【scikit-learn】交叉验证及其用于参数选择、模型选择、特征选择的例子
2017-01-24 14:06
609 查看
内容概要¶
训练集/测试集分割用于模型验证的缺点K折交叉验证是如何克服之前的不足
交叉验证如何用于选择调节参数、选择模型、选择特征
改善交叉验证
1. 模型验证回顾¶
进行模型验证的一个重要目的是要选出一个最合适的模型,对于监督学习而言,我们希望模型对于未知数据的泛化能力强,所以就需要模型验证这一过程来体现不同的模型对于未知数据的表现效果。最先我们用训练准确度(用全部数据进行训练和测试)来衡量模型的表现,这种方法会导致模型过拟合;为了解决这一问题,我们将所有数据分成训练集和测试集两部分,我们用训练集进行模型训练,得到的模型再用测试集来衡量模型的预测表现能力,这种度量方式叫测试准确度,这种方式可以有效避免过拟合。
测试准确度的一个缺点是其样本准确度是一个高方差估计(high
variance estimate),所以该样本准确度会依赖不同的测试集,其表现效果不尽相同。
高方差估计的例子¶
下面我们使用iris数据来说明利用测试准确度来衡量模型表现的方差很高。In [1]:
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier from sklearn import metrics
In [2]:
# read in the iris data iris = load_iris() X = iris.data y = iris.target
In [3]:
for i in xrange(1,5): print "random_state is ", i,", and accuracy score is:" X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=i) knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5) knn.fit(X_train, y_train) y_pred = knn.predict(X_test) print metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
random_state is 1 , and accuracy score is: 1.0 random_state is 2 , and accuracy score is: 1.0 random_state is 3 , and accuracy score is: 0.947368421053 random_state is 4 , and accuracy score is: 0.973684210526
上面的测试准确率可以看出,不同的训练集、测试集分割的方法导致其准确率不同,而交叉验证的基本思想是:将数据集进行一系列分割,生成一组不同的训练测试集,然后分别训练模型并计算测试准确率,最后对结果进行平均处理。这样来有效降低测试准确率的差异。
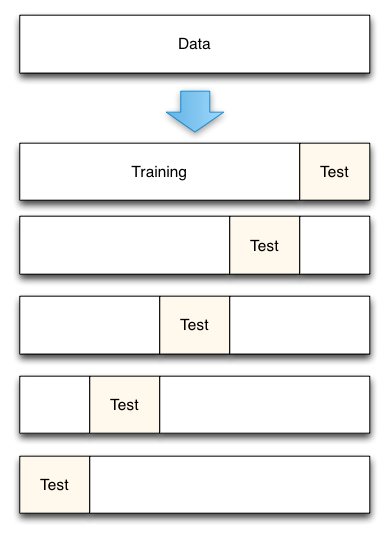
2. K折交叉验证¶
将数据集平均分割成K个等份使用1份数据作为测试数据,其余作为训练数据
计算测试准确率
使用不同的测试集,重复2、3步骤
对测试准确率做平均,作为对未知数据预测准确率的估计
In [4]:
# 下面代码演示了K-fold交叉验证是如何进行数据分割的
# simulate splitting a dataset of 25 observations into 5 folds
from sklearn.cross_validation import KFold
kf = KFold(25, n_folds=5, shuffle=False)
# print the contents of each training and testing set
print '{} {:^61} {}'.format('Iteration', 'Training set observations', 'Testing set observations')
for iteration, data in enumerate(kf, start=1):
print '{:^9} {} {:^25}'.format(iteration, data[0], data[1])Iteration Training set observations Testing set observations 1 [ 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24] [0 1 2 3 4] 2 [ 0 1 2 3 4 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24] [5 6 7 8 9] 3 [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24] [10 11 12 13 14] 4 [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 20 21 22 23 24] [15 16 17 18 19] 5 [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19] [20 21 22 23 24]
3. 使用交叉验证的建议¶
K=10是一个一般的建议如果对于分类问题,应该使用分层抽样(stratified sampling)来生成数据,保证正负例的比例在训练集和测试集中的比例相同
4. 交叉验证的例子¶
4.1 用于调节参数¶
交叉验证的方法可以帮助我们进行调参,最终得到一组最佳的模型参数。下面的例子我们依然使用iris数据和KNN模型,通过调节参数,得到一组最佳的参数使得测试数据的准确率和泛化能力最佳。In [6]:
from sklearn.cross_validation import cross_val_score
In [7]:
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5) # 这里的cross_val_score将交叉验证的整个过程连接起来,不用再进行手动的分割数据 # cv参数用于规定将原始数据分成多少份 scores = cross_val_score(knn, X, y, cv=10, scoring='accuracy') print scores
[ 1. 0.93333333 1. 1. 0.86666667 0.93333333 0.93333333 1. 1. 1. ]
In [8]:
# use average accuracy as an estimate of out-of-sample accuracy # 对十次迭代计算平均的测试准确率 print scores.mean()
0.966666666667
In [11]:
# search for an optimal value of K for KNN model k_range = range(1,31) k_scores = [] for k in k_range: knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k) scores = cross_val_score(knn, X, y, cv=10, scoring='accuracy') k_scores.append(scores.mean()) print k_scores
[0.95999999999999996, 0.95333333333333337, 0.96666666666666656, 0.96666666666666656, 0.96666666666666679, 0.96666666666666679, 0.96666666666666679, 0.96666666666666679, 0.97333333333333338, 0.96666666666666679, 0.96666666666666679, 0.97333333333333338, 0.98000000000000009, 0.97333333333333338, 0.97333333333333338, 0.97333333333333338, 0.97333333333333338, 0.98000000000000009, 0.97333333333333338, 0.98000000000000009, 0.96666666666666656, 0.96666666666666656, 0.97333333333333338, 0.95999999999999996, 0.96666666666666656, 0.95999999999999996, 0.96666666666666656, 0.95333333333333337, 0.95333333333333337, 0.95333333333333337]
