微服务框架开发(二)—扩展spring schema
2016-12-06 00:00
288 查看
摘要: 在上一篇的需求中,提到了扩展spring的配置文件,自定义标签,本篇将详细描述实现的过程。
一、实体bean的定义
回顾一下我们需要定义的4个标签
定义注册中心标签:
定义服务协议标签
定义服务提供标签:
定义服务引用标签:
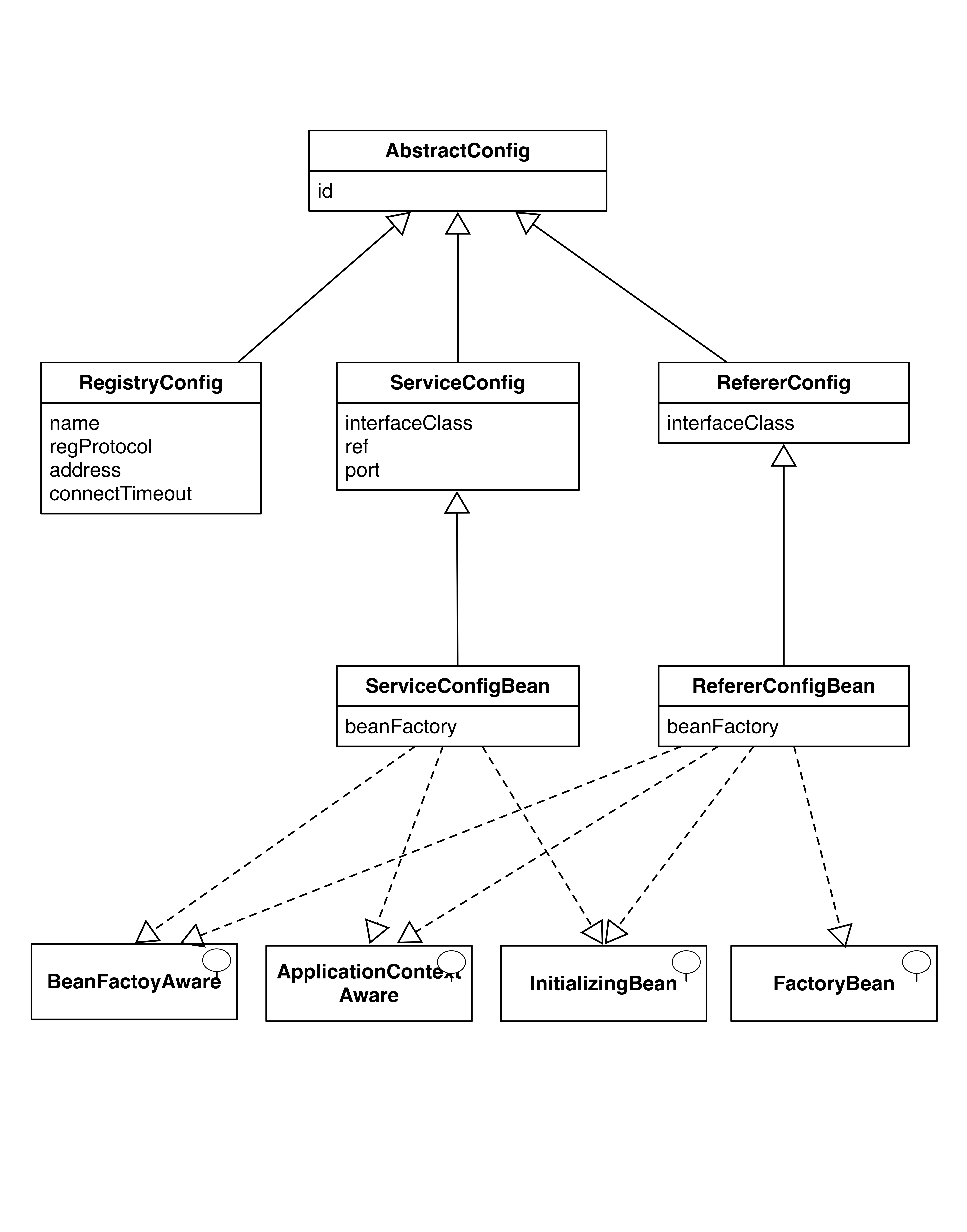
UML图设计如下
RegistyConfig、ServiceConfig、RefererConfig分别继承自抽象类AbstractConfig,并分别定义了三个标签的相关属性。ServiceConfigBean、RefererConfigBean用于实现spring的相关接口,达到对配置文件中bean进行处理的目的。
二、定义xsd文件(xmen.xsd)
三、定义handler处理文件(spring.schemas和spring.handlers)
四、编写具体的Handler类
一、实体bean的定义
回顾一下我们需要定义的4个标签
定义注册中心标签:
<xmen:registry name="registry" regProtocol="zookeeper" address="127.0.0.1:2181" connectTimeout="2000"/>
定义服务协议标签
<xmen:protocol name="xmen" port="20000" />
定义服务提供标签:
<xmen:service interface="xxx.xxx.xxx.service" class="xxx" port="8000"/>或者 <xmen:service interface="xxx.xxx.xxx.service" ref="xxx" port="8000"/>
定义服务引用标签:
<xmen:referer id="xxxService" interface="xxx.xxx.xxx.service"/>
UML图设计如下
RegistyConfig、ServiceConfig、RefererConfig分别继承自抽象类AbstractConfig,并分别定义了三个标签的相关属性。ServiceConfigBean、RefererConfigBean用于实现spring的相关接口,达到对配置文件中bean进行处理的目的。

二、定义xsd文件(xmen.xsd)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.solid4j.com/schema/xmen" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:tool="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tool" xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" targetNamespace="http://www.solid4j.com/schema/xmen"> <xsd:import namespace="http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace" /> <xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tool" /> <xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" /> <xsd:complexType name="abstractConfig"> <xsd:anyAttribute /> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:complexType name="abstractRegistryConfig"> <xsd:complexContent> <xsd:extension base="abstractConfig"> <xsd:attribute name="id" type="xsd:ID" /> <xsd:attribute name="name" type="xsd:string" use="optional"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 注册名称. ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> <xsd:attribute name="regProtocol" type="xsd:string" use="optional"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 注册协议. ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> <xsd:attribute name="address" type="xsd:string" use="optional"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 注册中心地址. ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> <xsd:attribute name="connectTimeout" type="xsd:integer" use="optional"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 注册中心连接超时时间(毫秒). ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> </xsd:extension> </xsd:complexContent> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:complexType name="abstractProtocolConfig"> <xsd:complexContent> <xsd:extension base="abstractConfig"> <xsd:attribute name="id" type="xsd:ID" /> <xsd:attribute name="name" type="xsd:string" use="optional"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 协议名称. ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> <xsd:attribute name="port" type="xsd:integer" use="optional"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 服务端口 ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> </xsd:extension> </xsd:complexContent> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:complexType name="abstractServiceConfig"> <xsd:complexContent> <xsd:extension base="abstractConfig"> <xsd:attribute name="id" type="xsd:ID" /> <xsd:attribute name="interface" type="xsd:token"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 定义接口,在注册中心中注册 ]]></xsd:documentation> <xsd:appinfo> <tool:annotation> <tool:expected-type type="java.lang.Class" /> </tool:annotation> </xsd:appinfo> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> <xsd:attribute name="ref" type="xsd:string" use="optional"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 接口实现 ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> <xsd:attribute name="class" type="xsd:string" use="optional"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 接口实现 ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> </xsd:extension> </xsd:complexContent> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:complexType name="abstractRefererConfig"> <xsd:complexContent> <xsd:extension base="abstractConfig"> <xsd:attribute name="id" type="xsd:ID" /> <xsd:attribute name="interface" type="xsd:token" use="required"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 调用的接口 ]]></xsd:documentation> <xsd:appinfo> <tool:annotation> <tool:expected-type type="java.lang.Class" /> </tool:annotation> </xsd:appinfo> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> </xsd:extension> </xsd:complexContent> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:element name="registry" type="abstractRegistryConfig"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 注册中心配置 ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="protocol" type="abstractProtocolConfig"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 服务协议 ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="service" type="abstractServiceConfig"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 服务配置 ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="referer" type="abstractRefererConfig"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ 引用服务配置 ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema>
