PCIe设备漫游记----BIOS篇
2017-01-19 15:22
399 查看
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/saloon_yuan/article/details/7519852
初步了解完PCI总线标准之后,我们接下来正式开始PCIe设备的漫游之旅。从我们按下PC的电源按钮开始,BIOS就接管系统控制权开始工作,它会先进行一些内存和设备的初始化工作(当然,也包括我们的PCI设备),由于商业上的原因,Phoenix等厂商的BIOS代码需要授权协议,在此,我们以另外一个款开源BIOS(openbios)为例,来剖析BIOS中,我们的PCIe设备是如何被找到以及初始化的。
PCI设备的扫描是基于深度优先搜索算法(DFS:Depth First Search),也就是说,下级分支最多的PCI桥将最先完成其子设备的扫描。下面我们以图片来具体说明,BIOS是如何一步步完成PCI
设备扫描的。
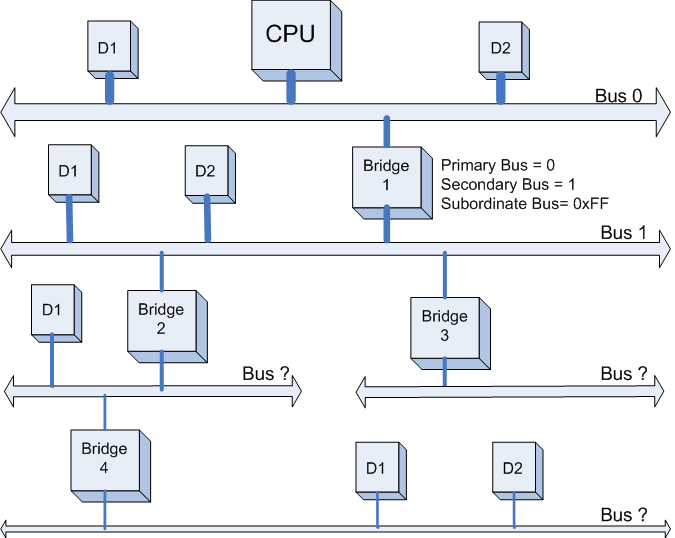
第一步:
PCI Host 主桥扫描Bus 0上的设备(在一个处理器系统中,一般将与HOST主桥直接相连的PCI总线被命名为PCI Bus 0),系统首先会忽略Bus 0上的D1,D2等不会挂接PCI桥的设备,主桥发现Bridge 1后,将Bridge1 下面的PCI Bus定为 Bus 1,系统将初始化Bridge 1的配置空间,并将该桥的Primary Bus Number 和 Secondary Bus Number寄存器分别设置成0和1,以表明Bridge1 的上游总线是0,下游总线是1,由于还无法确定Bridge1下挂载设备的具体情况,系统先暂时将Subordinate
Bus Number设为0xFF。如下图所示:
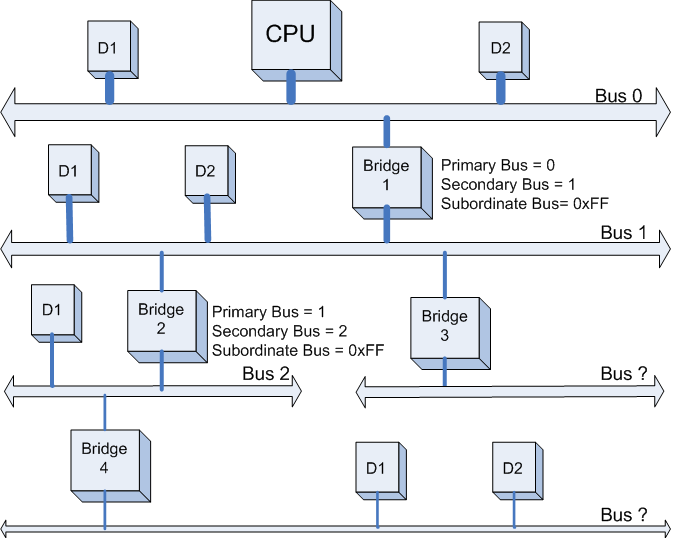
第二步:
系统开始扫描Bus 1,将会发现Bridge 2。系统将Bridge 2下面的PCI Bus定为Bus 2,并将该桥的Primary Bus Number 和 Secondary Bus Number寄存器分别设置成1和2,和上一步一样暂时把Bridge 2 的Subordinate Bus Number设为0xFF。如下图所示:
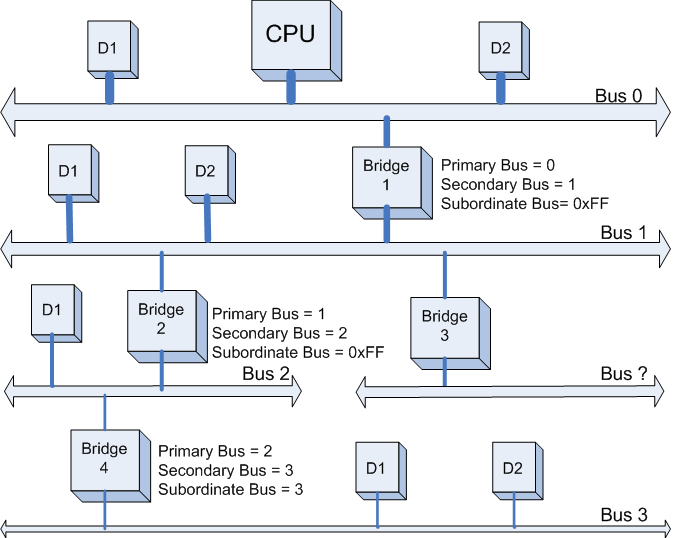
第三步:
系统继续扫描Bus 2,将会发现Bridge 4。系统将Bridge 4下面的PCI Bus定为Bus 3,并将该桥的Primary Bus Number 和 Secondary Bus Number寄存器分别设置成2和3,此后
系统继续扫描后发现Bus 3 下面已经没有任何Bridge了,意味着该PCI总线下已经没有任何挂载下游总线了,因此Bridge 4的Subordinate Bus Number的值已经可以确定为3了。
如下图所示:
第四步:
完成Bus 3的扫描后,系统返回到Bus 2继续扫描,发现Bus 2下面已经没有其他Bridge了。此时Bridge 2的Subordinate Bus Number的值也已经可以确定为3了。如下图所示:

第五步:
完成Bus 2的扫描后,系统返回到Bus1继续扫描,会发现Bridge 3,系统将Bridge 3下面的PCI Bus定为Bus 4。并将Bridge 4的Primary Bus Number 和 Secondary Bus Number寄存器分别设置成1和4,此后系统继续扫描后发现Bus 4 下面已经没有任何Bridge了,意味着该PCI总线下已经没有挂载任何下游总线了,因此Bridge 3 的Subordinate Bus Number的值已经可以确定为4了。如下图所示:
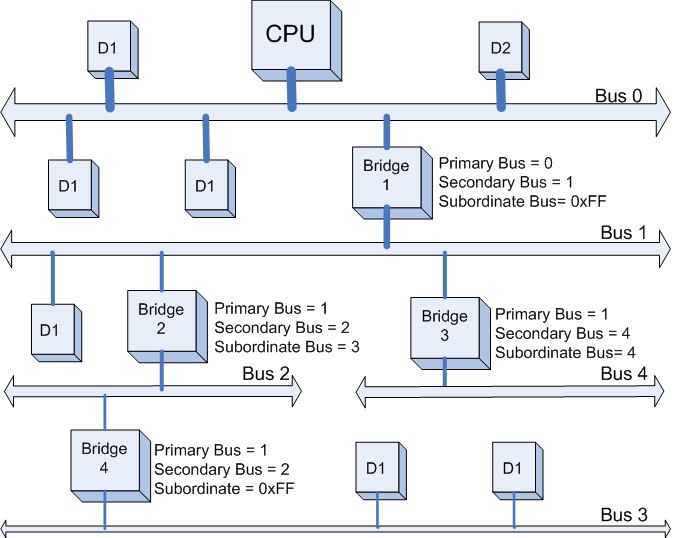
第六步:
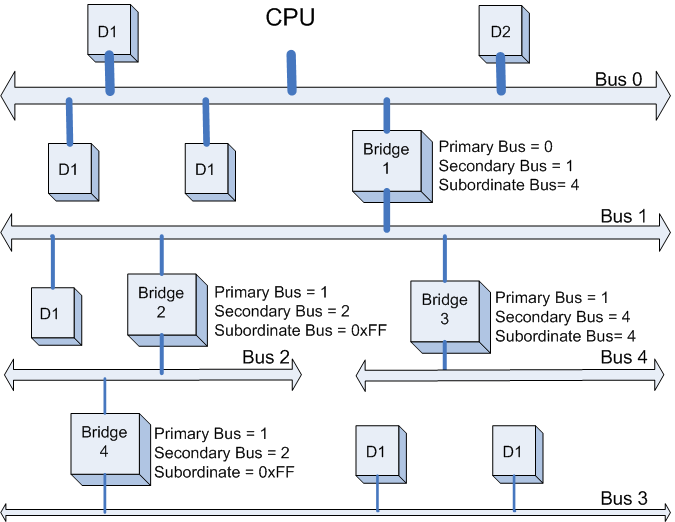
完成Bus 4的扫描后,系统返回到Bus 1继续扫描, 发现Bus 1下面已经没有其他Bridge了。此时Bridge 1的Subordinate Bus Number的值已经可以确定为4,系统返回Bus 0继续扫描(Bus 0下如果有其他它Bridge,将重复上述的步骤进行扫描)。至此,本例中的整个PCI的设备扫描已经完成了。最终的设备和总线的扫描结果如下图所示。
了解了上面PCI设备扫描的大概流程,我们接下来看看Bios代码中具体是如何实现这些扫描的。
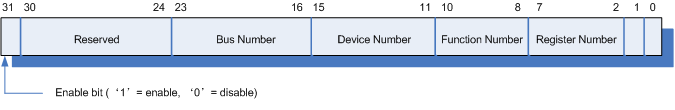
一般来说,我们可以通过两个寄存器来访问PCI的配置空间(寄存器CONFIG_ADDRESS与CONFIG_DATA),在x86体系下,这两个寄存器分别对应0xCF8和0xCFC端口,对配置空间的访问都是通过对这两个寄存器的读写来实现先。CONFIG_ADDRESS寄存器的具体位组成如下图所示:
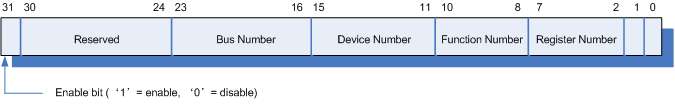
Bus Number : 总线号(8 bit),范围0--255。
Device Number: 设备号(5 bit),范围0--31。
Function Number: 功能号(3 bit),范围0--7。
Register Number: 寄存器号(6 bit),范围0--63 (配置空间一共256个字节,分割成64个4字节的寄存器,从0--63编号)。
每个PCI设备可根据上图所示的四个信息:Bus Number, Device Number, Function Number,Register Number 来进行具体设备的定位并对其配置空间访问。当我们要访问PCI设备的配置空间时,先根据以上格式设置CONFIG_ADDRESS寄存器,然后再读取CONFIG_DATA寄存器即可得到相应的配置空间寄存器的值。
