javascript中screenXY、clientXY、pageXY和offsetXY的区别
2016-12-23 15:03
615 查看
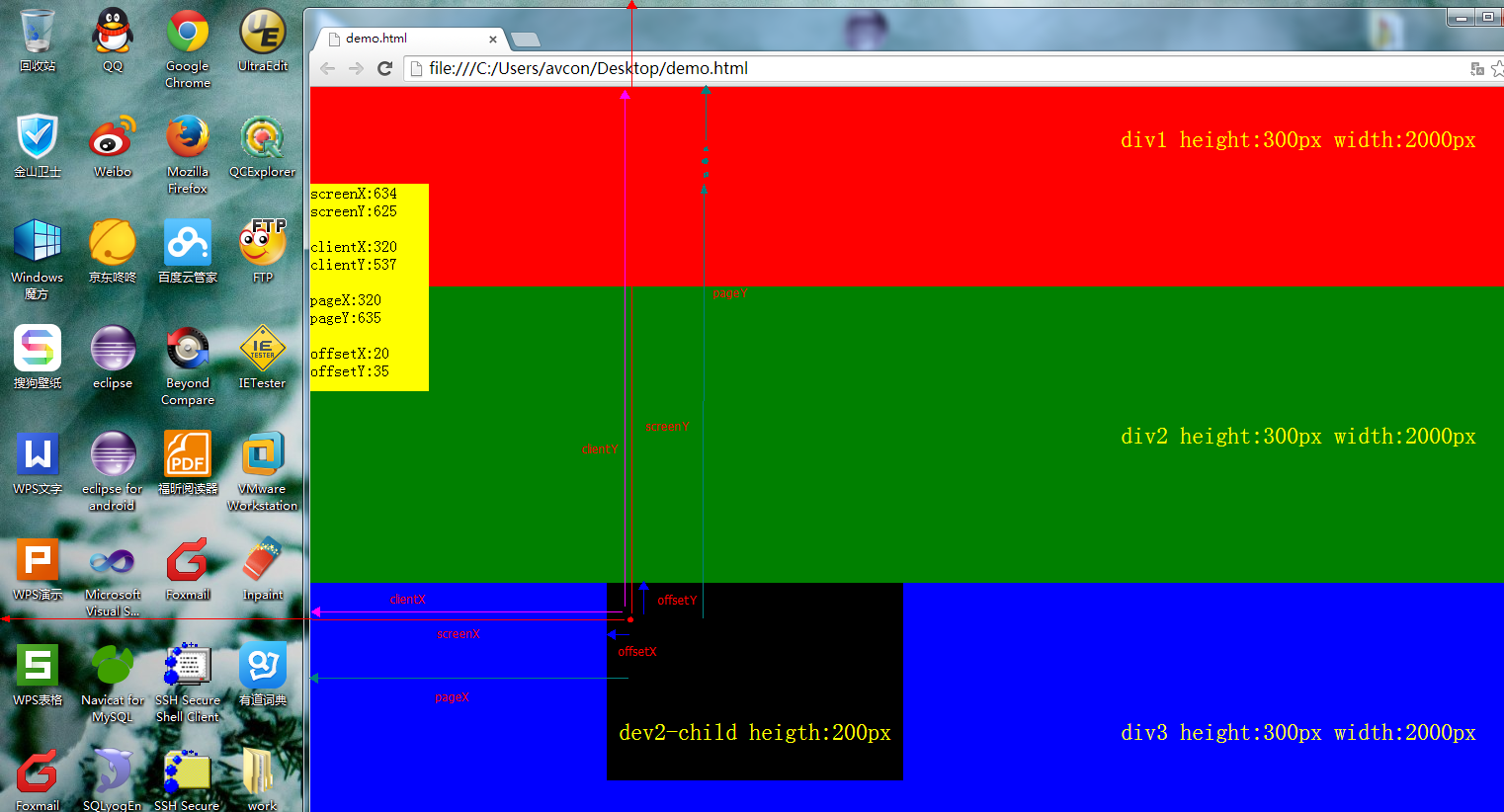
screenXY:screenX和screenY的参照点是用户屏幕左上角,screenX是鼠标位置相对于用户屏幕(左侧)水平偏移量,而screenY则是鼠标相对于屏幕(顶部)垂直方向的偏移量。
clientXY:screenX和screenY的参照点是浏览器内容区域的左上角,clientX是相对于用户浏览器(左侧)的水平偏移量,而clientY则是相对于浏览器内容区(顶部)垂直放心的偏移量。
pageXY:pageX和pageY的参照点是这个页面的左上角,和浏览器宽高、滚动条等无关,pageX是相对于整个页面(左侧)水平偏移量,而pageY则是相对于整个页面(顶部)垂直放心的偏移量。
offsetXY:offsetX和offsetY的参照点是鼠标当前的指向页面标签对象,offsetX是相对于当前指向标签(左侧)水平偏移量,而offsetY则是相对于当前指向标签(顶部)垂直方向的偏移量。
下图为实例图解述:
测试代码如下:
附:
scrollHeight:获取对象的滚动高度。
scrollLeft:设置或获取位于对象左边界和窗口中目前可见内容的最左端之间的距离
scrollTop:设置或获取位于对象最顶端和窗口中可见内容的最顶端之间的距离
scrollWidth:获取对象的滚动宽度
clientXY:screenX和screenY的参照点是浏览器内容区域的左上角,clientX是相对于用户浏览器(左侧)的水平偏移量,而clientY则是相对于浏览器内容区(顶部)垂直放心的偏移量。
pageXY:pageX和pageY的参照点是这个页面的左上角,和浏览器宽高、滚动条等无关,pageX是相对于整个页面(左侧)水平偏移量,而pageY则是相对于整个页面(顶部)垂直放心的偏移量。
offsetXY:offsetX和offsetY的参照点是鼠标当前的指向页面标签对象,offsetX是相对于当前指向标签(左侧)水平偏移量,而offsetY则是相对于当前指向标签(顶部)垂直方向的偏移量。
下图为实例图解述:

测试代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.9.1.min.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.div {
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
height: 300px;
width: 2000px;
line-height: 300px;
overflow:hidden;
color: yellow;
position:relative;
}
.dev-child{
width:300px;
height:200px;
margin:auto;
}
#d1 {
background-color: red;
}
#d2 {
background-color: green;
}
#d3 {
background-color: blue;
}
#d3-1{
background:black;
position:absolute;
top:0px;
left:300px;
}
#info {
position:fixed;
top:0px;
left:0px;
min-height: 150px;
max-height:210px;
width: 120px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function () {
