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 1 and
put it on the table.
Socks (1, 2) were on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 1,
and put this pair into the wardrobe.
Sock (2) was on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 3 and
put it on the table.
Socks (2, 3) were on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 2,
and put this pair into the wardrobe.
Sock (3) was on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 3 and
put this pair into the wardrobe.
Thus, at most two socks were on the table at the same time.
太水了不说了,直接判断已经是否已经出现这种袜子然后模拟一下就行。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 200000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
int a[MAXN];
int vis[MAXN] = { 0 };
int main() {
int n;
while (scanf("%d", &n)!=EOF) {
int cnt = 0;
int MAX = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 2*n; i++) {
scanf("%d", a + i);
if (vis[a[i]]) {
cnt--;
}
else {
cnt++;
vis[a[i]] = 1;
}
MAX = max(MAX, cnt);
}
printf("%d\n", MAX);
}
}
B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed
time limit per test
5 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
The main road in Bytecity is a straight line from south to north. Conveniently, there are coordinates measured in meters from the southernmost building in north direction.
At some points on the road there are n friends, and i-th
of them is standing at the point xi meters
and can move with any speed no greater than vi meters
per second in any of the two directions along the road: south or north.
You are to compute the minimum time needed to gather all the n friends at some point on the road. Note that the point they meet at
doesn't need to have integer coordinate.
Input
The first line contains single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 60 000) —
the number of friends.
The second line contains n integers x1, x2, ..., xn (1 ≤ xi ≤ 109) —
the current coordinates of the friends, in meters.
The third line contains n integers v1, v2, ..., vn (1 ≤ vi ≤ 109) —
the maximum speeds of the friends, in meters per second.
Output
Print the minimum time (in seconds) needed for all the n friends to meet at some point on the road.
Your answer will be considered correct, if its absolute or relative error isn't greater than 10 - 6.
Formally, let your answer be a, while jury's answer be b.
Your answer will be considered correct if
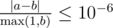
holds.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first sample, all friends can gather at the point 5 within 2 seconds.
In order to achieve this, the first friend should go south all the time at his maximum speed, while the second and the third friends should go north at their maximum speeds.
有很多个人去一个地方约会,给出地点和速度,问最小时间。
这种最小值的问题想一想应该是用二分。
二分之间,判断每个人到达范围,看是不是有交集即可。
注意用次数二分
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 200000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
double x[MAXN], v[MAXN];
double sum[MAXN];
int n;
struct node {
double x;
double v;
}a[MAXN];
int cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.x < b.x;
}
bool C(double t) {
double l = -1, r = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
double len = t*a[i].v;
if (l == -1) {
l = a[i].x - len;
r = a[i].x + len;
}
else {
l = max(l, a[i].x - len);
r = min(r, a[i].x + len);
}
}
if (r < l)
return false;
else
return true;
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
double res = INF;
double s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%lf", x + i);
a[i].x = x[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%lf", v + i);
a[i].v = v[i];
}
sort(a+1, a + n + 1,cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + 1.0 / a[i].v;
}
/*double temp=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
double ans = 0;
if (i == 1) {
for (int j = 2; j <= n; j++) {
ans += (a[j].x - a[i].x) / a[j].v;
}
}
else {
ans = temp + (sum[i - 1] + sum[i] - sum
-1.0/a[i].v)*(a[i].x - a[i - 1].x);
}
temp = ans;
res = min(ans, res);
}
printf("%.12f\n", res);*/
double lb = 0, rb = INF;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
double m = (lb + rb) /2;
if (C(m))
rb = m;
else
lb = m;
}
printf("%.12f\n", rb);
}
}
C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Andryusha goes through a park each day. The squares and paths between them look boring to Andryusha, so he decided to decorate them.
The park consists of n squares connected with (n - 1) bidirectional
paths in such a way that any square is reachable from any other using these paths. Andryusha decided to hang a colored balloon at each of the squares. The baloons' colors are described by positive integers, starting from 1.
