Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) -- C. Hongcow Builds A Nation(并查集)
2016-12-18 11:21
417 查看
大体题意:
给你n 个点m个边的图,告诉其中一些点是政府点,如果任意两个政府点 不能直接或者间接到达的话,那么称这个图就是一个稳定的图,要求让你在这个图中加尽量多的边,使得 这个图还是稳定的!
思路:
其实思路很简单:简单的并查集应用!
因为题目保证输入的图一定是一个稳定的图,那么每一个政府点 都在一个独立的并查集内部!
我们先给每一个并查集内部的点进行连接! 任意连接都是合法的!
然后把所有不包括政府点的 独立并查集 归结到 最大包含政府点的并查集的内部!
然后求每一个并查集的完全图即可!
详细见代码:
加上数学计算的代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define Size(x) ((int)(x).size())
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1000 + 10;
int fa[maxn], belong[maxn],a[maxn],have[maxn];
set<int>g[maxn];
int id = 0;
int find(int x){
return fa[x] == x ? fa[x] : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
int main(){
int n,m , k;
scanf("%d %d %d",&n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) scanf("%d",a+i);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
int u,v;
scanf("%d %d",&u, &v);
fa[find(u)] = find(v);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if (find(i) == i){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
if (find(j) == i) g[id].insert(j), belong[j] = id;
}
++id;
}
}
int sum = 0;
int Max = -1,po;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i){
int v = a[i];
int pos = belong[v];
have[pos]++;
int t = Size(g[pos]);
if (t > Max){
Max = t;
po = pos;
}
}
int sum2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < id; ++i){
if (!have[i])sum2 += Size(g[i]);
}
// printf("sum2 = %d\n",sum2);
for (int i = 0; i < id; ++i){
if (have[i]){
int t;
if (i != po){
t = Size(g[i]);
}
else t = Size(g[po]) + sum2;;
// printf(" t = %d\n",t);
sum += t * (t-1)/2;
}
}
printf("%d\n",sum - m);
return 0;
}
纯暴力的代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define Size(x) ((int)(x).size())
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1000 + 10;
int fa[maxn], belong[maxn],a[maxn],have[maxn];
set<int>g[maxn];
int id = 0;
int find(int x){
return fa[x] == x ? fa[x] : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
int main(){
int n,m , k;
scanf("%d %d %d",&n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) scanf("%d",a+i);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
int u,v;
scanf("%d %d",&u, &v);
fa[find(u)] = find(v);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if (find(i) == i){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
if (find(j) == i) g[id].insert(j), belong[j] = id;
}
++id;
}
}
int sum = 0;
int Max = -1,po;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i){
int v = a[i];
int pos = belong[v];
have[pos]++;
int t = Size(g[pos]);
if (t > Max){
Max = t;
po = pos;
}
}
int sum2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < id; ++i){
if (!have[i])sum2 += Size(g[i]);
}
// printf("sum2 = %d\n",sum2);
for (int i = 0; i < id; ++i){
if (have[i]){
int t;
if (i != po){
t = Size(g[i]);
}
else t = Size(g[po]) + sum2;;
// printf(" t = %d\n",t);
sum += t * (t-1)/2;
}
}
printf("%d\n",sum - m);
return 0;
}
C. Hongcow Builds A Nation
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Hongcow is ruler of the world. As ruler of the world, he wants to make it easier for people to travel by road within their own countries.
The world can be modeled as an undirected graph with n nodes and m edges. k of
the nodes are home to the governments of the kcountries that make up the world.
There is at most one edge connecting any two nodes and no edge connects a node to itself. Furthermore, for any two nodes corresponding to governments, there is no path between those two nodes.
Any graph that satisfies all of these conditions is stable.
Hongcow wants to add as many edges as possible to the graph while keeping it stable. Determine the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add.
Input
The first line of input will contain three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 1 000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) —
the number of vertices and edges in the graph, and the number of vertices that are homes of the government.
The next line of input will contain k integers c1, c2, ..., ck (1 ≤ ci ≤ n).
These integers will be pairwise distinct and denote the nodes that are home to the governments in this world.
The following m lines of input will contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n).
This denotes an undirected edge between nodes ui and vi.
It is guaranteed that the graph described by the input is stable.
Output
Output a single integer, the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add to the graph while keeping it stable.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
For the first sample test, the graph looks like this:
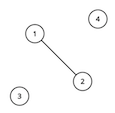
Vertices 1 and 3 are special.
The optimal solution is to connect vertex 4 to vertices 1 and 2.
This adds a total of 2 edges. We cannot add any more edges, since vertices 1 and 3 cannot
have any path between them.
For the second sample test, the graph looks like this:
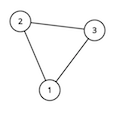
We cannot add any more edges to this graph. Note that we are not allowed to add self-loops, and the graph must be simple.
给你n 个点m个边的图,告诉其中一些点是政府点,如果任意两个政府点 不能直接或者间接到达的话,那么称这个图就是一个稳定的图,要求让你在这个图中加尽量多的边,使得 这个图还是稳定的!
思路:
其实思路很简单:简单的并查集应用!
因为题目保证输入的图一定是一个稳定的图,那么每一个政府点 都在一个独立的并查集内部!
我们先给每一个并查集内部的点进行连接! 任意连接都是合法的!
然后把所有不包括政府点的 独立并查集 归结到 最大包含政府点的并查集的内部!
然后求每一个并查集的完全图即可!
