Servlet小结
2017-02-17 19:27
190 查看
serverlet配置注意事项:
1.以“/”开头:”/”代表的是工程路径(/工程名称) — 必须要加“/”2.以* 开头: 必须要加后缀名(后缀名任意) — 后缀名不能用“*”代替
注意:/ *.后缀名此种情况不允许
3.如果配置时只写一个”/”则此Servlet就是一个默认的Servlet,其作用是处理所有找不到匹配url的请求
匹配servlet时url冲突的解决
servlet创建的时机
1.一般情况servlet创建与用户访问时。2.当在配置文件中使用用< load-on-startup>2< load-on-startup>标签时,则此servlet将在服务器启动时创建。— 数字2代表的是启动的优先级
创建servlet的几种方法
1.实现servlet接口(麻烦,如无特殊需求没必要使用,不推荐)2.继承于GenericServlet(不推荐)
3.继承于HttpServlet(推荐)
servlet的线程安全问题
明确:servlet的设计是一个单实例多线程。线程安全要求将变量创建成一个局部变量,而不要创建成实例变量。
servlet类图:
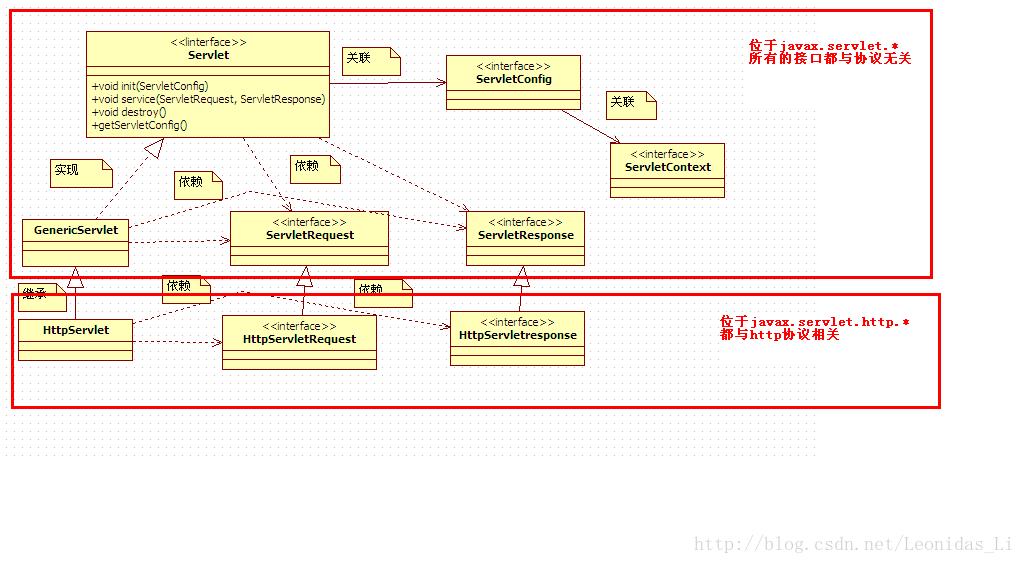
图中关系说明:
关联:指的是能够从”箭头始端类”的对象能够拿到”箭头末端类”的对象。图中类说明:
ServletConfig(servlet配置信息):获取方式:
采用带参的init方法,也就是直接获取系统自动创建的ServletConfig对象。
采用servlet实例拿去
注意:此时servlet中不能写带参的init方法,如果写了带参的init方法后,父类的带参的init将会被覆盖而不会执行,因而在从父类继承下来的ServletConfig对象将为null,因而将拿不到ServletConfig对象。
获取servlet配置信息的方法步骤
获取单个配置信息时:
1.拿到ServletConfig对象。
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
2.获取单个配置信息。
//name指的是想要获得的配置信息的”键”
String name = sc.getInitParameter(“name”);
获取多个配置信息时:
1.拿到ServletConfig对象。
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
2.获取单个配置信息。
Enumeration enu = sc.getInitParameterNames();
while(enu.hasMoreElements()){
String name = enu.nextElement();
ServletContext – 重要(一个ServletContext对象对应一个工程,一个工程只有一个ServletContext对象)
获取ServletContext对象:
1.采用ServletConfig对象获取(config指的是ServletConfig对象)
ServletContext sc = config.getServletContext();
2.采用servlet实例对象获取(this指的是servlet实例对象)
注意:使用此方法时需要注意不要覆盖父类的init方法,原因与上述第二种获取ServletConfig对象的方法的原因一样(如果覆盖了则需要手动调用父类的init方法)。
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext();
3.采用request对象获取(request指的是Request类的对象)
ServletContext sc = request.getSession().getServletContext();
ServletContext的应用:
获取全局对象中存储的数据:
//------存储部分------
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取全局对象
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext() ;
//存储数据
sc.setAttribute("name", "张三丰") ;
System.out.println("数据存储完毕");
}//------获取部分------
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//拿取全局对象
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext() ;
//从sc中拿取数据
String name = (String)sc.getAttribute("name") ;
System.out.println(name);
}获取全局配置参数:
//------获取单个配置参数------
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//拿到全局对象
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext() ;
//获取单个配置参数(获取姓名)
String name = sc.getInitParameter("name") ;
System.out.println(name);
}//------获取多个配置参数------
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//拿到全局对象
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext() ;
//拿取多个配置参数的值
Enumeration<String> enu = sc.getInitParameterNames() ;
while(enu.hasMoreElements()){
String name = enu.nextElement() ;
System.out.println(name + ":" + sc.getInitParameter(name));
}
}请求转发(某一个servlet接受到请求后将此请求交给另外一个servlet进行处理):
//------请求转发部分------
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//拿到全局对象
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext() ;
request.setAttribute("name", "乔峰") ;
//拿到请求转发器
RequestDispatcher rd = sc.getRequestDispatcher("/servlet/ServletContext6") ;
//转发过去
rd.forward(request, response) ;
}//------接收请求转发部分------
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("你终于过来了");