因此,BIOS中PCI配置空间的读写可以封装成下面的函数:
static inline uint32_t pci_config_read32(pci_addr dev, uint8_t reg)
{
outl(dev | reg, 0xcf8);
return inl(0xcfc | reg);
}
static inline void pci_config_write32(pci_addr dev, uint8_t reg, uint32_t val)
{
outl(dev | reg, 0xcf8);
outl(val, 0xcfc);
}
总体来说。该BIOS扫描过程中调用如下几个主要的函数:
ob_pci_init ----> ob_scan_pci_bus ----> pci_find_device ----> ob_pci_configure
下面我们来具体看看代码,首先BIOS执行ob_pci_init(void)函数
int ob_pci_init(void)
{
int bus;
unsigned long mem_base, io_base;
char *path;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PCI
printk("Initializing PCI devices...\n");
#endif
/* brute force bus scan */
/* Find all PCI bridges */
//获取系统指定的memeory与I/O空间的范围,分配给PCIe设备。
mem_base = arch->mem_base;
/* I/O ports under 0x400 are used by devices mapped at fixed
location. */
io_base = arch->io_base + 0x400;
path = strdup("");
/*遍历256条总线*/
for (bus = 0; bus<0x100; bus++) {
ob_scan_pci_bus(bus, &mem_base, &io_base, &path);
}
free(path);
return 0;
}
总线扫描具体实现:
static void ob_scan_pci_bus(int bus, unsigned long *mem_base,
unsigned long *io_base, char **path)
{
int devnum, fn, is_multi, vid, did;
unsigned int htype;
pci_addr addr;
pci_config_t config;
const pci_dev_t *pci_dev;
uint32_t ccode;
uint8_t class, subclass, iface, rev;
activate_device("/");
for (devnum = 0; devnum < 32; devnum++) {
is_multi = 0;
for (fn = 0; fn==0 || (is_multi && fn<8); fn++) {
#ifdef CONFIG_XBOX
if (pci_xbox_blacklisted (bus, devnum, fn))
continue;
#endif
addr = PCI_ADDR(bus, devnum, fn); /*获取设备配置空间地址*/
vid = pci_config_read16(addr, PCI_VENDOR_ID); /*获取Vendor ID*/
did = pci_config_read16(addr, PCI_DEVICE_ID); /*获取Device ID*/
if (vid==0xffff || vid==0)
continue;
ccode = pci_config_read16(addr, PCI_CLASS_DEVICE);
class = ccode >> 8;
subclass = ccode;
iface = pci_config_read8(addr, PCI_CLASS_PROG);
rev = pci_config_read8(addr, PCI_REVISION_ID);
pci_dev = pci_find_device(class, subclass, iface,/*具体设备查找以及初始化*/
vid, did);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PCI
printk("%x:%x.%x - %x:%x - ", bus, devnum, fn,
vid, did);
#endif
htype = pci_config_read8(addr, PCI_HEADER_TYPE);
if (fn == 0)
is_multi = htype & 0x80;
if (pci_dev == NULL || pci_dev->name == NULL)
snprintf(config.path, sizeof(config.path),
"%s/pci%x,%x", *path, vid, did);
else
snprintf(config.path, sizeof(config.path),
"%s/%s", *path, pci_dev->name);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PCI
printk("%s - ", config.path);
#endif
config.dev = addr & 0x00FFFFFF;
REGISTER_NAMED_NODE(ob_pci_node, config.path);