In order to make the park varicolored, Andryusha wants to choose the colors in a special way. More precisely, he wants to use such colors that if a, b and c are
distinct squares that a and b have
a direct path between them, and b and c have
a direct path between them, then balloon colors on these three squares are distinct.
Andryusha wants to use as little different colors as possible. Help him to choose the colors!
Input
The first line contains single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) —
the number of squares in the park.
Each of the next (n - 1) lines contains two integers x and y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n) —
the indices of two squares directly connected by a path.
It is guaranteed that any square is reachable from any other using the paths.
Output
In the first line print single integer k — the minimum number of colors Andryusha has to use.
In the second line print n integers, the i-th
of them should be equal to the balloon color on the i-th square. Each of these numbers should be within range from 1 to k.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first sample the park consists of three squares: 1 → 3 → 2. Thus, the balloon colors have to be distinct.
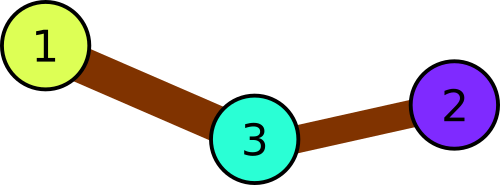
Illustration
for the first sample.
In the second example there are following triples of consequently connected squares:
1 → 3 → 2
1 → 3 → 4
1 → 3 → 5
2 → 3 → 4
2 → 3 → 5
4 → 3 → 5
We can see that each pair of squares is encountered in some triple, so all colors have to be distinct.
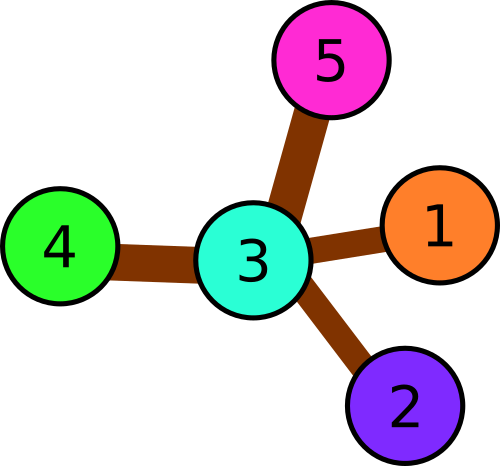
Illustration
for the second sample.
In the third example there are following triples:
1 → 2 → 3
2 → 3 → 4
3 → 4 → 5
We can see that one or two colors is not enough, but there is an answer that uses three colors only.
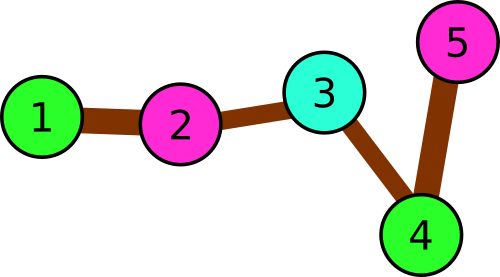
Illustration
for the third sample.
给一棵树染色,三个相连的点必须是不同的颜色。求染色方案。
每一个点不能和它的兄弟节点和父亲节点和父亲的父亲节点相同。顺着下来染就行。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 200000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
struct edge {
int v,next;
}e[MAXN<<1];
int head[MAXN] = { -1 };
int tot = 0;
int c[MAXN];
void add(int u, int v) { e[tot].v = v; e[tot].next = head[u]; head[u] = tot++; }
int res = 0;
int p[MAXN];
int son[MAXN];
void dfs(int u,int pre) {
for (int k = head[u]; k != -1; k = e[k].next) {
int v = e[k].v;
if (v != pre) {
p[v] = u;
dfs(v, u);
}
}
}
void solve(int u) {
int cur = 1;
for (int k = head[u]; k != -1; k = e[k].next) {
int v = e[k].v;
if (v != p[u]) {
while (cur == c[u] || cur == c[p[u]]) {
cur++;
}
c[v] = cur++;
}
}
for (int k = head[u]; k != -1; k = e[k].next) {
int v = e[k].v;
if (v != p[u]) {
solve(v);
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int u, v;
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add(u, v);
add(v, u);
}
p[1] = 0;
dfs(1,0);
c[0] = 0;
c[1] = 1;
res = 1;
solve(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
res = max(res, c[i]);
printf("%d\n", res);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("%d%c", c[i], i == n ? '\n' : ' ');
}
}
}
D. Innokenty and a Football League
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Innokenty is a president of a new football league in Byteland. The first task he should do is to assign short names to all clubs to be shown on TV next to the score. Of course, the short names should be distinct, and Innokenty wants that all short names consist
of three letters.
