bzoj 2038 A-小Z的袜子[hose] - 莫队算法
2017-01-17 08:14
423 查看
作为一个生活散漫的人,小Z每天早上都要耗费很久从一堆五颜六色的袜子中找出一双来穿。终于有一天,小Z再也无法忍受这恼人的找袜子过程,于是他决定听天由命……
具体来说,小Z把这N只袜子从1到N编号,然后从编号L到R(L 尽管小Z并不在意两只袜子是不是完整的一双,甚至不在意两只袜子是否一左一右,他却很在意袜子的颜色,毕竟穿两只不同色的袜子会很尴尬。
你的任务便是告诉小Z,他有多大的概率抽到两只颜色相同的袜子。当然,小Z希望这个概率尽量高,所以他可能会询问多个(L,R)以方便自己选择。
Input
输入文件第一行包含两个正整数N和M。N为袜子的数量,M为小Z所提的询问的数量。接下来一行包含N个正整数Ci,其中Ci表示第i只袜子的颜色,相同的颜色用相同的数字表示。再接下来M行,每行两个正整数L,R表示一个询问。
Output
包含M行,对于每个询问在一行中输出分数A/B表示从该询问的区间[L,R]中随机抽出两只袜子颜色相同的概率。若该概率为0则输出0/1,否则输出的A/B必须为最简分数。(详见样例)
Sample Input
Sample Output
这个是支持离线的一道题,那么可以试试用莫队算法。
那么看能不能在已知一个区间[l, r]的情况下,快速知道[l - 1, r],[l +1, r],[l, r - 1]和[l, r + 1]。这列主要最难(其实也不难)找的是方案数。那么来看,如果某种袜子现有x个,那么新加同一种袜子增加的方案数为
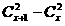
。然后再展开:
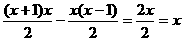
删除同理。
具体来说,小Z把这N只袜子从1到N编号,然后从编号L到R(L 尽管小Z并不在意两只袜子是不是完整的一双,甚至不在意两只袜子是否一左一右,他却很在意袜子的颜色,毕竟穿两只不同色的袜子会很尴尬。
你的任务便是告诉小Z,他有多大的概率抽到两只颜色相同的袜子。当然,小Z希望这个概率尽量高,所以他可能会询问多个(L,R)以方便自己选择。
Input
输入文件第一行包含两个正整数N和M。N为袜子的数量,M为小Z所提的询问的数量。接下来一行包含N个正整数Ci,其中Ci表示第i只袜子的颜色,相同的颜色用相同的数字表示。再接下来M行,每行两个正整数L,R表示一个询问。
Output
包含M行,对于每个询问在一行中输出分数A/B表示从该询问的区间[L,R]中随机抽出两只袜子颜色相同的概率。若该概率为0则输出0/1,否则输出的A/B必须为最简分数。(详见样例)
Sample Input
6 4 1 2 3 3 3 2 2 6 1 3 3 5 1 6
Sample Output
2/5 0/1 1/1 4/15 【样例解释】 询问1:共C(5,2)=10种可能,其中抽出两个2有1种可能,抽出两个3有3种可能,概率为(1+3)/10=4/10=2/5。 询问2:共C(3,2)=3种可能,无法抽到颜色相同的袜子,概率为0/3=0/1。 询问3:共C(3,2)=3种可能,均为抽出两个3,概率为3/3=1/1。 注:上述C(a, b)表示组合数,组合数C(a, b)等价于在a个不同的物品中选取b个的选取方案数。 【数据规模和约定】 30%的数据中 N,M ≤ 5000; 60%的数据中 N,M ≤ 25000; 100%的数据中 N,M ≤ 50000,1 ≤ L < R ≤ N,Ci ≤ N。
这个是支持离线的一道题,那么可以试试用莫队算法。
那么看能不能在已知一个区间[l, r]的情况下,快速知道[l - 1, r],[l +1, r],[l, r - 1]和[l, r + 1]。这列主要最难(其实也不难)找的是方案数。那么来看,如果某种袜子现有x个,那么新加同一种袜子增加的方案数为
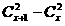
。然后再展开:
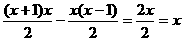
删除同理。
Code
/**
* bzoj
* Problem2038
* Accepted
* Time:820ms
* Memory:3264k
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<ctime>
#include<cctype>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
#define smin(a, b) (a) = min((a), (b))
#define smax(a, b) (a) = max((a), (b))
template<typename T>
inline void readInteger(T& u){
char x;
int aFlag = 1;
while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != '-' && x != -1);
if(x == -1) return;
if(x == '-'){
x = getchar();
aFlag = -1;
}
for(u = x - '0'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 3) + (u << 1) + x - '0');
ungetc(x, stdin);
u *= aFlag;
}
typedef class Segment{
public:
int from;
int end;
int id;
int index;
Segment():from(0), end(0), index(0){ }
boolean operator < (Segment another) const{
if(this->id != another.id) return this->id < another.id;
return this->end < another.end;
}
}Segment;
int n, m;
Segment* seg;
int *colors;
int divs;
int blocks;
inline long long C(int x){
return (x * 1LL * (x - 1) / 2);
}
template<typename T>