activate_device(config.path);
ob_pci_configure(addr, &config, mem_base, io_base); /*配置设备的配置空间*/
ob_pci_add_properties(addr, pci_dev, &config);
if (class == PCI_BASE_CLASS_BRIDGE &&
(subclass == PCI_SUBCLASS_BRIDGE_HOST ||
subclass == PCI_SUBCLASS_BRIDGE_PCI)) {
/* host or bridge */
free(*path);
*path = strdup(config.path);
}
}
}
device_end();
}具体某条总线上的设备扫描由以下函数实现:
<pre name="code" class="cpp">const pci_dev_t *pci_find_device (uint8_t class, uint8_t subclass,
uint8_t iface, uint16_t vendor,
uint16_t product)
{
int (*config_cb)(const pci_config_t *config);
const pci_class_t *pclass;
const pci_subclass_t *psubclass;
const pci_iface_t *piface;
const pci_dev_t *dev;
const void *private;
pci_dev_t *new;
const char *name, *type;
name = "unknown";
type = "unknown";
config_cb = NULL;
private = NULL;
if (class == 0x00 && subclass == 0x01) {
/* Special hack for old style VGA devices */
class = 0x03;
subclass = 0x00;
} else if (class == 0xFF) {
/* Special case for misc devices */
dev = misc_pci;
goto find_device;
}
if (class > (sizeof(pci_classes) / sizeof(pci_class_t))) {
name = "invalid PCI device";
type = "invalid";
goto bad_device;
}
pclass = &pci_classes[class];
name = pclass->name;
type = pclass->type;
for (psubclass = pclass->subc; ; psubclass++) {
if (psubclass->subclass == 0xFF)
goto bad_device;
if (psubclass->subclass == subclass) {
if (psubclass->name != NULL)
name = psubclass->name;
if (psubclass->type != NULL)
type = psubclass->type;
if (psubclass->config_cb != NULL) {
config_cb = psubclass->config_cb;
}
if (psubclass->private != NULL)
private = psubclass->private;
if (psubclass->iface != NULL)
break;
dev = psubclass->devices;
goto find_device;
}
}
for (piface = psubclass->iface; ; piface++) {
if (piface->iface == 0xFF) {
dev = psubclass->devices;
break;
}
if (piface->iface == iface) {
if (piface->name != NULL)
name = piface->name;
if (piface->type != NULL)
type = piface->type;
if (piface->config_cb != NULL) {
config_cb = piface->config_cb;
}
if (piface->private != NULL)
private = piface->private;
dev = piface->devices;
break;
}
}
find_device:
if (dev == NULL)
goto bad_device;
for (;; dev++) {
if (dev->vendor == 0xFFFF && dev->product == 0xFFFF) {
goto bad_device;
}
if (dev->vendor == vendor && dev->product == product) {
if (dev->name != NULL)
name = dev->name;
if (dev->type != NULL)
type = dev->type;
if (dev->config_cb != NULL) {
config_cb = dev->config_cb;
}
if (dev->private != NULL)
private = dev->private;
new = malloc(sizeof(pci_dev_t));
if (new == NULL)
