Codeforces Round #397 D. Artsem and Saunders(构造)
2017-02-17 10:57
369 查看
D. Artsem and Saunders
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
512 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Artsem has a friend Saunders from University of Chicago. Saunders presented him with the following problem.
Let [n] denote the set {1, ..., n}.
We will also write f: [x] → [y] when a function f is
defined in integer points 1, ..., x, and all its
values are integers from 1 to y.
Now then, you are given a function f: [n] → [n]. Your task is to find a positive integer m,
and two functions g: [n] → [m],h: [m] → [n],
such that g(h(x)) = x for all
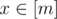
,
and h(g(x)) = f(x) for all

,
or determine that finding these is impossible.
Input
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105).
The second line contains n space-separated integers — values f(1), ..., f(n) (1 ≤ f(i) ≤ n).
Output
If there is no answer, print one integer -1.
Otherwise, on the first line print the number m (1 ≤ m ≤ 106).
On the second line print n numbers g(1), ..., g(n).
On the third line printm numbers h(1), ..., h(m).
If there are several correct answers, you may output any of them. It is guaranteed that if a valid answer exists, then there is an answer satisfying the above restrictions.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
题解:
构造题。
因为:
g(h(x))=x.
h(g(x))=f(x).
所以,h(x)=f(f(x)) && 必须有一个 x= f(x).(观察可以发现)
从而得到 g(x) =g(f(x)).
所以将这些x全部映射到[1,m]中,再映射到f(x)和g(x)中就可以了。
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/*
因为:
g(h(x))=x
h(g(x))=f(x)
所以,h(x)=f(f(x)) && 必须有一个 x= f(x)
从而得到 g(x) =g(f(x))
*/
int f[100000+7],g[100000+7];
int h[100000+7];
int main()
{
int n;
int hn=0;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>f[i];
if(f[i]==i){ //x=f(x)
hn++;
g[i]=hn;
h[g[i]]=i; //h(g(x))=f(x)=f(x);
}
}
//for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<"g[f[i]]="<<g[f[i]]<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!g[f[i]])return 0*puts("-1");
}
cout<<hn<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<g[f[i]]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=hn;i++)
cout<<h[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
512 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Artsem has a friend Saunders from University of Chicago. Saunders presented him with the following problem.
Let [n] denote the set {1, ..., n}.
We will also write f: [x] → [y] when a function f is
defined in integer points 1, ..., x, and all its
values are integers from 1 to y.
Now then, you are given a function f: [n] → [n]. Your task is to find a positive integer m,
and two functions g: [n] → [m],h: [m] → [n],
such that g(h(x)) = x for all
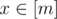
,
and h(g(x)) = f(x) for all

,
or determine that finding these is impossible.
Input
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105).
The second line contains n space-separated integers — values f(1), ..., f(n) (1 ≤ f(i) ≤ n).
Output
If there is no answer, print one integer -1.
Otherwise, on the first line print the number m (1 ≤ m ≤ 106).
On the second line print n numbers g(1), ..., g(n).
On the third line printm numbers h(1), ..., h(m).
If there are several correct answers, you may output any of them. It is guaranteed that if a valid answer exists, then there is an answer satisfying the above restrictions.
Examples
input
3 1 2 3
output
3 1 2 31 2 3
input
3 2 2 2
output
1 1 1 1 2
input
2 2 1
output
-1
题解:
构造题。
因为:
g(h(x))=x.
h(g(x))=f(x).
所以,h(x)=f(f(x)) && 必须有一个 x= f(x).(观察可以发现)
从而得到 g(x) =g(f(x)).
所以将这些x全部映射到[1,m]中,再映射到f(x)和g(x)中就可以了。
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/*
因为:
g(h(x))=x
h(g(x))=f(x)
所以,h(x)=f(f(x)) && 必须有一个 x= f(x)
从而得到 g(x) =g(f(x))
*/
int f[100000+7],g[100000+7];
int h[100000+7];
int main()
{
int n;
int hn=0;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>f[i];
if(f[i]==i){ //x=f(x)
hn++;
g[i]=hn;
h[g[i]]=i; //h(g(x))=f(x)=f(x);
}
}
//for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<"g[f[i]]="<<g[f[i]]<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!g[f[i]])return 0*puts("-1");
}
cout<<hn<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<g[f[i]]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=hn;i++)
cout<<h[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces Round #397 by Kaspersky Lab and Barcelona Bootcamp (Div. 1 + Div. 2 combined) D. Artsem and Saunders 数学 构造
- Codeforces 765D Artsem and Saunders 构造
- 【Codeforces 756 D. Artsem and Saunders】+ 思维 + 构造
- 【构造】Codeforces Round #397 by Kaspersky Lab and Barcelona Bootcamp (Div. 1 + Div. 2 combined) D. Artsem and Saunders
- Codeforces 765D Artsem and Saunders 【构造】
- 【CodeForces 765D】 Artsem and Saunders(数学,构造)
- codeforces 765 D Artsem and Saunders(构造)
- D. Artsem and Saunders
- D. Artsem and Saunders
- 【codeforces 765D】Artsem and Saunders
- D. Artsem and Saunders
- D. Artsem and Saunders
- D. Artsem and Saunders
- Codeforces 765D Artsem and Saunders(数学)
- Codeforces_765_D. Artsem and Saunders_(数学)
- D. Artsem and Saunders
- D. Artsem and Saunders
- Codeforces Round #397 Problem D. Artsem and Saunders 解题报告
- Codeforces Round #397(Div. 1 + Div. 2 combined)D. Artsem and Saunders【思维+乱搞】
- codeforces 397div2 D Artsem and Saunders