In [10]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline
In [12]:
plt.plot(k_range, k_scores)
plt.xlabel("Value of K for KNN")
plt.ylabel("Cross validated accuracy")Out[12]:
<matplotlib.text.Text at 0x6dd0fb0>
上面的例子显示了偏置-方差的折中,K较小的情况时偏置较低,方差较高;K较高的情况时,偏置较高,方差较低;最佳的模型参数取在中间位置,该情况下,使得偏置和方差得以平衡,模型针对于非样本数据的泛化能力是最佳的。
4.2 用于模型选择¶
交叉验证也可以帮助我们进行模型选择,以下是一组例子,分别使用iris数据,KNN和logistic回归模型进行模型的比较和选择。In [13]:
# 10-fold cross-validation with the best KNN model knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=20) print cross_val_score(knn, X, y, cv=10, scoring='accuracy').mean()
0.98
In [14]:
# 10-fold cross-validation with logistic regression from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression logreg = LogisticRegression() print cross_val_score(logreg, X, y, cv=10, scoring='accuracy').mean()
0.953333333333
4.3 用于特征选择¶
下面我们使用advertising数据,通过交叉验证来进行特征的选择,对比不同的特征组合对于模型的预测效果。In [15]:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
In [16]:
# read in the advertising dataset
data = pd.read_csv('http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~gareth/ISL/Advertising.csv', index_col=0)In [17]:
# create a Python list of three feature names feature_cols = ['TV', 'Radio', 'Newspaper'] # use the list to select a subset of the DataFrame (X) X = data[feature_cols] # select the Sales column as the response (y) y = data.Sales
In [18]:
# 10-fold cv with all features lm = LinearRegression() scores = cross_val_score(lm, X, y, cv=10, scoring='mean_squared_error') print scores
[-3.56038438 -3.29767522 -2.08943356 -2.82474283 -1.3027754 -1.74163618 -8.17338214 -2.11409746 -3.04273109 -2.45281793]
这里要注意的是,上面的scores都是负数,为什么均方误差会出现负数的情况呢?因为这里的mean_squared_error是一种损失函数,优化的目标的使其最小化,而分类准确率是一种奖励函数,优化的目标是使其最大化。
In [19]:
# fix the sign of MSE scores mse_scores = -scores print mse_scores
[ 3.56038438 3.29767522 2.08943356 2.82474283 1.3027754 1.74163618 8.17338214 2.11409746 3.04273109 2.45281793]
In [20]:
# convert from MSE to RMSE rmse_scores = np.sqrt(mse_scores) print rmse_scores
[ 1.88689808 1.81595022 1.44548731 1.68069713 1.14139187 1.31971064 2.85891276 1.45399362 1.7443426 1.56614748]
In [21]:
# calculate the average RMSE print rmse_scores.mean()
1.69135317081
In [22]:
# 10-fold cross-validation with two features (excluding Newspaper) feature_cols = ['TV', 'Radio'] X = data[feature_cols] print np.sqrt(-cross_val_score(lm, X, y, cv=10, scoring='mean_squared_error')).mean()
1.67967484191
由于不加入Newspaper这一个特征得到的分数较小(1.68 < 1.69),所以,使用所有特征得到的模型是一个更好的模型。
相关文章推荐
- 【scikit-learn】交叉验证及其用于参数选择、模型选择、特征选择的例子
- 【scikit-learn】交叉验证及其用于参数选择、模型选择、特征选择的例子
- scikit-learn中交叉验证及其用于参数选择、模型选择、特征选择的例子
- 交叉验证及其用于参数选择、模型选择、特征选择的例子
- cross_val_score交叉验证及其用于参数选择、模型选择、特征选择
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】模型选择:选择估计量及其参数 - 关于科学数据处理的统计学习教程 - scikit-learn 教程 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】模型选择:选择估计量及其参数 - 关于科学数据处理的统计学习教程 - scikit-learn 教程 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】模型选择:选择估计量及其参数 - 关于科学数据处理的统计学习教程 - scikit-learn 教程 | ApacheCN
- [翻译中]【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】二十八:交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】交叉验证 - 模型选择和评估 - 用户指南 | ApacheCN
- Scikit-learn:模型选择Model selection之pipline和交叉验证
- 【Scikit-Learn 中文文档】模型选择:选择估计量及其参数 - 关于科学数据处理的统计学习教程 - scikit-learn 教程 | ApacheCN