String name = (String)request.getAttribute("name") ;
System.out.println("转发过来的数据: " + name);
}获取资源文件:

package com.heima.four;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
//演示获取资源文件
/*
* 获取资源文件有三种方式:
* 1.采用 ServletContext对象获取
* 2.采用ResourceBundle类来获取
* 3.采用类加载器获取
*
* 第一种方式:优点: 任意文件,任意路径
* 缺点: 必须有web环境
* 第二种方式: 优点:简单方便
* 缺点: 1.只能拿取properties文件 2. 只能拿取非web环境下的资源
* 第三种方式: 优点: 任意文件,任意路径
* 缺点: 编写稍显麻烦
*
*/
public class ServletContext7 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//下面test后的第一个数字代表的是第几中方法,第二个数字代表的是拿去的是上图中的哪一个文件。
//test11() ;
//test12() ;
//test13();
//test22();
//test31();
//test32();
//test33();
//test34();
}
// 获取p1资源文件的内容
public void test11() {
// 拿到全局对象
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext();
// 获取p1.properties文件的路径
String path = sc.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/p1.properties");
System.out.println(path);
// 创建一个Properties对象
Properties pro = new Properties();
// 加载文件
try {
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 读取k的值
System.out.println(pro.get("k"));
}
// 获取p2资源文件的内容
public void test12() {
// 拿到全局对象
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext();
// 获取p1.properties文件的路径
String path = sc
.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/com/heima/four/p2.properties");
System.out.println(path);
// 创建一个Properties对象
Properties pro = new Properties();
// 加载文件
try {
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 读取k的值
System.out.println(pro.get("k"));
}
// 获取p3资源文件的内容
public void test13() {
// 拿到全局对象
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext();
// 获取p1.properties文件的路径
String path = sc.getRealPath("/p3.properties");
System.out.println(path);
// 创建一个Properties对象
Properties pro = new Properties();
// 加载文件
try {
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 读取k的值
System.out.println(pro.get("k"));
}
// 采用resourceBunble拿取资源文件:获取p1资源文件的内容 默认路径是src,对用到web环境就是classes目录
public void test21() {
// 拿取ResourceBundle对象(专门用来获取properties文件的信息)
ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("p1");
// 拿取文件中的内容太
System.out.println(rb.getString("k"));
}
// 采用resourceBunble拿取资源文件:获取p2资源文件的内容
public void test22() {
// 拿取ResourceBundle对象(专门用来获取properties文件的信息)
ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.heima.four.p2");
// 拿取文件中的内容太
System.out.println(rb.getString("k"));
}
// 采用类加载器拿取资源文件:获取p1资源文件的内容 : 默认路径是src,对用到web环境就是classes目录
public void test31() {
// 获取类加载器的方式
/*
* 1. 通过类名 ServletContext7.class.getClassLoader() 2. 通过对象
* this.getClass().getClassLoader() 3. Class.forName()
* 获取Class.forName("ServletContext7").getClassLoader()
*/
InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("p1.properties");
// 创建Properties对象
Properties pro = new Properties();
try {
pro.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 拿取文件的数据
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("k"));
}
// 采用类加载器拿取资源文件:获取p2资源文件的内容 : 默认路径是src,对用到web环境就是classes目录
public void test32() {
// 获取类加载器的方式
/*
* 1. 通过类名 ServletContext7.class.getClassLoader() 2. 通过对象
* this.getClass().getClassLoader() 3. Class.forName()
* 获取Class.forName("ServletContext7").getClassLoader()
*/
InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("com/heima/four/p2.properties");