三、定义handler处理文件(spring.schemas和spring.handlers)
http\://www.solid4j.com/schema/xmen.xsd=META-INF/xmen.xsd http\://www.solid4j.com/schema/xmen=com.solid4j.xmen.config.spring.handler.XmenNamespaceHandler
四、编写具体的Handler类
public class XmenNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new XmenBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new XmenBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new XmenBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceConfigBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("referer", new XmenBeanDefinitionParser(RefererConfigBean.class, false));
}
}public class XmenBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BeanDefinitionParser.class);
private final Class<?> beanClass;
private final boolean required;
public XmenBeanDefinitionParser(Class<?> beanClass, boolean required) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
this.required = required;
}
@Override
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parseContext) {
try {
return parse(element, parseContext, beanClass, required);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
private BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, Class<?> beanClass, boolean required) throws ClassNotFoundException {
RootBeanDefinition bd = new RootBeanDefinition();
bd.setBeanClass(beanClass);
bd.setLazyInit(false);
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
if ((id == null || id.length() == 0) && required) {
String generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("name");
if (generatedBeanName == null || generatedBeanName.length() == 0) {
generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("class");
}
if (generatedBeanName == null || generatedBeanName.length() == 0) {
generatedBeanName = beanClass.getName();
}
id = generatedBeanName;
int counter = 2;
while (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
id = generatedBeanName + (counter++);
}
}
if (id != null) {
if (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate spring bean config, id = " + id);
}
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(id, bd);
}
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("id", id);
if(ServiceConfigBean.class.equals(beanClass)) {
String className = element.getAttribute("class");
if(className != null && className.length() > 0) {
RootBeanDefinition classDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
classDefinition.setBeanClass(Class.forName(className, true, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()));
classDefinition.setLazyInit(false);
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("ref", new BeanDefinitionHolder(classDefinition, id + "Impl"));
}
}
for (Method setter : beanClass.getMethods()) {
String name = setter.getName();
if (name.length() <= 3 || !name.startsWith("set") || !Modifier.isPublic(setter.getModifiers())) {
continue;
}
String property = name.substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + name.substring(4);
if ("id".equals(property)) {
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("id", id);
continue;
}
String value = element.getAttribute(property);
value = value.trim();
if (value.length() == 0 || value == null) {
continue;
}
Object reference;
if ("ref".equals(property)) {
reference = new RuntimeBeanReference(value);
} else {
reference = new TypedStringValue(value);
}
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(property, reference);
}
return bd;
}
}
相关文章推荐
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(二)
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(三)
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(三)
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(五)
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解:注解
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(三)
- 微服务框架Spring Cloud介绍 Part3: Mysteam项目结构与开发用户注册服务
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解:属性配置
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(四)
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(五)
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(四)
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(四)
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解:集成Mybatis
- 微服务开发的入门级框架Spring Boot详解(二)
- 基于Spring的可扩展Schema进行开发自定义配置标签支持
- Spring2.5、Struts2、Ibatis开发框架搭建