inline T gcd(T a, T b){
if(b == 0) return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
inline void init(){
readInteger(n);
readInteger(m);
seg = new Segment[(const int)(m + 1)];
colors = new int[(const int)(n + 1)];
divs = (int)(sqrt(n + 0.5));
blocks = n / divs + (n % divs == 0) ? (1) : (0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
readInteger(colors[i]);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
readInteger(seg[i].from);
readInteger(seg[i].end);
seg[i].index = i;
seg[i].id = seg[i].from / divs;
}
}
int* ccolor;
long long *resa, *resb;
inline void solve(){
sort(seg + 1, seg + m + 1);
ccolor = new int[(const int)(n + 1)];
resa = new long long[(const int)(m + 1)];
resb = new long long[(const int)(m + 1)];
int pseg = 1;
int mdzzf = 1, mdzzr = 1; //莫队指针,左闭右开
long long qk = 0;
memset(ccolor, 0, sizeof(int) * (n + 1));
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
if(seg[i].from == seg[i].end){
resa[seg[i].index] = 0;
continue;
}
while(mdzzr > seg[pseg].end + 1) qk -= --ccolor[colors[--mdzzr]];
while(mdzzf > seg[pseg].from) qk += ccolor[colors[--mdzzf]]++;
while(mdzzr <= seg[pseg].end) qk += ccolor[colors[mdzzr++]]++;
while(mdzzf < seg[pseg].from) qk -= --ccolor[colors[mdzzf++]];
resa[seg[pseg].index] = qk;
resb[seg[pseg].index] = C(seg[pseg].end - seg[pseg].from + 1);
pseg++;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
if(resa[i] == 0){
printf("0/1\n");
continue;
}
long long g = gcd(resa[i], resb[i]);
printf("%lld/%lld\n", resa[i] / g, resb[i] / g);
}
}
int main(){
init();
solve();
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 小Z的袜子(hose) - bzoj 2038 莫队算法
- BZOJ 2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose)&&莫队算法
- BZOJ 2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose) 【莫队算法】
- BZOJ 2038 小Z的袜子(hose) [莫队算法]
- BZOJ 2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose)(莫队算法)
- BZOJ 2038 小Z的袜子(hose) 莫队算法
- bzoj 2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose)(莫队算法)
- BZOJ 2038 小Z的袜子(hose) (莫队算法)
- BZOJ 2038([2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose)-莫队算法序列)
- BZOJ 2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose) [莫队算法]【学习笔记】
- BZOJ 2038 小Z的袜子(hose) 莫队算法
- [BZOJ]2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose) 莫队算法
- bzoj 2038 [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose)(莫队算法)
- bzoj 2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose) 莫队算法
- bzoj 2038 小Z的袜子(hose)(莫队算法)
- BZOJ 2038 小Z的袜子(hose)(莫队算法)
- bzoj 2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose) 【莫队算法】
- bzoj 2038 [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose)(莫队算法)
- BZOJ 2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose)【莫队算法裸题&&学习笔记】
- BZOJ 2038: [2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子(hose)(莫队算法)
