codeforces 750D New Year and Fireworks(bfs or dfs)
2016-12-31 07:34
507 查看
New Year and Fireworks
time limit per test
2.5 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
One tradition of welcoming the New Year is launching fireworks into the sky. Usually a launched firework flies vertically upward for some period of time, then explodes, splitting into several parts flying in different directions. Sometimes those parts also
explode after some period of time, splitting into even more parts, and so on.
Limak, who lives in an infinite grid, has a single firework. The behaviour of the firework is described with a recursion depth n and
a duration for each level of recursion t1, t2, ..., tn.
Once Limak launches the firework in some cell, the firework starts moving upward. After covering t1cells
(including the starting cell), it explodes and splits into two parts, each moving in the direction changed by 45 degrees (see the pictures
below for clarification). So, one part moves in the top-left direction, while the other one moves in the top-right direction. Each part explodes again after covering t2 cells,
splitting into two parts moving in directions again changed by 45 degrees. The process continues till the n-th
level of recursion, when all 2n - 1 existing
parts explode and disappear without creating new parts. After a few levels of recursion, it's possible that some parts will be at the same place and at the same time — it is allowed and such parts do not crash.
Before launching the firework, Limak must make sure that nobody stands in cells which will be visited at least once by the firework. Can you count the number of those cells?
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 30) —
the total depth of the recursion.
The second line contains n integers t1, t2, ..., tn (1 ≤ ti ≤ 5).
On the i-th level each of 2i - 1 parts
will cover ti cells
before exploding.
Output
Print one integer, denoting the number of cells which will be visited at least once by any part of the firework.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
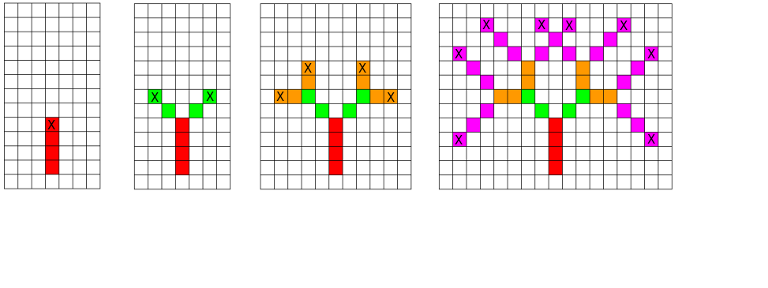
For the first sample, the drawings below show the situation after each level of recursion. Limak launched the firework from the bottom-most red cell. It covered t1 = 4 cells
(marked red), exploded and divided into two parts (their further movement is marked green). All explosions are marked with an 'X' character. On the last drawing,
there are 4 red, 4 green, 8 orange
and 23 pink cells. So, the total number of visited cells is 4 + 4 + 8 + 23 = 39.
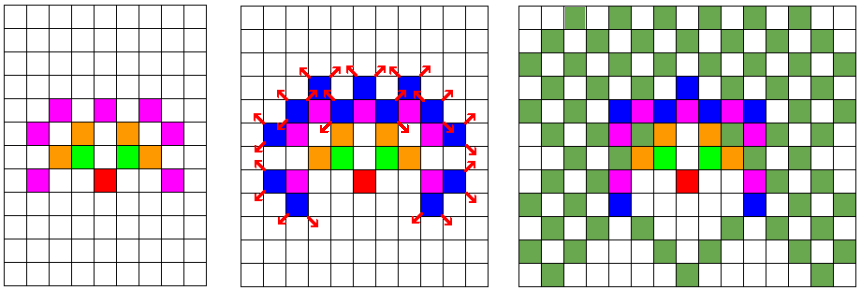
For the second sample, the drawings below show the situation after levels 4, 5 and 6.
The middle drawing shows directions of all parts that will move in the next level.
题意:烟花绽放时分为n层,每层会前进ti格,当进入下一层是向左右45°分开前进。 问在网格中,有多少网格至少被烟花经过一次?
