MFC|Console Output from a GUI program(MFC调用cout输出)
2017-03-03 17:56
627 查看
https://www.codeproject.com/kb/cpp/editbin.aspx
Visibility of the output may be desirable at some point in time for diagnostic or functional purposes. Or you may wish to add command line operation of the program. Then to be consistent with command line operation, text should automatically be output to
the command/dos window.
This article documents the use of EditBin utility to activate console mode operation of a Windows (or GUI ) program. (And for those who want some source code, the program contains an EditBin program relating to redirection of the
object.)
Reassign the standard output and error output handles to be piped or sent to another file using
You may write a console program that remaps the
This obscure tool offers the key for enabling text console output from Windows mode programs written in Visual C++ 6 (or Visual Basic 6). You can toggle the program executable between Windows mode and console mode.
EditBin MyProgram.exe /SUBSYSTEM:CONSOLE
EditBin MyProgram.exe /SUBSYSTEM:WINDOWS
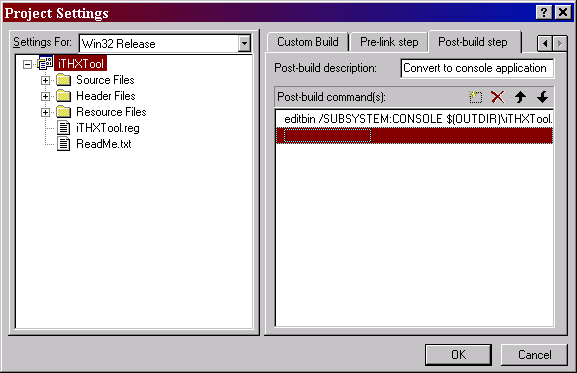
The "Post-Build Step" tab of the Projects Settings dialog allows you to enter in a command on your final executable. The picture shows the example:
Error text.
You may have to create two copies of your application: a strictly GUI program, and a command line version. The programs will involve the same compiled code, but one will be modified using the EditBin tool.
Also a Microsoft help entry mentioned that the file handles 0,1 and 2 (that should be equivalent somehow to
may be able to modify the CRT using the files from thevc98\CRT\source directory.)
should be redirectable.
The application consists of a text editor window that is automatically filled with the time of day at ten seconds intervals. The program relies on piped output which is being read by a
The heart of the redirection occurs within the initialization of the main application object. For all related code, search for the "April 2005" string which will lead you to all code modifications to the standard wizard generated code.
This program shows a little bit of how redirection can be done. Note that the buffering of text (for text being inserted into the RTF document) is not designed ruggedly. The code bypasses the need to use the MicrosoftEditBin.exe tool in some but
not all cases.
It would have been desirable to write the data to a memory file instead of sending data through a pipe. Then there would not have been a need to create a thread to watch the output of the pipe. Anyhow, the
memory map handle to a typical file handle (in

Introduction
If you create a Windows program using the MFC Application Wizard, the program will not show text output which has been sent to the Standard Output or Standard Error handles.Visibility of the output may be desirable at some point in time for diagnostic or functional purposes. Or you may wish to add command line operation of the program. Then to be consistent with command line operation, text should automatically be output to
the command/dos window.
This article documents the use of EditBin utility to activate console mode operation of a Windows (or GUI ) program. (And for those who want some source code, the program contains an EditBin program relating to redirection of the
coutstream
object.)
Alternatives for obtaining text output
Run the Windows program from a command prompt and redirect the output using the redirection feature of the command window: ">out.txt" and "2>errors.txt"Reassign the standard output and error output handles to be piped or sent to another file using
::SetStdHandle(). This process seems to be tricky to achieve.
You may write a console program that remaps the
stdout,
stdin, and
stderrprovided to a spawned program. The spawn program would be the one which has the output that you want to collect.
The Microsoft EditBin Utility
EditBin.exe is found in the VC98\bin subpath of Visual Studio 6.This obscure tool offers the key for enabling text console output from Windows mode programs written in Visual C++ 6 (or Visual Basic 6). You can toggle the program executable between Windows mode and console mode.
