Java实现动态表查找--二叉排序树
2017-03-04 15:01
507 查看
定义
二叉排序树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:(1)若左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的键值均小于或等于它的根结点的键值;
(2)若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的键值均大于或等于它的根结点的键值;
(3)左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树;
如下图:
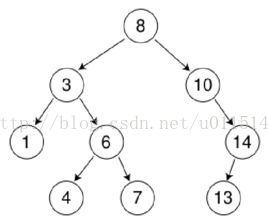
树的遍历方法:
(1)层次遍历:按照树的层次进行遍历,如图树:8、3、10、1、6、14、4、7、13(2)先序遍历:节点遍历顺序为当前节点、左节点、右节点。如图树:8、3、1、6、4、7、10、14、13
(3)中序遍历:节点遍历顺序为左节点、当前节点、右节点。如图树:1、3、4、6、7、8、10、13、14
(4)后续遍历:节点遍历顺序为左节点、右节点、当前节点。如图树:1、4、7、6、3、8、13、14、10
从二叉排序树的中序遍历可以看出它是一个递增的有序表。
下面一段程序代码主要实现以下功能:二叉排序树的建立,插入,查询,四种遍历:
代码实现:
package yao.demo;
import java.util.*;
//二叉树的定义
class BinaryTree{
int val;
BinaryTree left;
BinaryTree right;
public BinaryTree(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
/**
* @author leo
* @param f 如果在查找的过程中,查找成功,则f指向查找成功的节点;如果查找失败,f指向查找路径上的最后一个节点,也即待插入节点
* @param root 指向二叉排序树的根节点
*/
public class BinarySortTree {
static BinaryTree f;
static BinaryTree root;
//二叉排序树的创建
public static void createBST(BinaryTree root, int key){
BinaryTree newNode = new BinaryTree(key);
if(key > root.val){
if(root.right == null)
root.right = newNode;
else
createBST(root.right, key);
}
else if(key < root.val){
if(root.left == null)
root.left = newNode;
else
createBST(root.left, key);
}
else{
System.out.println("The node " + key + " is already exists");
return;
}
}
//二叉排序树的查找
//如果查找成功,则f指向查找成功的节点;如果查找失败,f指向查找路径上的最后一个节点,也即待插入节点
public static boolean sort(BinaryTree root, int key, BinaryTree p){
if(root == null){
f = p;
System.out.println("查找失败!");
return false;
}
else if(root.val == key){
f = root;
System.out.println("查找成功!");
return true;
}
else if(root.val >= key)
return sort(root.left, key, root);
else
return sort(root.right, key, root);
}
//二叉排序树的插入
public static void insert(BinaryTree rt, int key){
if(sort(root, 100, null) == false){
BinaryTree newNode = new BinaryTree(100);
if(f == null)
root = newNode;
else if(key > f.val)
f.right = newNode;
else
f.left = newNode;
System.out.println("插入成功!");
return;
}
System.out.println("不允许插入重复元素!");
}
//二叉树的先序遍历
public static void preOrder(BinaryTree rt){
if(rt != null){
System.out.print(rt.val + " ");
preOrder(rt.left);
preOrder(rt.right);
}
}
//二叉树的中序遍历
public static void inOrder(BinaryTree rt){
if(rt != null){
inOrder(rt.left);
System.out.print(rt.val + " ");
inOrder(rt.right);
}
}
//二叉树的后序遍历
public static void postOrder(BinaryTree rt){
if(rt != null){
postOrder(rt.left);
postOrder(rt.right);
System.out.print(rt.val + " ");
}
}
//二叉树的层次遍历
//用队列实现
public static void levelOrder(BinaryTree rt){
if(rt == null)
return;
Queue<BinaryTree> queue = new LinkedList<BinaryTree>();
queue.add(rt);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
BinaryTree temp = queue.remove();
System.out.print(temp.val + " ");
if(temp.left != null)
queue.add(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null)
queue.add(temp.right);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {35, 76, 12, 22, 16, 48, 90, 46, 9, 40};
root = new BinaryTree(array[0]);
for(int i = 1; i < array.length; i++){
createBST(root, array[i]);
}
System.out.println(sort(root, 22, null));
System.out.println(sort(root, 100, null));
insert(root, 100);
System.out.print("先序遍历:");
preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("中序遍历:");
inOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("后序遍历:");
postOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("层次遍历:");
leverOrder(root);
}
}
相关文章推荐
- Java实现二叉排序树的插入、查找、删除
- 数据结构编程笔记二十五:第九章 查找 二叉排序树(动态查找表)查找算法的实现
- 动态查找之二叉排序树,C++代码实现
- java实现二叉排序树的建立,查找,插入,删除
- 二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree)查找、插入、删除 Java实现
- Java实现二叉排序树的插入、查找、删除
- java实现二叉排序树的生成、查找、打印
- Java动态代理的两种实现方法
- Java实现的快速查找算法示例
- java实现动态代理 → AOP
- java动态代理实现步骤解析
- Java中动态代理的实现
- Java实现折半查找(二分查找)的递归和非递归算法
- 二分查找递归和非递归(java实现)
- Java动态代理借助Proxy与InvocationHandler实现
- Java实现80亿长字符串子串查找(多线程升级)
- JAVA动态绑定的内部实现机制
- java动态代理的实现
- 动态规划问题,金矿模型的java实现
- Java动态代理实现接口invocationHandler
