HDU 3362 Fix(状压dp)
2017-01-16 12:54
225 查看
Fix
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1037 Accepted Submission(s): 349
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
There are a few points on a plane, and some are fixed on the plane, some are not. We want to connect these points by some sticks so that all the points are fixed on the plane. Of course, we want to know the minimum length of the sum of the sticks.
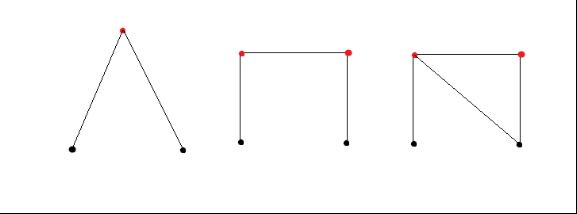
As in the images, the black points are fixed on the plane and red ones are not, which need to be fixed by sticks.
All the points in the left image have been fixed. But the middle one is not, which we need add one stick to fix those four points (the right image shows that stick). Triangle is steady, isn’t it?\
[align=left]Input[/align]
The input consists of multiply test cases. The first line of each test case contains one integer, n (1 <= n <= 18), which is the number of points. The next n lines, each line consists of three integers, x, y, c (0 <= x, y < 100). (x, y) indicate the coordinate of one point; c = 1 indicates this point is fixed; c = 0 indicates this point is not fixed. You can assume that no two points have the same coordinate.
The last test case is followed by a line containing one zero, which means the end of the input.
[align=left]Output[/align]
Output the minimum length with six factional digits for each test case in a single line. If you cannot fix all the points, then output “No Solution”.
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
4
0 0 1
1 0 1
0 1 0
1 1 0
3
0 0 1
1 1 0
2 2 0
0
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
4.414214
No Solution
[align=left]Source[/align]
“光庭杯”第五届华中北区程序设计邀请赛 暨 WHU第八届程序设计竞赛
题目大意:把动点固定最少需要多长的木棒。
题解:状态压缩+dp
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
double inf=100000000000.0;
double dis[300000];
int n;
int start,target;
struct node
{
double x,y;
bool fix;
}p[20];
double cal(int a,int b)
{
return sqrt((double)((p[a].x-p[b].x)*(p[a].x-p[b].x)+(p[a].y-p[b].y)*(p[a].y-p[b].y)));
}
double work(int k,int t)
{
double dis[20];
int l=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if (k&(1<<i)) dis[l++]=cal(i,t); //判断第i个点是否固定
if (l<2) return -1;
sort(dis,dis+l);//sort的第一个参数首地址,第二个参数尾地址,排序范围为“[,)”
return dis[0]+dis[1];
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
if (n==0) break;
start=0;
target=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%d",&p[i].x,&p[i].y,&p[i].fix);
start=start|(p[i].fix<<i);
target=target|(1<<i);
}
for(int i=0;i<=target;i++) dis[i]=inf;
dis[start]=0;
for(int k=start;k<=target;k++)
{
//if (dis[k]==inf) continue; 这句最好加上
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if ( !(k&(1<<i)) )//判断第i个点是否可以移动,如果可以继续做
{
double res=work(k,i);
if(res>0) dis[k|(1<<i)]=min(dis[k|(1<<i)],dis[k]+res);
}
}
if (dis[target]==inf) printf("No Solution\n");
else printf("%.6lf\n",dis[target]);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- HDU 3362 Fix(状压DP)
- HDU 3362 Fix(状压DP)
- HDU 3362 Fix (状压DP)
- HDU 3362 Fix (状态压缩DP)
- HDU 4084 Campus Design 状压dp
- hdu 4539 郑厂长系列故事——排兵布阵 (状压DP)
- hdu 2686(状压dp)
- hdu 2809(状压dp)
- hdu 3001(状压dp)
- hdu 2809(状压dp)
- hdu 1074 Doing Homework(状压dp)
- HDU 4539 状压DP
- hdu 4114(状压dp)
- hdu 2167(状压dp)
- hdu 4539(状压dp)
- HDU 1074 状压DP
- hdu 4539(状压dp)
- HDU 4539 状压DP
- hdu 4739 Zhuge Liang's Mines(状压DP)
- hdu 3001(状压dp)