EditBin MyProgram.exe /SUBSYSTEM:CONSOLE
EditBin MyProgram.exe /SUBSYSTEM:WINDOWS
Including the Editbin utility in the build process
The article image shows Visual Studio 6 Project Settings to show in situ how the Microsoft EditBin utility appears when added to become part of the build process.The "Post-Build Step" tab of the Projects Settings dialog allows you to enter in a command on your final executable. The picture shows the example:
editbin /SUBSYTEM:CONSOLE $(OUTDIR)\iTHXTool.exe
Side Effect for a Console version of the program
The console window will be appear along with the application window. Such may be the desired option if you want to view diagnostic information. If you start the program from a command prompt, the command window will show the Standard Output and StandardError text.
You may have to create two copies of your application: a strictly GUI program, and a command line version. The programs will involve the same compiled code, but one will be modified using the EditBin tool.
Also a Microsoft help entry mentioned that the file handles 0,1 and 2 (that should be equivalent somehow to
stdoutand
stderr) do not get reassigned since these values are assigned in the CRT startup of the Windows program. (Yet you
may be able to modify the CRT using the files from thevc98\CRT\source directory.)
One last observation on the VS6 project settings...
You may notice "/subsystem:windows" as appears in an MFC Wizard generated application under the Project Settings Link tab. Yet console output can't be obtained by simply changing this entry to/subsystem:console.Some code for redirection of cout
The source code program here, provides an example for redirecting thecoutstream object. For some reason(s), the source code doesn't properly redirect the
stdoutfile handle, though various websites describe that the
stdout
should be redirectable.
The application consists of a text editor window that is automatically filled with the time of day at ten seconds intervals. The program relies on piped output which is being read by a
ReadFilecall operating within a thread.
The heart of the redirection occurs within the initialization of the main application object. For all related code, search for the "April 2005" string which will lead you to all code modifications to the standard wizard generated code.
Initialization Steps
rval = CreatePipe(&hRead,&hWrite,0,0); rval = SetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE,hWrite); //Now assign hWrite to stdout, cout FILE *fp; int hConHandle; long lStdHandle; lStdHandle = (long)GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE); hConHandle = _open_osfhandle(lStdHandle, _O_TEXT); fp = _fdopen( hConHandle, "w" ); // The stdout reassignment didn't seem to work // *stdout = *fp; // redefine the stdout to point to the pipe setvbuf( fp, NULL, _IONBF, 0 ); // Filebuf object attached to "test.dat" filebuf *fb = new filebuf(_fileno(fp ) ); cout = fb;
This program shows a little bit of how redirection can be done. Note that the buffering of text (for text being inserted into the RTF document) is not designed ruggedly. The code bypasses the need to use the MicrosoftEditBin.exe tool in some but
not all cases.
It would have been desirable to write the data to a memory file instead of sending data through a pipe. Then there would not have been a need to create a thread to watch the output of the pipe. Anyhow, the
_open_osfhandlefailed to convert a
memory map handle to a typical file handle (in
hConHandle).
Conclusion
The Windows GUI development doesn't conveniently support the access tocout,
cerr,
stdout, or
stderr. It may be difficult to obtain these under direct control of the window program. At least there exist some tricks to obtain the information if really needed.
License
This article, along with any associated source code and files, is licensed underThe Code Project Open License (CPOL)相关文章推荐
- MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf
- (转)MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf
- Eclipse CDT 调用printf/cout 控制台(console)无输出
- MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf(AllocConsole后,使用GetStdHandle取得句柄,然后就可以操作了)
- MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf
- MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf
- WPF工程打开控制台并输出 Output to console from a WPF application
- Eclipse CDT 调用printf/cout 控制台(console)无输出
- MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf
- printf/cout调用在Eclipse CDT控制台(console)中无实时输出
- Eclipse CDT 调用printf/cout 控制台(console)无输出
- MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf
- MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf
- MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf
- VS2013 MFC 调用控制台 用于显示cout输出流
- GUI程序如何使用控制台输出调试信息[zz][MFC调用win32窗口显示调试信息,使用AllocConsole 函数 ]
- Eclipse中console调用printf/cout无输出显示
- Eclipse CDT 调用printf/cout 控制台(console)无输出
- MFC的GUI窗口使用Console输出函数printf
- MFC(win32GUI)程序中显示Dos调试信息.console.显示控制台界面.标准输出.