Each club's full name consist of two words: the team's name and the hometown's name, for example, "DINAMO BYTECITY". Innokenty doesn't want to assign strange
short names, so he wants to choose such short names for each club that:
the short name is the same as three first letters of the team's name, for example, for the mentioned club it is "DIN",
or, the first two letters of the short name should be the same as the first two letters of the team's name, while the third letter is the same as the first letter in the hometown's name. For the mentioned club it is "DIB".
Apart from this, there is a rule that if for some club x the second option of short name is chosen, then there should be no club, for
which the first option is chosen which is the same as the first option for the club x. For example, if the above mentioned club has
short name "DIB", then no club for which the first option is chosen can have short name equal to "DIN".
However, it is possible that some club have short name "DIN", where "DI"
are the first two letters of the team's name, and "N" is the first letter of hometown's name. Of course, no two teams can have the same short name.
Help Innokenty to choose a short name for each of the teams. If this is impossible, report that. If there are multiple answer, any of them will suit Innokenty. If for some team the two options of short name are equal, then Innokenty will formally think that
only one of these options is chosen.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000) —
the number of clubs in the league.
Each of the next n lines contains two words — the team's name and the hometown's name for some club. Both team's name and hometown's
name consist of uppercase English letters and have length at least 3 and at most 20.
Output
It it is not possible to choose short names and satisfy all constraints, print a single line "NO".
Otherwise, in the first line print "YES". Then print n lines,
in each line print the chosen short name for the corresponding club. Print the clubs in the same order as they appeared in input.
If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first sample Innokenty can choose first option for both clubs.
In the second example it is not possible to choose short names, because it is not possible that one club has first option, and the other has second option if the first options are equal for both clubs.
In the third example Innokenty can choose the second options for the first two clubs, and the first option for the third club.
In the fourth example note that it is possible that the chosen short name for some club x is the same as the first option of another
club yif the first options of x and y are
different.
有很多只队伍,每个队伍有队伍名和家乡名。有两种命名方式,分别是取队伍名的前三个字母,或者队伍名的前两个字母加上家乡名的前一个字母。
并且如果某两个队伍第一种命名方式冲突则必须使用第二种命名方式。
先把第一种命名方式相同的队伍找出来以第二种方式命名,然后处理第一种命名方式不冲突的队伍。相当于贪心。
(不过我的代码有错。。过不了大数据,也不知道为啥)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 1000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
int n;
struct node{
string s, t;
string res;
int u, v;
int no;
}st[MAXN];
int cmp1(node a, node b) {
if (a.s == b.s)
return a.t < b.t;
return a.s < b.s;
}
int cmp2(node a, node b) {
return a.no < b.no;
}
int vis[MAXN];
int ok = 1;
void solve(int l, int r) {
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
st[i].res = st[i].t;
vis[i] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (vis[j]&&st[j].res == st[i].res) {
ok = 0;
return;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> st[i].s >> st[i].t;
st[i].s = st[i].s.substr(0, 3);
st[i].t = st[i].s.substr(0, 2)+st[i].t[0];
st[i].no = i;
}
sort(st, st + n,cmp1);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
int pre = 0;;
for (int i = 0; i < n&&ok; i++) {
if (st[i].s != st[i+1].s) {
if (i > pre) {
solve(pre, i);
}
pre = i + 1;
}
}
if (ok == 0) {
puts("NO");
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n&&ok; i++) {
if (vis[i])
continue;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i != j && st[i].s == st[j].res) {
if (vis[j]) {
st[i].res = st[i].t;
vis[i] = 1;
}
}
}
if (!vis[i]) {
st[i].res = st[i].s;
vis[i] = 1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n&&ok; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i != j&&st[i].res == st[j].res) {
ok = 0;
break;
}
}
}
if (!ok) {
puts("NO");
continue;
}
puts("YES");
sort(st, st + n, cmp2);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << st[i].res << endl;
}
}
}
E. Underground Lab
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
The evil Bumbershoot corporation produces clones for gruesome experiments in a vast underground lab. On one occasion, the corp cloned a boy Andryusha who was smarter than his comrades. Immediately Andryusha understood that something fishy was going on there.