return NULL;
new->vendor = vendor;
new->product = product;
new->type = type;
new->name = name;
new->model = dev->model;
new->compat = dev->compat;
new->acells = dev->acells;
new->scells = dev->scells;
new->icells = dev->icells;
new->config_cb = config_cb;
new->private = private;
return new;
}
}
bad_device:
printk("Cannot manage '%s' PCI device type '%s':\n %x %x (%x %x %x)\n",
name, type, vendor, product, class, subclass, iface);
return NULL;
}
配置具体设备的配置空间
static void ob_pci_configure(pci_addr addr, pci_config_t *config, unsigned long *mem_base,
unsigned long *io_base)
{
uint32_t smask, omask, amask, size, reloc, min_align;
unsigned long base;
pci_addr config_addr;
int reg;
uint8_t irq_pin, irq_line;
/*配置中断引脚与中断编号*/
irq_pin = pci_config_read8(addr, PCI_INTERRUPT_PIN);
if (irq_pin) {
config->irq_pin = irq_pin;
irq_pin = (((config->dev >> 11) & 0x1F) + irq_pin - 1) & 3;
irq_line = arch->irqs[irq_pin];
pci_config_write8(addr, PCI_INTERRUPT_LINE, irq_line);
config->irq_line = irq_line;
} else
config->irq_line = -1;
/*配置memory空间和I/O空间*/
omask = 0x00000000;
for (reg = 0; reg < 7; reg++) {
config->assigned[reg] = 0x00000000;
config->sizes[reg] = 0x00000000;
if ((omask & 0x0000000f) == 0x4) {
/* 64 bits memory mapping */
continue;
}
if (reg == 6)
config_addr = PCI_ROM_ADDRESS;
else
config_addr = PCI_BASE_ADDR_0 + reg * 4;
config->regions[reg] = pci_config_read32(addr, config_addr);
/* get region size */
pci_config_write32(addr, config_addr, 0xffffffff);
smask = pci_config_read32(addr, config_addr);
if (smask == 0x00000000 || smask == 0xffffffff)
continue;
if (smask & 0x00000001 && reg != 6) {
/* I/O space */
base = *io_base;
min_align = 1 << 7;
amask = 0x00000001;
pci_config_write16(addr, PCI_COMMAND,
pci_config_read16(addr,
PCI_COMMAND) |
PCI_COMMAND_IO);
} else {
/* Memory Space */
base = *mem_base;
min_align = 1 << 16;
amask = 0x0000000F;
if (reg == 6) {
smask |= 1; /* ROM */
}
pci_config_write16(addr, PCI_COMMAND,
pci_config_read16(addr,
PCI_COMMAND) |
PCI_COMMAND_MEMORY);
}
omask = smask & amask;
smask &= ~amask;
size = (~smask) + 1;
config->sizes[reg] = size;
reloc = base;
if (size < min_align)
size = min_align;
reloc = (reloc + size -1) & ~(size - 1);
if (*io_base == base) {
*io_base = reloc + size;
reloc -= arch->io_base;
} else {
*mem_base = reloc + size;
}
pci_config_write32(addr, config_addr, reloc | omask);
config->assigned[reg] = reloc | omask;
}
}
通过以上这些步骤,Bios就完成了所有PCI设备的扫描,并且为每个设备分配好了系统资源。<br>
</pre>
<pre></pre>