题解:最多30层,每层最多前进5格,烟花的活动半径最大为150,每一层的方向都可以由上一层决定,所以一定 小于300*300中情况,直接暴力绽放的过程就行了。bfs和dfs都可以做。
bfs代码:
看了下wonter的代码,感觉dfs更巧妙
注意:vis[][][][][],map[][]两个标记数组用bool型, 用int型MLE了两发
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 305;
bool vis[maxn][maxn][8][6][32];//vis[x][y][dir][step][cnt] dir表示方向,cnt表示层数 ,step表示0 ~ a[cnt]-1
int n,a[32];
bool map[maxn][maxn];
int asp[][2]={{0,1},{1,1},{1,0},{1,-1},{0,-1},{-1,-1},{-1,0},{-1,1}};
void dfs(int x,int y,int dir,int step,int cnt)
{
if(vis[x][y][dir][step][cnt] || cnt>n)
return ;
vis[x][y][dir][step][cnt]=1;
map[x][y]=1;
if(step)//沿当前方向前进
dfs(x+asp[dir][0],y+asp[dir][1],dir,step-1,cnt);
else//烟花炸裂,进入下一层
{
dfs(x,y,(dir-1+8)%8,a[cnt+1],cnt+1);//往左45°找
dfs(x,y,(dir+1)%8,a[cnt+1],cnt+1);//往右45°找
}
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
dfs(150,150,0,a[1]-1,1);//map[150][150]就是烟花到达的第一个位置(图中第一个被标记的点)
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<=300;++i)
for(int j=0;j<=300;++j)
if(map[i][j])
ans++;
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
time limit per test
2.5 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
One tradition of welcoming the New Year is launching fireworks into the sky. Usually a launched firework flies vertically upward for some period of time, then explodes, splitting into several parts flying in different directions. Sometimes those parts also
explode after some period of time, splitting into even more parts, and so on.
Limak, who lives in an infinite grid, has a single firework. The behaviour of the firework is described with a recursion depth n and
a duration for each level of recursion t1, t2, ..., tn.
Once Limak launches the firework in some cell, the firework starts moving upward. After covering t1cells
(including the starting cell), it explodes and splits into two parts, each moving in the direction changed by 45 degrees (see the pictures
below for clarification). So, one part moves in the top-left direction, while the other one moves in the top-right direction. Each part explodes again after covering t2 cells,
splitting into two parts moving in directions again changed by 45 degrees. The process continues till the n-th
level of recursion, when all 2n - 1 existing
parts explode and disappear without creating new parts. After a few levels of recursion, it's possible that some parts will be at the same place and at the same time — it is allowed and such parts do not crash.
Before launching the firework, Limak must make sure that nobody stands in cells which will be visited at least once by the firework. Can you count the number of those cells?
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 30) —
the total depth of the recursion.
The second line contains n integers t1, t2, ..., tn (1 ≤ ti ≤ 5).
On the i-th level each of 2i - 1 parts
will cover ti cells
before exploding.
Output
Print one integer, denoting the number of cells which will be visited at least once by any part of the firework.
Examples
input
4 4 2 2 3
output
39
input
6 1 1 1 1 1 3
output
85
input
1 3
output
3
Note
For the first sample, the drawings below show the situation after each level of recursion. Limak launched the firework from the bottom-most red cell. It covered t1 = 4 cells
(marked red), exploded and divided into two parts (their further movement is marked green). All explosions are marked with an 'X' character. On the last drawing,
there are 4 red, 4 green, 8 orange
and 23 pink cells. So, the total number of visited cells is 4 + 4 + 8 + 23 = 39.

For the second sample, the drawings below show the situation after levels 4, 5 and 6.
The middle drawing shows directions of all parts that will move in the next level.

题意:烟花绽放时分为n层,每层会前进ti格,当进入下一层是向左右45°分开前进。 问在网格中,有多少网格至少被烟花经过一次?