He rallied fellow clones to go on a feud against the evil corp, and they set out to find an exit from the lab. The corp had to reduce to destroy the lab complex.
The lab can be pictured as a connected graph with n vertices and m edges. k clones
of Andryusha start looking for an exit in some of the vertices. Each clone can traverse any edge once per second. Any number of clones are allowed to be at any vertex simultaneously. Each clone is allowed to stop looking at any time moment, but he must look
at his starting vertex at least. The exit can be located at any vertex of the lab, hence each vertex must be visited by at least one clone.
Each clone can visit at most

vertices
before the lab explodes.
Your task is to choose starting vertices and searching routes for the clones. Each route can have at most

vertices.
Input
The first line contains three integers n, m,
and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105, n - 1 ≤ m ≤ 2·105, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) —
the number of vertices and edges in the lab, and the number of clones.
Each of the next m lines contains two integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ n) —
indices of vertices connected by the respective edge. The graph is allowed to have self-loops and multiple edges.
The graph is guaranteed to be connected.
Output
You should print k lines. i-th
of these lines must start with an integer ci (
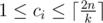
) —
the number of vertices visited by i-th clone, followed by ci integers —
indices of vertices visited by this clone in the order of visiting. You have to print each vertex every time it is visited, regardless if it was visited earlier or not.
It is guaranteed that a valid answer exists.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first sample case there is only one clone who may visit vertices in order (2, 1, 3), which fits the constraint of 6 vertices per clone.
In the second sample case the two clones can visited vertices in order (2, 1, 3) and (4, 1, 5), which fits the constraint of 5 vertices per clone.
超级水的一道E。
有一个n点m边的图,有k个人,每个人每秒可以走一条边,每个人走过的边数不小于2*n/k向上取整。
直接dfs序,然后划分一下就行。
太水了= =
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 400000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m, k;
int head[MAXN];
int tot = 0;
struct edge {
int v,next;
}e[MAXN<<1];
void add(int u, int v) {
e[tot].v = v;
e[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
}
int res[MAXN];
int vis[MAXN];
int num = 0;
void dfs(int u) {
res[++num] = u;
vis[u] = 1;
for (int k = head[u]; k != -1; k = e[k].next) {
int v = e[k].v;
if (!vis[v]) {
dfs(v);
res[++num] = u;
}
}
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k) != EOF) {
int u, v;
num = 0;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int u, v;
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add(u, v);
add(v, u);
}
dfs(1);
int ans = (2 * n + k - 1)/k;
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
temp = min(ans, num);
if (temp == 0) {
printf("1 1\n");
continue;
}
printf("%d", temp);
for (int i = 0; i < temp; i++) {
printf(" %d", res[num--]);
if (num == 0)
break;
}
puts("");
}
}
}
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Andryusha is an orderly boy and likes to keep things in their place.
Today he faced a problem to put his socks in the wardrobe. He has n distinct pairs of socks which are initially in a bag. The pairs
are numbered from 1 to n.
Andryusha wants to put paired socks together and put them in the wardrobe. He takes the socks one by one from the bag, and for each sock he looks whether the pair of this sock has been already took out of the bag, or not. If not (that means the pair of this
sock is still in the bag), he puts the current socks on the table in front of him. Otherwise, he puts both socks from the pair to the wardrobe.
Andryusha remembers the order in which he took the socks from the bag. Can you tell him what is the maximum number of socks that were on the table at the same time?
Input
The first line contains the single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) —
the number of sock pairs.
