Codeforces 471D MUH and Cube Walls【思维+KMP】
2017-01-02 17:33
417 查看
D. MUH and Cube Walls
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Polar bears Menshykov and Uslada from the zoo of St. Petersburg and elephant Horace from the zoo of Kiev got hold of lots of wooden cubes somewhere. They started making cube towers by placing the cubes one on top of the other. They defined multiple towers
standing in a line as a wall. A wall can consist of towers of different heights.
Horace was the first to finish making his wall. He called his wall an elephant. The wall consists of
w towers. The bears also finished making their wall but they didn't give it a name. Their wall consists of
n towers. Horace looked at the bears' tower and wondered: in how many parts of the wall can he "see an elephant"? He can "see an elephant" on a segment of
w contiguous towers if the heights of the towers on the segment match as a sequence the heights of the towers in Horace's wall. In order to see as many elephants as possible, Horace can raise and lower his wall. He even
can lower the wall below the ground level (see the pictures to the samples for clarification).
Your task is to count the number of segments where Horace can "see an elephant".
Input
The first line contains two integers n and
w (1 ≤ n, w ≤ 2·105) — the number of towers in the bears' and the elephant's walls correspondingly. The second line contains
n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109)
— the heights of the towers in the bears' wall. The third line contains
w integers bi (1 ≤ bi ≤ 109) — the heights of the towers
in the elephant's wall.
Output
Print the number of segments in the bears' wall where Horace can "see an elephant".
Examples
Input
Output
Note
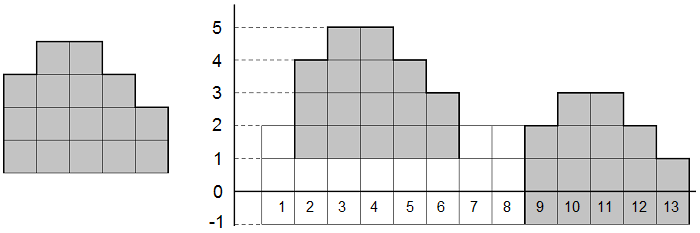
The picture to the left shows Horace's wall from the sample, the picture to the right shows the bears' wall. The segments where Horace can "see an elephant" are in gray.
问题比较抽象,我们对于题目大意进行简化说明:
给你一个数组A,再给你一个数组B,我们可以任意将数组B整体增加或者减少值X(整数),我们可以进行修改值的操作无限次,每次我们要在数组A中找寻有几段和数组B完全匹配的子段。
思路:
如果我们枚举这个修改值X的话,时间复杂度非常的高,这里我们只要想到了差值,那么这个题就结束了。
对应数组B,我们无论对于整体修改值X为多大,其差值都是一样的:
3 4 4 3 2
-1 0 1 1
所以我们只要对于这个差值进行KMP匹配即可。
当M==1的时候需要特判,答案为N.
Ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int tmpa[2500050];
int tmpb[2500050];
int a[250050];
int b[250050];
int next[250050];
int n,m;
int lena;
int lenb;
int output;
void set_naxt()//子串的next数组
{
int i=0,j=-1;
next[0]=-1;
while(i<lenb)
{
if(j==-1||b[i]==b[j])
{
i++; j++;
next[i]=j;
}
else
j=next[j];
}
}
int kmp()
{
int i=0,j=0;
set_naxt();
while(i<lena)
{
if(j==-1||a[i]==b[j])
{
i++;j++;
}
else
j=next[j];
if(j==lenb)
{
output++;
j=next[j];
//printf("%d\n",j);
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)scanf("%d",&tmpa[i]);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)scanf("%d",&tmpb[i]);
if(m==1)
{
printf("%d\n",n);
continue;
}
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)tmpa[i]=tmpa[i]-tmpa[i+1];
for(int i=0;i<m-1;i++)tmpb[i]=tmpb[i]-tmpb[i+1];
lena=n-1;
lenb=m-1;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)a[i]=tmpa[i];
for(int i=0;i<m-1;i++)b[i]=tmpb[i];
output=0;
kmp();
printf("%d\n",output);
}
}
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Polar bears Menshykov and Uslada from the zoo of St. Petersburg and elephant Horace from the zoo of Kiev got hold of lots of wooden cubes somewhere. They started making cube towers by placing the cubes one on top of the other. They defined multiple towers
standing in a line as a wall. A wall can consist of towers of different heights.
