libevent源码详解(一)数据结构之尾队列
2017-03-01 18:22
309 查看
libevent中的队列一个很重要的数据结构就是尾队列。CSDN已经有很多文章分析libevent的尾队列了,但是跟其它常见的数据结构例如单项列表、双向链表比较得比较少。在这里我来解析一下尾队列相对这些常见数据结构的不同。
单链表图解

双向链表
双向链表图解

尾队列图解(盗用一下别人的图 :-P )
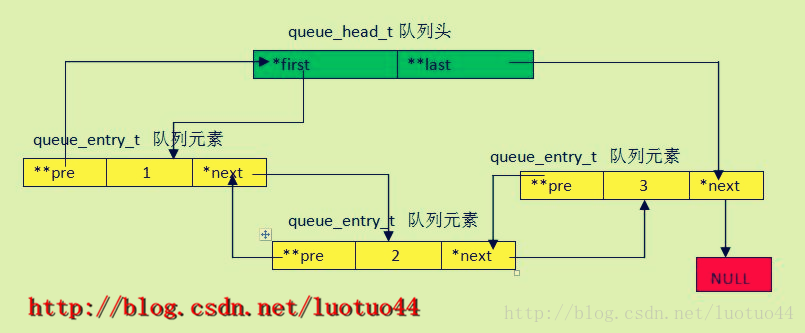
可以看到,尾队列比单向链表、双向链表多了一个二级指针,这个指针用来指向前一个元素中的尾队列入口节点指向下一个元素的指针。详见图解。
为了达到这个目的,尾队列的使用方法也是相当复杂,也分一二三四步。
我们先贴出尾队列的定义。这个定义可以在libevent的源码包中的compat/sys/queue.h文件中找到。
2定义自己的队列名
3初始化并使用其它接口操作
关于尾队列其它接口的更详细的使用例子,可以参考这篇文章Libevent源码分析—–TAILQ_QUEUE队列
而libevent早就给我们实现好了这些接口,具体的实现还在同一个文件compat/sys/queue.h中。该文件用同样的技巧重新实现的双向循环队列跟尾队列一样的效果。
下面仅仅贴出双向循环队列定义。感兴趣的可以自己去下libevent的源码来研究具体实现。
常见的数据结构
单链表struct slist {
struct slist *next;
int val;
};单链表图解

双向链表
struct dlist {
struct dlist *next;
struct dlist *prev;
int val;
};双向链表图解

尾队列数据结构
struct tailq_entry {
struct tailq_entry *next;
struct tailq_entry **prev;
int val;
};尾队列图解(盗用一下别人的图 :-P )