The second line contains 2n integers x1, x2, ..., x2n (1 ≤ xi ≤ n),
which describe the order in which Andryusha took the socks from the bag. More precisely, xi means
that the i-th sock Andryusha took out was from pair xi.
It is guaranteed that Andryusha took exactly two socks of each pair.
Output
Print single integer — the maximum number of socks that were on the table at the same time.
Examples
input
1 1 1
output
1
input
3 2 1 1 3 2 3
output
2
Note
In the first example Andryusha took a sock from the first pair and put it on the table. Then he took the next sock which is from the first pair as well, so he immediately puts both socks to the wardrobe. Thus, at most one sock was on the table at the same time.
In the second example Andryusha behaved as follows:
Initially the table was empty, he took out a sock from pair 2 and put it on the table.
Sock (2) was on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 1 and
put it on the table.
Socks (1, 2) were on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 1,
and put this pair into the wardrobe.
Sock (2) was on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 3 and
put it on the table.
Socks (2, 3) were on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 2,
and put this pair into the wardrobe.
Sock (3) was on the table. Andryusha took out a sock from pair 3 and
put this pair into the wardrobe.
Thus, at most two socks were on the table at the same time.
太水了不说了,直接判断已经是否已经出现这种袜子然后模拟一下就行。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 200000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
int a[MAXN];
int vis[MAXN] = { 0 };
int main() {
int n;
while (scanf("%d", &n)!=EOF) {
int cnt = 0;
int MAX = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 2*n; i++) {
scanf("%d", a + i);
if (vis[a[i]]) {
cnt--;
}
else {
cnt++;
vis[a[i]] = 1;
}
MAX = max(MAX, cnt);
}
printf("%d\n", MAX);
}
}
B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed
time limit per test
5 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
The main road in Bytecity is a straight line from south to north. Conveniently, there are coordinates measured in meters from the southernmost building in north direction.
At some points on the road there are n friends, and i-th
of them is standing at the point xi meters
and can move with any speed no greater than vi meters
per second in any of the two directions along the road: south or north.
You are to compute the minimum time needed to gather all the n friends at some point on the road. Note that the point they meet at
doesn't need to have integer coordinate.
Input
The first line contains single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 60 000) —
the number of friends.
The second line contains n integers x1, x2, ..., xn (1 ≤ xi ≤ 109) —
the current coordinates of the friends, in meters.
The third line contains n integers v1, v2, ..., vn (1 ≤ vi ≤ 109) —
the maximum speeds of the friends, in meters per second.
Output
Print the minimum time (in seconds) needed for all the n friends to meet at some point on the road.
Your answer will be considered correct, if its absolute or relative error isn't greater than 10 - 6.
Formally, let your answer be a, while jury's answer be b.
Your answer will be considered correct if
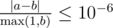
holds.
Examples
input
3
7 1 3
1 2 1
output
2.000000000000
input
4
5 10 3 22 3 2 4
output
1.400000000000
Note
In the first sample, all friends can gather at the point 5 within 2 seconds.
In order to achieve this, the first friend should go south all the time at his maximum speed, while the second and the third friends should go north at their maximum speeds.
有很多个人去一个地方约会,给出地点和速度,问最小时间。
这种最小值的问题想一想应该是用二分。
二分之间,判断每个人到达范围,看是不是有交集即可。
注意用次数二分
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 200000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
double x[MAXN], v[MAXN];
double sum[MAXN];
int n;
struct node {
double x;
double v;
}a[MAXN];
int cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.x < b.x;
}
bool C(double t) {
double l = -1, r = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
double len = t*a[i].v;
if (l == -1) {
l = a[i].x - len;
r = a[i].x + len;
}
else {
l = max(l, a[i].x - len);
r = min(r, a[i].x + len);
}
}
if (r < l)
return false;
else
return true;
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
double res = INF;
double s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%lf", x + i);
a[i].x = x[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%lf", v + i);
a[i].v = v[i];
}
sort(a+1, a + n + 1,cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + 1.0 / a[i].v;
}
/*double temp=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
double ans = 0;
if (i == 1) {
for (int j = 2; j <= n; j++) {
ans += (a[j].x - a[i].x) / a[j].v;
}
}
else {
ans = temp + (sum[i - 1] + sum[i] - sum
-1.0/a[i].v)*(a[i].x - a[i - 1].x);
}
temp = ans;
res = min(ans, res);
}
printf("%.12f\n", res);*/
double lb = 0, rb = INF;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
double m = (lb + rb) /2;
if (C(m))
rb = m;
else
lb = m;
}
printf("%.12f\n", rb);
}
}
C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Andryusha goes through a park each day. The squares and paths between them look boring to Andryusha, so he decided to decorate them.