初步了解完PCI总线标准之后,我们接下来正式开始PCIe设备的漫游之旅。从我们按下PC的电源按钮开始,BIOS就接管系统控制权开始工作,它会先进行一些内存和设备的初始化工作(当然,也包括我们的PCI设备),由于商业上的原因,Phoenix等厂商的BIOS代码需要授权协议,在此,我们以另外一个款开源BIOS(openbios)为例,来剖析BIOS中,我们的PCIe设备是如何被找到以及初始化的。

PCI设备的扫描是基于深度优先搜索算法(DFS:Depth First Search),也就是说,下级分支最多的PCI桥将最先完成其子设备的扫描。下面我们以图片来具体说明,BIOS是如何一步步完成PCI
设备扫描的。
第一步:
PCI Host 主桥扫描Bus 0上的设备(在一个处理器系统中,一般将与HOST主桥直接相连的PCI总线被命名为PCI Bus 0),系统首先会忽略Bus 0上的D1,D2等不会挂接PCI桥的设备,主桥发现Bridge 1后,将Bridge1 下面的PCI Bus定为 Bus 1,系统将初始化Bridge 1的配置空间,并将该桥的Primary Bus Number 和 Secondary Bus Number寄存器分别设置成0和1,以表明Bridge1 的上游总线是0,下游总线是1,由于还无法确定Bridge1下挂载设备的具体情况,系统先暂时将Subordinate
Bus Number设为0xFF。如下图所示:

第二步:
系统开始扫描Bus 1,将会发现Bridge 2。系统将Bridge 2下面的PCI Bus定为Bus 2,并将该桥的Primary Bus Number 和 Secondary Bus Number寄存器分别设置成1和2,和上一步一样暂时把Bridge 2 的Subordinate Bus Number设为0xFF。如下图所示:

第三步:
系统继续扫描Bus 2,将会发现Bridge 4。系统将Bridge 4下面的PCI Bus定为Bus 3,并将该桥的Primary Bus Number 和 Secondary Bus Number寄存器分别设置成2和3,此后
系统继续扫描后发现Bus 3 下面已经没有任何Bridge了,意味着该PCI总线下已经没有任何挂载下游总线了,因此Bridge 4的Subordinate Bus Number的值已经可以确定为3了。
如下图所示:

第四步:
完成Bus 3的扫描后,系统返回到Bus 2继续扫描,发现Bus 2下面已经没有其他Bridge了。此时Bridge 2的Subordinate Bus Number的值也已经可以确定为3了。如下图所示:

第五步:
完成Bus 2的扫描后,系统返回到Bus1继续扫描,会发现Bridge 3,系统将Bridge 3下面的PCI Bus定为Bus 4。并将Bridge 4的Primary Bus Number 和 Secondary Bus Number寄存器分别设置成1和4,此后系统继续扫描后发现Bus 4 下面已经没有任何Bridge了,意味着该PCI总线下已经没有挂载任何下游总线了,因此Bridge 3 的Subordinate Bus Number的值已经可以确定为4了。如下图所示:

第六步:
完成Bus 4的扫描后,系统返回到Bus 1继续扫描, 发现Bus 1下面已经没有其他Bridge了。此时Bridge 1的Subordinate Bus Number的值已经可以确定为4,系统返回Bus 0继续扫描(Bus 0下如果有其他它Bridge,将重复上述的步骤进行扫描)。至此,本例中的整个PCI的设备扫描已经完成了。最终的设备和总线的扫描结果如下图所示。

了解了上面PCI设备扫描的大概流程,我们接下来看看Bios代码中具体是如何实现这些扫描的。
一般来说,我们可以通过两个寄存器来访问PCI的配置空间(寄存器CONFIG_ADDRESS与CONFIG_DATA),在x86体系下,这两个寄存器分别对应0xCF8和0xCFC端口,对配置空间的访问都是通过对这两个寄存器的读写来实现先。CONFIG_ADDRESS寄存器的具体位组成如下图所示:

Bus Number : 总线号(8 bit),范围0--255。
Device Number: 设备号(5 bit),范围0--31。
Function Number: 功能号(3 bit),范围0--7。
Register Number: 寄存器号(6 bit),范围0--63 (配置空间一共256个字节,分割成64个4字节的寄存器,从0--63编号)。
每个PCI设备可根据上图所示的四个信息:Bus Number, Device Number, Function Number,Register Number 来进行具体设备的定位并对其配置空间访问。当我们要访问PCI设备的配置空间时,先根据以上格式设置CONFIG_ADDRESS寄存器,然后再读取CONFIG_DATA寄存器即可得到相应的配置空间寄存器的值。
因此,BIOS中PCI配置空间的读写可以封装成下面的函数:
static inline uint32_t pci_config_read32(pci_addr dev, uint8_t reg)
{
outl(dev | reg, 0xcf8);
return inl(0xcfc | reg);
}
static inline void pci_config_write32(pci_addr dev, uint8_t reg, uint32_t val)
{
outl(dev | reg, 0xcf8);
outl(val, 0xcfc);
}
总体来说。该BIOS扫描过程中调用如下几个主要的函数:
ob_pci_init ----> ob_scan_pci_bus ----> pci_find_device ----> ob_pci_configure
下面我们来具体看看代码,首先BIOS执行ob_pci_init(void)函数
int ob_pci_init(void)
{
