nyoj 234 吃土豆
2016-12-01 17:42
295 查看
吃土豆
时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB难度:4
描述Bean-eating is an interesting game, everyone owns an M*N matrix, which is filled with different qualities beans. Meantime, there is only one bean in any 1*1 grid. Now you want to
eat the beans and collect the qualities, but everyone must obey by the following rules: if you eat the bean at the coordinate(x, y), you can’t eat the beans anyway at the coordinates listed (if exiting): (x, y-1), (x, y+1), and the both rows whose abscissas
are x-1 and x+1.
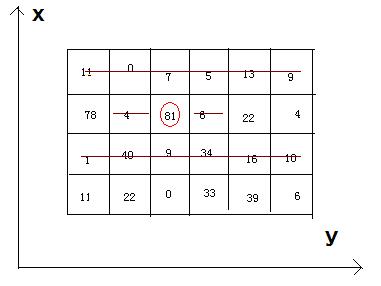
Now, how much qualities can you eat and then get ?
输入There are a few cases. In each case, there are two integer M (row number) and N (column number). The next M lines each contain N integers, representing the qualities of the beans. We can make sure that the quality of bean
isn't beyond 1000, and 1<=M,N<=500.
输出For each case, you just output the MAX qualities you can eat and then get.
样例输入
4 6 11 0 7 5 13 9 78 4 81 6 22 4 1 40 9 34 16 10 11 22 0 33 39 6
样例输出
242
//#include<stdio.h>
//int max(int m,int *a)
//{
// int i,f[550];
// for(i=1; i<=m; i++)
// {
// if(i==1) f[i]=a[i];
// else if(i==2) f[i]=a[i]>a[i-1]?a[i]:a[i-1];
// else
// {
// f[i]=(f[i-2]+a[i])>f[i-1]?f[i-2]+a[i]:f[i-1];
// }
// }
// return f[m];
//}
////非递归推算法
///*int max(int m,int *a){
// if(m==1)return a[1];
// if(m==2)return a[2]=a[1]>a[2]?a[1]:a[2];
// return max(m-2,a)+a[m]>max(m-1,a)?max(m-2,a)+a[m]:max(m-1,a);
//}*/
//
////递归分制算法
//int main()
//{
// int a[510],b[510],i,j,m,n;
// while(scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)==2)
// {
// for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
// {
// for(j=1; j<=m; j++)
// {
// scanf("%d",&a[j]);
// }
// b[i]=max(m,a);
// }
// printf("%d\n",max(n,b));
// }
// return 0;
//}
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int map,dp[510],R[510][510];
int main()
{
int m,n,i,j;
while(~scanf("%d %d",&m,&n))
{
memset(R,0,sizeof(R));
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(i=3; i<m+3; ++i) //把n,m都扩大2,方便dp
{
for(j=3; j<n+3; ++j)
{
scanf("%d",&map);
R[i][j]=max(R[i][j-2],R[i][j-3])+map; //累积i行到j列的最大和
}
}
for(i=3; i<m+3; ++i)
{
dp[i]=max(dp[i-2],dp[i-3])+max(R[i][n+1],R[i][n+2]); //累积到i行的最大和
}
printf("%d\n",max(dp[m+1],dp[m+2]));
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- NYOJ 题目234 吃土豆
- NYOJ 234 吃土豆(基础dp)
- NYOJ-234 吃土豆
- NYOJ_234_吃土豆
- NYOJ-234-DP(吃土豆)
- nyoj-234-吃土豆(动态规划)
- NYOJ 234 吃土豆
- 吃土豆_nyoj_234(动态规划).java
- nyoj 吃土豆 234 (双层DP)
- NYOJ234吃土豆(双层动态规划)
- NYOJ234吃土豆
- nyoj 234 吃土豆
- NYOJ234-吃土豆(双层DP)
- NYOJ 234 吃土豆
- Nyoj 234 吃土豆
- hdu-Beans(动态规划,nyoj-234-吃土豆)
- nyoj234 吃土豆 01背包
- nyoj 234 吃土豆
- nyoj-动态规划-234-吃土豆-201308131021
- 题目234 吃土豆