window.onscroll = function () {
$("#info").css("top", getScrollTop());
};
document.onmousemove = function (e) {
if (e == null) {
e = window.event;
}
var html = "screenX:" + e.screenX + "<br/>";
html += "screenY:" + e.screenY + "<br/><br/>";
html += "clientX:" + e.clientX + "<br/>";
html += "clientY:" + e.clientY + "<br/><br/>";
if (e.pageX == null) {
html += "pageX:" + e.x + "<br/>";
html += "pageY:" + e.y + "<br/>";
} else {
html += "pageX:" + e.pageX + "<br/>";
html += "pageY:" + e.pageY + "<br/><br/>";
}
if(e.offsetX != null){
html += "offsetX:" + e.offsetX + "<br/>";
html += "offsetY:" + e.offsetY + "<br/><br/>";
}
$("#info").html(html);
};
});
function getScrollTop() {
var top = (document.documentElement && document.documentElement.scrollTop) ||
document.body.scrollTop;
return top;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="d1" class="div">div1 height:300px width:2000px</div>
<div id="d2" class="div">div2 height:300px width:2000px</div>
<div id="d3" class="div">div3 height:300px width:2000px<div id="d3-1" class="dev-child">dev2-child heigth:200px width:300px</div></div>
<div id="info"></div>
</body>
</html>附:
scrollHeight:获取对象的滚动高度。
scrollLeft:设置或获取位于对象左边界和窗口中目前可见内容的最左端之间的距离
scrollTop:设置或获取位于对象最顶端和窗口中可见内容的最顶端之间的距离
scrollWidth:获取对象的滚动宽度
相关文章推荐
- 关于对clientX(Y)/pageX(Y)/screenX(Y)的认识
- iframe 子父窗口中js相互调用
- $("#id").ajaxSubmit()使用自己遇到的问题
- json带转义字符的处理方法
- JS实现继承
- 简单了解JS 中的indexOf方法
- javaScript关键字和保留字
- js实现键盘自动打字效果
- js中的arguments
- 深入理解JavaScript箭头函数
- js脚本执行顺序
- 创建基于jsp的商品浏览器的四个步骤
- angular.js中的事件
- 根据下表,去JSONArray对应的值
- JS敏感词过滤代码
- JS怎么把字符串数组转换成整型数组
- JS字符串常用操作
- js 短信验证码 计时器
- js省市二级联动
- JS函数-硬性保留小数位后位数(不四舍五入)不够位数以0补齐