The park consists of n squares connected with (n - 1) bidirectional
paths in such a way that any square is reachable from any other using these paths. Andryusha decided to hang a colored balloon at each of the squares. The baloons' colors are described by positive integers, starting from 1.
In order to make the park varicolored, Andryusha wants to choose the colors in a special way. More precisely, he wants to use such colors that if a, b and c are
distinct squares that a and b have
a direct path between them, and b and c have
a direct path between them, then balloon colors on these three squares are distinct.
Andryusha wants to use as little different colors as possible. Help him to choose the colors!
Input
The first line contains single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) —
the number of squares in the park.
Each of the next (n - 1) lines contains two integers x and y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n) —
the indices of two squares directly connected by a path.
It is guaranteed that any square is reachable from any other using the paths.
Output
In the first line print single integer k — the minimum number of colors Andryusha has to use.
In the second line print n integers, the i-th
of them should be equal to the balloon color on the i-th square. Each of these numbers should be within range from 1 to k.
Examples
input
3 2 3 1 3
output
3 1 3 2
input
5 2 3 5 3 4 3 1 3
output
5 1 3 2 5 4
input
5
2 13 24 3
5 4
output
3 1 2 3 1 2
Note
In the first sample the park consists of three squares: 1 → 3 → 2. Thus, the balloon colors have to be distinct.

Illustration
for the first sample.
In the second example there are following triples of consequently connected squares:
1 → 3 → 2
1 → 3 → 4
1 → 3 → 5
2 → 3 → 4
2 → 3 → 5
4 → 3 → 5
We can see that each pair of squares is encountered in some triple, so all colors have to be distinct.

Illustration
for the second sample.
In the third example there are following triples:
1 → 2 → 3
2 → 3 → 4
3 → 4 → 5
We can see that one or two colors is not enough, but there is an answer that uses three colors only.

Illustration
for the third sample.
给一棵树染色,三个相连的点必须是不同的颜色。求染色方案。
每一个点不能和它的兄弟节点和父亲节点和父亲的父亲节点相同。顺着下来染就行。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 200000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
struct edge {
int v,next;
}e[MAXN<<1];
int head[MAXN] = { -1 };
int tot = 0;
int c[MAXN];
void add(int u, int v) { e[tot].v = v; e[tot].next = head[u]; head[u] = tot++; }
int res = 0;
int p[MAXN];
int son[MAXN];
void dfs(int u,int pre) {
for (int k = head[u]; k != -1; k = e[k].next) {
int v = e[k].v;
if (v != pre) {
p[v] = u;
dfs(v, u);
}
}
}
void solve(int u) {
int cur = 1;
for (int k = head[u]; k != -1; k = e[k].next) {
int v = e[k].v;
if (v != p[u]) {
while (cur == c[u] || cur == c[p[u]]) {
cur++;
}
c[v] = cur++;
}
}
for (int k = head[u]; k != -1; k = e[k].next) {
int v = e[k].v;
if (v != p[u]) {
solve(v);
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int u, v;
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add(u, v);
add(v, u);
}
p[1] = 0;
dfs(1,0);
c[0] = 0;
c[1] = 1;
res = 1;
solve(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
res = max(res, c[i]);
printf("%d\n", res);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("%d%c", c[i], i == n ? '\n' : ' ');
}
}
}
D. Innokenty and a Football League
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Innokenty is a president of a new football league in Byteland. The first task he should do is to assign short names to all clubs to be shown on TV next to the score. Of course, the short names should be distinct, and Innokenty wants that all short names consist
of three letters.