Horace was the first to finish making his wall. He called his wall an elephant. The wall consists of
w towers. The bears also finished making their wall but they didn't give it a name. Their wall consists of
n towers. Horace looked at the bears' tower and wondered: in how many parts of the wall can he "see an elephant"? He can "see an elephant" on a segment of
w contiguous towers if the heights of the towers on the segment match as a sequence the heights of the towers in Horace's wall. In order to see as many elephants as possible, Horace can raise and lower his wall. He even
can lower the wall below the ground level (see the pictures to the samples for clarification).
Your task is to count the number of segments where Horace can "see an elephant".
Input
The first line contains two integers n and
w (1 ≤ n, w ≤ 2·105) — the number of towers in the bears' and the elephant's walls correspondingly. The second line contains
n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109)
— the heights of the towers in the bears' wall. The third line contains
w integers bi (1 ≤ bi ≤ 109) — the heights of the towers
in the elephant's wall.
Output
Print the number of segments in the bears' wall where Horace can "see an elephant".
Examples
Input
13 5 2 4 5 5 4 3 2 2 2 3 3 2 1 3 4 4 3 2
Output
2
Note
The picture to the left shows Horace's wall from the sample, the picture to the right shows the bears' wall. The segments where Horace can "see an elephant" are in gray.

问题比较抽象,我们对于题目大意进行简化说明:
给你一个数组A,再给你一个数组B,我们可以任意将数组B整体增加或者减少值X(整数),我们可以进行修改值的操作无限次,每次我们要在数组A中找寻有几段和数组B完全匹配的子段。
思路:
如果我们枚举这个修改值X的话,时间复杂度非常的高,这里我们只要想到了差值,那么这个题就结束了。
对应数组B,我们无论对于整体修改值X为多大,其差值都是一样的:
3 4 4 3 2
-1 0 1 1
所以我们只要对于这个差值进行KMP匹配即可。
当M==1的时候需要特判,答案为N.
Ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int tmpa[2500050];
int tmpb[2500050];
int a[250050];
int b[250050];
int next[250050];
int n,m;
int lena;
int lenb;
int output;
void set_naxt()//子串的next数组
{
int i=0,j=-1;
next[0]=-1;
while(i<lenb)
{
if(j==-1||b[i]==b[j])
{
i++; j++;
next[i]=j;
}
else
j=next[j];
}
}
int kmp()
{
int i=0,j=0;
set_naxt();
while(i<lena)
{
if(j==-1||a[i]==b[j])
{
i++;j++;
}
else
j=next[j];
if(j==lenb)
{
output++;
j=next[j];
//printf("%d\n",j);
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)scanf("%d",&tmpa[i]);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)scanf("%d",&tmpb[i]);
if(m==1)
{
printf("%d\n",n);
continue;
}
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)tmpa[i]=tmpa[i]-tmpa[i+1];
for(int i=0;i<m-1;i++)tmpb[i]=tmpb[i]-tmpb[i+1];
lena=n-1;
lenb=m-1;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)a[i]=tmpa[i];
for(int i=0;i<m-1;i++)b[i]=tmpb[i];
output=0;
kmp();
printf("%d\n",output);
}
}
相关文章推荐
- Password CodeForces - 126B [KMP+DP思维]
- codeforces-757-【B、C思维】
- CodeForces 554B Ohana Cleans Up 【思维+map】
- Codeforces 152C Pocket Book 思维
- CodeForces 552C. Vanya and Scales(进制+思维)
- CodeForces 865D Buy Low Sell High(思维)
- Codeforces 598B Queries on a String 【思维】
- CodeForces 471D MUH and Cube Walls -KMP
- 【组合数学思维】CodeForces - 233C Cycles
- codeforces 931E. Game with String(思维+预处理+概率)
- codeforces 384C Milking cows(脑洞+思维)
- Codeforces--675C--Money Transfers(思维)
- CodeForces 246A. Buggy Sorting【思维】
- Codeforces 155C Hometask【思维+Dp】
- CodeForces 828C String Reconstruction【并查集+思维】
- 【CodeForces - 638】C 【思维+DFS】
- Codeforces 914C - Travelling Salesman and Special Numbers 【思维】
- Codeforces 615 C Running Track【KMP匹配】
- Codeforces 536B Tavas and Malekas 求自身首尾的重叠位置 KMP
- codeforces 776c Molly's Chemicals 【思维】