可以看到,尾队列比单向链表、双向链表多了一个二级指针,这个指针用来指向前一个元素中的尾队列入口节点指向下一个元素的指针。详见图解。
与其它数据结构的不同
尾队列用处与其它数据结构的最大区别就是那个二级指针造成的。这个指针的作用就是能让尾队列能以O(1)时间删除队列中的一个节点。而像上面定义的单向链表双向链表,要删除队列中的一个节点,一般都要遍历一遍队列,花费O(N)的时间。为了达到这个目的,尾队列的使用方法也是相当复杂,也分一二三四步。
我们先贴出尾队列的定义。这个定义可以在libevent的源码包中的compat/sys/queue.h文件中找到。
/*
* Tail queue definitions.
*/
#define TAILQ_HEAD(name, type) \
struct name { \
struct type *tqh_first; /* first element */ \
struct type **tqh_last; /* addr of last next element */ \
}
#define TAILQ_HEAD_INITIALIZER(head) \
{ NULL, &(head).tqh_first }
#define TAILQ_ENTRY(type) \
struct { \
struct type *tqe_next; /* next element */ \
struct type **tqe_prev; /* address of previous next element */ \
}
/*
* tail queue access methods
*/
#define TAILQ_FIRST(head) ((head)->tqh_first)
#define TAILQ_END(head) NULL
#define TAILQ_NEXT(elm, field) ((elm)->field.tqe_next)
#define TAILQ_LAST(head, headname) \
(*(((struct headname *)((head)->tqh_last))->tqh_last))
/* XXX */
#define TAILQ_PREV(elm, headname, field) \
(*(((struct headname *)((elm)->field.tqe_prev))->tqh_last))
#define TAILQ_EMPTY(head) \
(TAILQ_FIRST(head) == TAILQ_END(head))
#define TAILQ_FOREACH(var, head, field) \
for((var) = TAILQ_FIRST(head); \
(var) != TAILQ_END(head); \
(var) = TAILQ_NEXT(var, field))
#define TAILQ_FOREACH_REVERSE(var, head, headname, field) \
for((var) = TAILQ_LAST(head, headname); \
(var) != TAILQ_END(head); \
(var) = TAILQ_PREV(var, headname, field))
/*
* Tail queue functions.
*/
#define TAILQ_INIT(head) do { \
(head)->tqh_first = NULL; \
(head)->tqh_last = &(head)->tqh_first; \
} while (0)
#define TAILQ_INSERT_HEAD(head, elm, field) do { \
if (((elm)->field.tqe_next = (head)->tqh_first) != NULL) \
(head)->tqh_first->field.tqe_prev = \
&(elm)->field.tqe_next; \
else \
(head)->tqh_last = &(elm)->field.tqe_next; \
(head)->tqh_first = (elm); \
(elm)->field.tqe_prev = &(head)->tqh_first; \
} while (0)
#define TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(head, elm, field) do { \
(elm)->field.tqe_next = NULL; \
(elm)->field.tqe_prev = (head)->tqh_last; \
*(head)->tqh_last = (elm); \
(head)->tqh_last = &(elm)->field.tqe_next; \
} while (0)
#define TAILQ_INSERT_AFTER(head, listelm, elm, field) do { \
if (((elm)->field.tqe_next = (listelm)->field.tqe_next) != NULL)\
(elm)->field.tqe_next->field.tqe_prev = \
&(elm)->field.tqe_next; \
else \
(head)->tqh_last = &(elm)->field.tqe_next; \
(listelm)->field.tqe_next = (elm); \
(elm)->field.tqe_prev = &(listelm)->field.tqe_next; \
} while (0)
#define TAILQ_INSERT_BEFORE(listelm, elm, field) do { \
(elm)->field.tqe_prev = (listelm)->field.tqe_prev; \
(elm)->field.tqe_next = (listelm); \
*(listelm)->field.tqe_prev = (elm); \
(listelm)->field.tqe_prev = &(elm)->field.tqe_next; \
} while (0)
#define TAILQ_REMOVE(head, elm, field) do { \
if (((elm)->field.tqe_next) != NULL) \
(elm)->field.tqe_next->field.tqe_prev = \
(elm)->field.tqe_prev; \
else \
(head)->tqh_last = (elm)->field.tqe_prev; \
*(elm)->field.tqe_prev = (elm)->field.tqe_next; \
} while (0)
#define TAILQ_REPLACE(head, elm, elm2, field) do { \
if (((elm2)->field.tqe_next = (elm)->field.tqe_next) != NULL) \
(elm2)->field.tqe_next->field.tqe_prev = \
&(elm2)->field.tqe_next; \
else \
(head)->tqh_last = &(elm2)->field.tqe_next; \
(elm2)->field.tqe_prev = (elm)->field.tqe_prev; \
*(elm2)->field.tqe_prev = (elm2); \
} while (0)尾队列的具体使用技巧
1在自己定义的结构体中用TAILQ_ENTRY声明一个节点入口。struct event {
TAILQ_ENTRY(event_entry);
int val;
};2定义自己的队列名
//event是我们上面定义的结构体的名称,event_list就是这个队列的名称。event_list中包含的节点类型为struct event。 TAILQ_HEAD(event_list, event);
3初始化并使用其它接口操作
//我们用TAILQ_HEAD声明了一个名称为event_list的队列结构。现在我们可以用它来声明尾队列了。
struct event_list evlist;
//初始化队列
TAILQ_INIT(evlist);
//插入数据
struct event *p;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
p=(struct event *)malloc(sizeof(struct event));
p->val=i;
//这个插入的接口宏参数有点奇怪,第二个参数是要插入的结构体,第三个参数是我们
//结构体中用TAILQ_ENTRY定义的入口的名称event_entry
TAILQ_INSERT_HEAD(evlist, p, event_entry);
}
//遍历数据
struct event *iter;
TAILQ_FOREACH(iter,event_list, tqe)
{
printf("val=%d\n", iter->val);
}关于尾队列其它接口的更详细的使用例子,可以参考这篇文章Libevent源码分析—–TAILQ_QUEUE队列
尾队列应用
既然尾队列那样的数据结构能够帮我们避免一般队列删除操作带来的O(N)复杂度,我们也可以将尾队列中那个二级指针以及把链表entry作为数据结构的成员的技巧应用到其它一般队列中,而达到跟尾队列一样的效果。而使用这些后,普通的数据结构的定义和使用接口也会发生相应的变化。而libevent早就给我们实现好了这些接口,具体的实现还在同一个文件compat/sys/queue.h中。该文件用同样的技巧重新实现的双向循环队列跟尾队列一样的效果。
下面仅仅贴出双向循环队列定义。感兴趣的可以自己去下libevent的源码来研究具体实现。
/*
* Circular queue definitions.
*/
#define CIRCLEQ_HEAD(name, type) \
struct name { \
struct type *cqh_first; /* first element */ \
struct type *cqh_last; /* last element */ \
}
#define CIRCLEQ_HEAD_INITIALIZER(head) \
{ CIRCLEQ_END(&head), CIRCLEQ_END(&head) }
#define CIRCLEQ_ENTRY(type) \
struct { \
struct type *cqe_next; /* next element */ \
struct type *cqe_prev; /* previous element */ \
}
相关文章推荐
- libevent源码详解(二)数据结构之最小堆
- Libevent源码分析-----TAILQ_QUEUE队列
- libevent源码阅读笔记——通用时间队列
- 3-3-行编辑程序-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- 3-8-循环队列-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- 3-7-队列的链式存储-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- 解析从源码分析常见的基于Array的数据结构动态扩容机制的详解
- Libevent源码分析-----TAILQ_QUEUE队列
- 3-1-栈的顺序存储结构-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- 3-9-模拟银行排队过程-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- Libevent源码分析(一)--- 基本数据结构
- Python实现的数据结构与算法之双端队列详解
- 3-2-进制转换-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- 3-1-栈的顺序存储结构-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- 3-2-进制转换-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- Libevent源码分析-----TAILQ_QUEUE队列
- Linux内核中RAID5源码详解之基本架构与数据结构
- 3-4-迷宫寻路-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- 3-5-表达式求值-栈和队列-第3章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- 详解数据结构C语言实现之循环队列