Each club's full name consist of two words: the team's name and the hometown's name, for example, "DINAMO BYTECITY". Innokenty doesn't want to assign strange
short names, so he wants to choose such short names for each club that:
the short name is the same as three first letters of the team's name, for example, for the mentioned club it is "DIN",
or, the first two letters of the short name should be the same as the first two letters of the team's name, while the third letter is the same as the first letter in the hometown's name. For the mentioned club it is "DIB".
Apart from this, there is a rule that if for some club x the second option of short name is chosen, then there should be no club, for
which the first option is chosen which is the same as the first option for the club x. For example, if the above mentioned club has
short name "DIB", then no club for which the first option is chosen can have short name equal to "DIN".
However, it is possible that some club have short name "DIN", where "DI"
are the first two letters of the team's name, and "N" is the first letter of hometown's name. Of course, no two teams can have the same short name.
Help Innokenty to choose a short name for each of the teams. If this is impossible, report that. If there are multiple answer, any of them will suit Innokenty. If for some team the two options of short name are equal, then Innokenty will formally think that
only one of these options is chosen.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000) —
the number of clubs in the league.
Each of the next n lines contains two words — the team's name and the hometown's name for some club. Both team's name and hometown's
name consist of uppercase English letters and have length at least 3 and at most 20.
Output
It it is not possible to choose short names and satisfy all constraints, print a single line "NO".
Otherwise, in the first line print "YES". Then print n lines,
in each line print the chosen short name for the corresponding club. Print the clubs in the same order as they appeared in input.
If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
Examples
input
2DINAMO BYTECITY
FOOTBALL MOSCOW
output
YES DIN FOO
input
2DINAMO BYTECITY
DINAMO BITECITY
output
NO
input
3 PLAYFOOTBALL MOSCOW PLAYVOLLEYBALL SPB GOGO TECHNOCUP
output
YES PLM PLS GOG
input
3 ABC DEF ABC EFG ABD OOO
output
YES ABD ABE ABO
Note
In the first sample Innokenty can choose first option for both clubs.
In the second example it is not possible to choose short names, because it is not possible that one club has first option, and the other has second option if the first options are equal for both clubs.
In the third example Innokenty can choose the second options for the first two clubs, and the first option for the third club.
In the fourth example note that it is possible that the chosen short name for some club x is the same as the first option of another
club yif the first options of x and y are
different.
有很多只队伍,每个队伍有队伍名和家乡名。有两种命名方式,分别是取队伍名的前三个字母,或者队伍名的前两个字母加上家乡名的前一个字母。
并且如果某两个队伍第一种命名方式冲突则必须使用第二种命名方式。
先把第一种命名方式相同的队伍找出来以第二种方式命名,然后处理第一种命名方式不冲突的队伍。相当于贪心。
(不过我的代码有错。。过不了大数据,也不知道为啥)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 1000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
int n;
struct node{
string s, t;
string res;
int u, v;
int no;
}st[MAXN];
int cmp1(node a, node b) {
if (a.s == b.s)
return a.t < b.t;
return a.s < b.s;
}
int cmp2(node a, node b) {
return a.no < b.no;
}
int vis[MAXN];
int ok = 1;
void solve(int l, int r) {
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
st[i].res = st[i].t;
vis[i] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (vis[j]&&st[j].res == st[i].res) {
ok = 0;
return;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> st[i].s >> st[i].t;
st[i].s = st[i].s.substr(0, 3);
st[i].t = st[i].s.substr(0, 2)+st[i].t[0];
st[i].no = i;
}
sort(st, st + n,cmp1);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
int pre = 0;;
for (int i = 0; i < n&&ok; i++) {
if (st[i].s != st[i+1].s) {
if (i > pre) {
solve(pre, i);
}
pre = i + 1;
}
}
if (ok == 0) {
puts("NO");
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n&&ok; i++) {
if (vis[i])
continue;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i != j && st[i].s == st[j].res) {
if (vis[j]) {
st[i].res = st[i].t;
vis[i] = 1;
}
}
}
if (!vis[i]) {
st[i].res = st[i].s;
vis[i] = 1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n&&ok; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i != j&&st[i].res == st[j].res) {
ok = 0;
break;
}
}
}
if (!ok) {
puts("NO");
continue;
}
puts("YES");
sort(st, st + n, cmp2);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << st[i].res << endl;
}
}
}
E. Underground Lab
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
The evil Bumbershoot corporation produces clones for gruesome experiments in a vast underground lab. On one occasion, the corp cloned a boy Andryusha who was smarter than his comrades. Immediately Andryusha understood that something fishy was going on there.