详细见代码:
加上数学计算的代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define Size(x) ((int)(x).size())
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1000 + 10;
int fa[maxn], belong[maxn],a[maxn],have[maxn];
set<int>g[maxn];
int id = 0;
int find(int x){
return fa[x] == x ? fa[x] : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
int main(){
int n,m , k;
scanf("%d %d %d",&n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) scanf("%d",a+i);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
int u,v;
scanf("%d %d",&u, &v);
fa[find(u)] = find(v);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if (find(i) == i){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
if (find(j) == i) g[id].insert(j), belong[j] = id;
}
++id;
}
}
int sum = 0;
int Max = -1,po;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i){
int v = a[i];
int pos = belong[v];
have[pos]++;
int t = Size(g[pos]);
if (t > Max){
Max = t;
po = pos;
}
}
int sum2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < id; ++i){
if (!have[i])sum2 += Size(g[i]);
}
// printf("sum2 = %d\n",sum2);
for (int i = 0; i < id; ++i){
if (have[i]){
int t;
if (i != po){
t = Size(g[i]);
}
else t = Size(g[po]) + sum2;;
// printf(" t = %d\n",t);
sum += t * (t-1)/2;
}
}
printf("%d\n",sum - m);
return 0;
}
纯暴力的代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define Size(x) ((int)(x).size())
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1000 + 10;
int fa[maxn], belong[maxn],a[maxn],have[maxn];
set<int>g[maxn];
int id = 0;
int find(int x){
return fa[x] == x ? fa[x] : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
int main(){
int n,m , k;
scanf("%d %d %d",&n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) scanf("%d",a+i);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
int u,v;
scanf("%d %d",&u, &v);
fa[find(u)] = find(v);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if (find(i) == i){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
if (find(j) == i) g[id].insert(j), belong[j] = id;
}
++id;
}
}
int sum = 0;
int Max = -1,po;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i){
int v = a[i];
int pos = belong[v];
have[pos]++;
int t = Size(g[pos]);
if (t > Max){
Max = t;
po = pos;
}
}
int sum2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < id; ++i){
if (!have[i])sum2 += Size(g[i]);
}
// printf("sum2 = %d\n",sum2);
for (int i = 0; i < id; ++i){
if (have[i]){
int t;
if (i != po){
t = Size(g[i]);
}
else t = Size(g[po]) + sum2;;
// printf(" t = %d\n",t);
sum += t * (t-1)/2;
}
}
printf("%d\n",sum - m);
return 0;
}
C. Hongcow Builds A Nation
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Hongcow is ruler of the world. As ruler of the world, he wants to make it easier for people to travel by road within their own countries.
The world can be modeled as an undirected graph with n nodes and m edges. k of
the nodes are home to the governments of the kcountries that make up the world.
There is at most one edge connecting any two nodes and no edge connects a node to itself. Furthermore, for any two nodes corresponding to governments, there is no path between those two nodes.
Any graph that satisfies all of these conditions is stable.
Hongcow wants to add as many edges as possible to the graph while keeping it stable. Determine the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add.
Input
The first line of input will contain three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 1 000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) —
the number of vertices and edges in the graph, and the number of vertices that are homes of the government.
The next line of input will contain k integers c1, c2, ..., ck (1 ≤ ci ≤ n).
These integers will be pairwise distinct and denote the nodes that are home to the governments in this world.
The following m lines of input will contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n).
This denotes an undirected edge between nodes ui and vi.
It is guaranteed that the graph described by the input is stable.
Output
Output a single integer, the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add to the graph while keeping it stable.
Examples
input
4 1 2 1 3 1 2
output
2
input
3 3 1
21 21 3
2 3
output
0
Note
For the first sample test, the graph looks like this:

Vertices 1 and 3 are special.
The optimal solution is to connect vertex 4 to vertices 1 and 2.
This adds a total of 2 edges. We cannot add any more edges, since vertices 1 and 3 cannot
have any path between them.
For the second sample test, the graph looks like this:

We cannot add any more edges to this graph. Note that we are not allowed to add self-loops, and the graph must be simple.
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) C. Hongcow Builds A Nation 并查集+贪心+组合学、图论、dfs
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2)C. Hongcow Builds A Nation【并查集+贪心】好题~
- 745 C. Hongcow Builds A Nation codeforces (并查集)
- CF745C_Hongcow Builds A Nation(并查集+贪心)
- Codeforces 745C - Hongcow Builds A Nation 并查集乱搞,注意路径压缩
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 1)A. Hongcow Builds A Nation
- C. Hongcow Builds A Nation
- Hongcow Builds A Nation ___codeforces 744A
- Hongcow Builds A Nation ___codeforces 744A
- 【26.42%】【codeforces 745C】Hongcow Builds A Nation
- C. Hongcow Builds A Nation 并查集
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) B. Hongcow Solves A Puzzle 几何、思维题
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) -- B. Hongcow Solves A Puzzle (判断是否是矩形,水题)
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) B. Hongcow Solves A Puzzle
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2)A.Hongcow Learns the Cyclic Shift【暴力】水题
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 1) C. Hongcow Buys a Deck of Cards(DP/模拟退火)
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2)B. Hongcow Solves A Puzzle【思维+暴力】
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 1) B. Hongcow's Game(bitmask)
- CodeForces745C C - Hongcow Builds A Nation 图论+容斥
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) E. Hongcow Buys a Deck of Cards DP+好题