// 创建Properties对象
Properties pro = new Properties();
try {
pro.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 拿取文件的数据
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("k"));
}
// 采用类加载器拿取资源文件:获取p3资源文件的内容 : 默认路径是src,对用到web环境就是classes目录
public void test33() {
// 获取类加载器的方式
/*
* 1. 通过类名 ServletContext7.class.getClassLoader() 2. 通过对象
* this.getClass().getClassLoader() 3. Class.forName()
* 获取Class.forName("ServletContext7").getClassLoader()
*/
InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("../../p3.properties");
// 创建Properties对象
Properties pro = new Properties();
try {
pro.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 拿取文件的数据
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("k"));
}
// 采用类加载器拿取资源文件:获取p3资源文件的内容 : 默认路径是src,对用到web环境就是classes目录
public void test34() {
// 获取类加载器的方式
/*
* 1. 通过类名 ServletContext7.class.getClassLoader() 2. 通过对象
* this.getClass().getClassLoader() 3. Class.forName()
* 获取Class.forName("ServletContext7").getClassLoader()
*/
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("p1.properties") ;
String path = url.getPath() ;
// 创建Properties对象
Properties pro = new Properties();
try {
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 拿取文件的数据
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("k"));
}
}其他小知识点:
a). 一个servlet可以映射到多个路径b). 匹配优先级: 精确匹配 > 以”/”开头的匹配 > 以*开头的匹配
c).注意:tomcat服务器不要安装到带有空格,中文字符或其他特殊字符的路径上,不然会导致一些相关的函数使用不了。(因为在对这些特殊字符进行编码是可能会有码表不一致的问题)
response对象的中文乱码解决:
package com.heima.one;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
//演示输出中文乱码的问题
public class ServletResponse1 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//采用字节流输出数据
String s = "黑马训练营1" ;
//response.getOutputStream().write(s.getBytes()) ; //不会出现乱码
//response.getOutputStream().write(s.getBytes("utf-8")) ;
//解决乱码问题
//第一种办法:让用户在浏览器中选择解码(不靠谱)
//第二种方式:通知浏览器采用某种编码进行解码
//response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8") ;
//第三种方式:输出一个字符串
// response.getOutputStream().write("<meta http-equiv='content-type' content='text/html; charset=UTF-8'>".getBytes()) ;
// response.getOutputStream().write(s.getBytes("utf-8")) ;
//第四种方式 让服务器的编码用一种编码,通知浏览器的解码
// response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8") ;
// response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8") ;
//
// response.getOutputStream().write(s.getBytes("utf-8")) ;
//第五种方法(推荐)
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8") ; //此句代码做了两件事情:1 设定服务器将数据编码时用的码表
// 2.通知浏览器解码用的码表
//
// response.getOutputStream().write(s.getBytes("UTF-8")) ;
//字符流输出中文
response.getWriter().write(s) ;
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
相关文章推荐
- Servlet小结
- servlet、jsp小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
- Servlet学习小结
- Servlet中文乱码处理小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
- Servlet小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
- Spring Mvc中DispatcherServlet和Servlet的区别小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
- servlet小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结 (包含IoC和非ioc方式获取request等)
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记11:HttpServlet(HttpServletRequest HttpServletRsponse) 以及关于 Servlet 小结
- servlet小结
- ActionContext和ServletActionContext小结