He rallied fellow clones to go on a feud against the evil corp, and they set out to find an exit from the lab. The corp had to reduce to destroy the lab complex.
The lab can be pictured as a connected graph with n vertices and m edges. k clones
of Andryusha start looking for an exit in some of the vertices. Each clone can traverse any edge once per second. Any number of clones are allowed to be at any vertex simultaneously. Each clone is allowed to stop looking at any time moment, but he must look
at his starting vertex at least. The exit can be located at any vertex of the lab, hence each vertex must be visited by at least one clone.
Each clone can visit at most

vertices
before the lab explodes.
Your task is to choose starting vertices and searching routes for the clones. Each route can have at most

vertices.
Input
The first line contains three integers n, m,
and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105, n - 1 ≤ m ≤ 2·105, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) —
the number of vertices and edges in the lab, and the number of clones.
Each of the next m lines contains two integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ n) —
indices of vertices connected by the respective edge. The graph is allowed to have self-loops and multiple edges.
The graph is guaranteed to be connected.
Output
You should print k lines. i-th
of these lines must start with an integer ci (
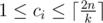
) —
the number of vertices visited by i-th clone, followed by ci integers —
indices of vertices visited by this clone in the order of visiting. You have to print each vertex every time it is visited, regardless if it was visited earlier or not.
It is guaranteed that a valid answer exists.
Examples
input
3 2 12 13 1
output
3 2 1 3
input
5 4 21 21 3
1 4
1 5
output
3 2 1 33 4 1 5
Note
In the first sample case there is only one clone who may visit vertices in order (2, 1, 3), which fits the constraint of 6 vertices per clone.
In the second sample case the two clones can visited vertices in order (2, 1, 3) and (4, 1, 5), which fits the constraint of 5 vertices per clone.
超级水的一道E。
有一个n点m边的图,有k个人,每个人每秒可以走一条边,每个人走过的边数不小于2*n/k向上取整。
直接dfs序,然后划分一下就行。
太水了= =
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 400000 + 10;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m, k;
int head[MAXN];
int tot = 0;
struct edge {
int v,next;
}e[MAXN<<1];
void add(int u, int v) {
e[tot].v = v;
e[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
}
int res[MAXN];
int vis[MAXN];
int num = 0;
void dfs(int u) {
res[++num] = u;
vis[u] = 1;
for (int k = head[u]; k != -1; k = e[k].next) {
int v = e[k].v;
if (!vis[v]) {
dfs(v);
res[++num] = u;
}
}
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k) != EOF) {
int u, v;
num = 0;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int u, v;
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add(u, v);
add(v, u);
}
dfs(1);
int ans = (2 * n + k - 1)/k;
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
temp = min(ans, num);
if (temp == 0) {
printf("1 1\n");
continue;
}
printf("%d", temp);
for (int i = 0; i < temp; i++) {
printf(" %d", res[num--]);
if (num == 0)
break;
}
puts("");
}
}
}
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) C (dfs+vector)
- 【贪心】【DFS】Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Change
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals)A模拟 B三分 C dfs D map
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals)
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals )D. Innokenty and a Football League(2-sat)
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) D. Innokenty and a Football League
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 1, based on Technocup 2017 Finals)
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) E Underground Lab
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals)
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals)A,B,C
- [Updating]Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals)解题报告
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) B.(三分)
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals)
- 【解题报告】Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals)
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals)【A,B,C】
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) B.(三分)
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals
- Codeforces Round #409 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2017 Round 2) 题解【ABCDE】
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) A