题解:最多30层,每层最多前进5格,烟花的活动半径最大为150,每一层的方向都可以由上一层决定,所以一定 小于300*300中情况,直接暴力绽放的过程就行了。bfs和dfs都可以做。
bfs代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 310;
int mark[maxn][maxn][32][6];
int n,a[32],map[maxn][maxn];
int asp[][2]={{0,1},{1,1},{1,0},{1,-1},{0,-1},{-1,-1},{-1,0},{-1,1}};
struct node
{
int x,y,cnt,dir; //cnt:烟花的层数 dir:烟花前进的方向
}temp;
void bfs()
{
queue<node> q;
temp.x=150; temp.y=150; temp.cnt=1; temp.dir=0;
q.push(temp);
mark[150][150][1][0]=1;
while(!q.empty())
{
temp=q.front();
q.pop();
int nx=temp.x, ny=temp.y, num=temp.cnt, k=temp.dir;
for(int i=1;i<=a[num];++i)//当前层走的路径
{
nx+=asp[k][0];
ny+=asp[k][1];
map[nx][ny]=1;
}
if(num!=n)
{
int kl=(k-1+8)%8, kr=(k+1)%8;//当前烟花炸裂后,分开的两个子烟花前进的方向
temp.x=nx; temp.y=ny; temp.cnt=num+1;
if(!mark[nx][ny][num+1][kl])//kl左45°
{
mark[nx][ny][num+1][kl]=1;
temp.dir=kl;
q.push(temp);
}
if(!mark[nx][ny][num+1][kr])//kr右45°
{
mark[nx][ny][num+1][kr]=1;
temp.dir=kr;
q.push(temp);
}
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<=300;++i)
for(int j=0;j<=300;++j)
if(map[i][j])
ans++;
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
memset(mark,0,sizeof(mark));
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
bfs();
}
return 0;
}看了下wonter的代码,感觉dfs更巧妙
注意:vis[][][][][],map[][]两个标记数组用bool型, 用int型MLE了两发
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 305;
bool vis[maxn][maxn][8][6][32];//vis[x][y][dir][step][cnt] dir表示方向,cnt表示层数 ,step表示0 ~ a[cnt]-1
int n,a[32];
bool map[maxn][maxn];
int asp[][2]={{0,1},{1,1},{1,0},{1,-1},{0,-1},{-1,-1},{-1,0},{-1,1}};
void dfs(int x,int y,int dir,int step,int cnt)
{
if(vis[x][y][dir][step][cnt] || cnt>n)
return ;
vis[x][y][dir][step][cnt]=1;
map[x][y]=1;
if(step)//沿当前方向前进
dfs(x+asp[dir][0],y+asp[dir][1],dir,step-1,cnt);
else//烟花炸裂,进入下一层
{
dfs(x,y,(dir-1+8)%8,a[cnt+1],cnt+1);//往左45°找
dfs(x,y,(dir+1)%8,a[cnt+1],cnt+1);//往右45°找
}
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
dfs(150,150,0,a[1]-1,1);//map[150][150]就是烟花到达的第一个位置(图中第一个被标记的点)
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<=300;++i)
for(int j=0;j<=300;++j)
if(map[i][j])
ans++;
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 打包debug版本的apk会混淆吗
- 需要做一个IP Carema 的安卓端!~求思路
- 关于storyBoard里的间距的问题
- NESTED LOOPS HASH JOIN
- 2016年度学习总结
- Leetcode 48. Rotate Image
- uri与url的区别
- 如何获取点击屏幕的位置
- linux下搭建sdk,为什么我的工具这么少?
- Android 图片 剪切 大小无法控制,
- oracle执行计划中NESTED LOOPS SEMI (即半嵌套循环)的解释
- android怎么录制SurfaceView中的图像?
- Oracle 执行计划(Explain Plan) 说明
- 第二天(就业班) html的引入、html常用标签、实体标签、超链接标签、图片标签、表格、框架标签、表单
- iOS GCD问题 帮忙看一下 谢谢
- 求救:导入的Android项目不能运行和导出apk
- android 广播消息的内存怎么释放?
- PullToRefreshlibrary 打包XML报错。
- LBS教程---如何使用Android SDK进行开发
- 自定义menu的布局
