解题报告:HDU 2196 Computer 简单树型DP
2016-12-14 11:44
351 查看
Computer
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 6360 Accepted Submission(s): 3202
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about
slow functioning of the net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.
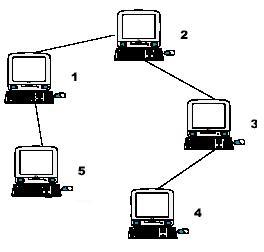
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also
get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
[align=left]Input[/align]
Input file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N (N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers - number of computer, to which
i-th computer is connected and length of cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9. Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each case output N lines. i-th line must contain number Si for i-th computer (1<=i<=N).
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
5
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
3
2
3
4
4
[align=left]Author[/align]
scnu
[align=left]Recommend[/align]
lcy
Statistic | Submit | Discuss
|
Note
题意:
给定一棵树,求树上所有点的最远点距
思路:
离一个点的最远的点要不是它的子树的叶子,要不就是先往上到它的某个祖先,然后再走另外的某个子树到叶子
在子树的最远距离很好求,一遍dfs就能解决
往上的最远距离从根往下递归 每层就只用考虑当前点到父亲节点的距离+父亲节点到兄弟的距离+兄弟在子树的最远距离
dp[i][0]表示节点i往下的最远距离,dp[i][1]表示节点i往上的最远距离
第一遍dfs: dp[i][0] = max(W[k] + dp[k][0] ) k 为 i 的儿子 , W[k]为k到k的父亲之间的距离。
第二遍dfs: dp[i][1] = max(dp[fa][1] , dp[j][0]+W[i]+W[j] ) fa 为 i 的父亲 , j 为 i 的兄弟
最后依次输出max(dp[i][0],dp[i][1])即可
思路就是这样,写法比较随意
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct edge{
int t,w;
edge(){};
edge(int _t,int _w){
t = _t ;
w = _w;
}
};
int n;
int dp[10005][2];
vector<edge>G[10005];
void dfs1(int x){
dp[x][0]=0;
for(int i=0;i<G[x].size();i++){
edge &j = G[x][i];
dfs1(j.t);
dp[x][0] = max(dp[x][0],dp[j.t][0]+j.w);
}return ;
}
void dfs2(int x,int fa=0){
dp[x][1]=dp[fa][1];
int w = 0;
for(int i=0;i<G[fa].size();i++){
edge &j = G[fa][i];
if(j.t!=x){
dp[x][1] = max(dp[x][1],dp[j.t][0]+j.w);
}else {
w = j.w;
}
}dp[x][1] += w;
for(int i=0;i<G[x].size();i++){
dfs2(G[x][i].t,x);
}return ;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n)==1){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
G[i].clear();
}
for(int i=2,f,w;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&f,&w);
G[f].push_back(edge(i,w));
}dfs1(1);dfs2(1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
printf("%d\n",max(dp[i][0],dp[i][1]));
}
}return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- HDU 2196解题报告
- HDU 4716 A Computer Graphics Problem 解题报告
- hdu 1913 computer 部分贪心+一维dp 解题报告
- HDU 1870 愚人节的礼物 解题报告
- hdu 1019解题报告
- HDU 3335 解题报告
- hdu 2516解题报告
- HDU第11版解题报告(农夫版)
- HDU 1231 畅通工程 解题报告
- hdu 2139解题报告
- HDU 2469 Fire-control System解题报告
- HDU 1587 Flowers 解题报告
- hdu 1102 pku 2421 解题报告
- HDU 3732 Ahui Writes Word 解题报告
- HDU 2680 Choose the best route 解题报告
- hdu 1064 解题报告
- HDU--2104--hide handkerchief--解题报告(辗转相除的运用)
- Hdu 1009 FatMouse' Trade解题报告
- 终曲(hdu 2572)解题报告
- HDU 1158 Emloyment Planning 解题报告