int bus;
unsigned long mem_base, io_base;
char *path;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PCI
printk("Initializing PCI devices...\n");
#endif
/* brute force bus scan */
/* Find all PCI bridges */
//获取系统指定的memeory与I/O空间的范围,分配给PCIe设备。
mem_base = arch->mem_base;
/* I/O ports under 0x400 are used by devices mapped at fixed
location. */
io_base = arch->io_base + 0x400;
path = strdup("");
/*遍历256条总线*/
for (bus = 0; bus<0x100; bus++) {
ob_scan_pci_bus(bus, &mem_base, &io_base, &path);
}
free(path);
return 0;
}
总线扫描具体实现:
static void ob_scan_pci_bus(int bus, unsigned long *mem_base,
unsigned long *io_base, char **path)
{
int devnum, fn, is_multi, vid, did;
unsigned int htype;
pci_addr addr;
pci_config_t config;
const pci_dev_t *pci_dev;
uint32_t ccode;
uint8_t class, subclass, iface, rev;
activate_device("/");
for (devnum = 0; devnum < 32; devnum++) {
is_multi = 0;
for (fn = 0; fn==0 || (is_multi && fn<8); fn++) {
#ifdef CONFIG_XBOX
if (pci_xbox_blacklisted (bus, devnum, fn))
continue;
#endif
addr = PCI_ADDR(bus, devnum, fn); /*获取设备配置空间地址*/
vid = pci_config_read16(addr, PCI_VENDOR_ID); /*获取Vendor ID*/
did = pci_config_read16(addr, PCI_DEVICE_ID); /*获取Device ID*/
if (vid==0xffff || vid==0)
continue;
ccode = pci_config_read16(addr, PCI_CLASS_DEVICE);
class = ccode >> 8;
subclass = ccode;
iface = pci_config_read8(addr, PCI_CLASS_PROG);
rev = pci_config_read8(addr, PCI_REVISION_ID);
pci_dev = pci_find_device(class, subclass, iface,/*具体设备查找以及初始化*/
vid, did);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PCI
printk("%x:%x.%x - %x:%x - ", bus, devnum, fn,
vid, did);
#endif
htype = pci_config_read8(addr, PCI_HEADER_TYPE);
if (fn == 0)
is_multi = htype & 0x80;
if (pci_dev == NULL || pci_dev->name == NULL)
snprintf(config.path, sizeof(config.path),
"%s/pci%x,%x", *path, vid, did);
else
snprintf(config.path, sizeof(config.path),
"%s/%s", *path, pci_dev->name);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PCI
printk("%s - ", config.path);
#endif
config.dev = addr & 0x00FFFFFF;
REGISTER_NAMED_NODE(ob_pci_node, config.path);
activate_device(config.path);
ob_pci_configure(addr, &config, mem_base, io_base); /*配置设备的配置空间*/
ob_pci_add_properties(addr, pci_dev, &config);
if (class == PCI_BASE_CLASS_BRIDGE &&
(subclass == PCI_SUBCLASS_BRIDGE_HOST ||
subclass == PCI_SUBCLASS_BRIDGE_PCI)) {
/* host or bridge */
free(*path);
*path = strdup(config.path);
}
}
}
device_end();
}具体某条总线上的设备扫描由以下函数实现:
<pre name="code" class="cpp">const pci_dev_t *pci_find_device (uint8_t class, uint8_t subclass,
uint8_t iface, uint16_t vendor,
uint16_t product)
{
int (*config_cb)(const pci_config_t *config);
const pci_class_t *pclass;
const pci_subclass_t *psubclass;
const pci_iface_t *piface;
const pci_dev_t *dev;
const void *private;
pci_dev_t *new;
const char *name, *type;
name = "unknown";
type = "unknown";
config_cb = NULL;
private = NULL;
if (class == 0x00 && subclass == 0x01) {
/* Special hack for old style VGA devices */
class = 0x03;
subclass = 0x00;
} else if (class == 0xFF) {
/* Special case for misc devices */
dev = misc_pci;
goto find_device;
}
if (class > (sizeof(pci_classes) / sizeof(pci_class_t))) {
name = "invalid PCI device";
type = "invalid";
goto bad_device;
}
pclass = &pci_classes[class];
name = pclass->name;
type = pclass->type;
for (psubclass = pclass->subc; ; psubclass++) {
if (psubclass->subclass == 0xFF)
goto bad_device;
if (psubclass->subclass == subclass) {
if (psubclass->name != NULL)
name = psubclass->name;
if (psubclass->type != NULL)
type = psubclass->type;
if (psubclass->config_cb != NULL) {
config_cb = psubclass->config_cb;
}
if (psubclass->private != NULL)
private = psubclass->private;
if (psubclass->iface != NULL)
break;
dev = psubclass->devices;
goto find_device;
}
}
for (piface = psubclass->iface; ; piface++) {
if (piface->iface == 0xFF) {
dev = psubclass->devices;
break;
}
if (piface->iface == iface) {
if (piface->name != NULL)
name = piface->name;
if (piface->type != NULL)
type = piface->type;
if (piface->config_cb != NULL) {
config_cb = piface->config_cb;
}
if (piface->private != NULL)
private = piface->private;
dev = piface->devices;
break;
}
}
find_device:
if (dev == NULL)
goto bad_device;
for (;; dev++) {
if (dev->vendor == 0xFFFF && dev->product == 0xFFFF) {
goto bad_device;
}
if (dev->vendor == vendor && dev->product == product) {
if (dev->name != NULL)
name = dev->name;
if (dev->type != NULL)
type = dev->type;
if (dev->config_cb != NULL) {
config_cb = dev->config_cb;
}
if (dev->private != NULL)
private = dev->private;
new = malloc(sizeof(pci_dev_t));
if (new == NULL)
return NULL;
new->vendor = vendor;
new->product = product;
new->type = type;
new->name = name;
new->model = dev->model;
new->compat = dev->compat;
new->acells = dev->acells;
new->scells = dev->scells;
new->icells = dev->icells;
new->config_cb = config_cb;
new->private = private;
return new;
}
}
bad_device:
printk("Cannot manage '%s' PCI device type '%s':\n %x %x (%x %x %x)\n",
name, type, vendor, product, class, subclass, iface);
return NULL;
}
配置具体设备的配置空间
static void ob_pci_configure(pci_addr addr, pci_config_t *config, unsigned long *mem_base,
unsigned long *io_base)
{
uint32_t smask, omask, amask, size, reloc, min_align;
unsigned long base;
pci_addr config_addr;
int reg;
uint8_t irq_pin, irq_line;
/*配置中断引脚与中断编号*/
irq_pin = pci_config_read8(addr, PCI_INTERRUPT_PIN);
if (irq_pin) {
config->irq_pin = irq_pin;
irq_pin = (((config->dev >> 11) & 0x1F) + irq_pin - 1) & 3;
irq_line = arch->irqs[irq_pin];
pci_config_write8(addr, PCI_INTERRUPT_LINE, irq_line);
config->irq_line = irq_line;
} else
config->irq_line = -1;
/*配置memory空间和I/O空间*/
omask = 0x00000000;
for (reg = 0; reg < 7; reg++) {
config->assigned[reg] = 0x00000000;
config->sizes[reg] = 0x00000000;
if ((omask & 0x0000000f) == 0x4) {
/* 64 bits memory mapping */
continue;
}
if (reg == 6)
config_addr = PCI_ROM_ADDRESS;
else
config_addr = PCI_BASE_ADDR_0 + reg * 4;
config->regions[reg] = pci_config_read32(addr, config_addr);
/* get region size */
pci_config_write32(addr, config_addr, 0xffffffff);
smask = pci_config_read32(addr, config_addr);
if (smask == 0x00000000 || smask == 0xffffffff)
continue;
if (smask & 0x00000001 && reg != 6) {
/* I/O space */
base = *io_base;
min_align = 1 << 7;
amask = 0x00000001;
pci_config_write16(addr, PCI_COMMAND,
pci_config_read16(addr,
PCI_COMMAND) |
PCI_COMMAND_IO);
} else {
/* Memory Space */
base = *mem_base;
min_align = 1 << 16;
amask = 0x0000000F;
if (reg == 6) {
smask |= 1; /* ROM */
}
pci_config_write16(addr, PCI_COMMAND,
pci_config_read16(addr,
PCI_COMMAND) |
PCI_COMMAND_MEMORY);
}
omask = smask & amask;
smask &= ~amask;
size = (~smask) + 1;
config->sizes[reg] = size;
reloc = base;
if (size < min_align)
size = min_align;
reloc = (reloc + size -1) & ~(size - 1);
if (*io_base == base) {
*io_base = reloc + size;
reloc -= arch->io_base;
} else {
*mem_base = reloc + size;
}
pci_config_write32(addr, config_addr, reloc | omask);
config->assigned[reg] = reloc | omask;
}
}
通过以上这些步骤,Bios就完成了所有PCI设备的扫描,并且为每个设备分配好了系统资源。<br>
</pre>
<pre></pre>
相关文章推荐
- PCIe设备漫游记----驱动加载篇
- PCIe设备漫游记----设备打开/关闭篇
- PCIe设备漫游记----BIOS篇
- PCIe设备漫游记----BIOS篇
- PCIe设备漫游记----寄存器读写篇
- PCIE-GEN3 是什么意思?LANES呢?可以拆分吗?如果配置不当的话,会造成某些PCIE设备资源不足,对吗?
- PCIe设备的配置空间
- PCIe-块设备驱动-Single DMA
- PCIe设备,功能,总线
- PCIe-块设备驱动-SG DMA
- PCIe设备的配置空间 分类: 浅谈PCI-E 2013-07-22 16:31 720人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
- linux 下PCIE控制器设备树 学习
- PCIe设备的配置空间
- 4.3 PCIe设备的扩展配置空间
- PCIe驱动开发-设备打开/关闭
- linux下pcie设备驱动
- PCIe配置空间和PCI设备中的寄存器
- pcie对设备的枚举
- PCI Express设备驱动 (4,PCIe配置空间和PCI设备中的寄存器)
- PCIe设备的配置空间
