A*带你踏上快车道
2016-11-28 12:01
471 查看
A*(A-Star)算法是一种静态路网中求解最短路最有效的直接搜索方法,也是许多其他问题的常用启发式算法。
公式表示为: f(n)=g(n)+h(n),
其中 f(n) 是从初始节点经由节点n到目标节点的代价估计,
g(n) 是在节点空间中从初始节点到节点n的实际代价,
h(n) 是从节点n到目标节点的最佳路径的估计代价。
帮助理解A*算法的文章:
A*算法原理图文详解
A*算法之寻路初探
A*搜索算法
A*,Dijkstra,BFS算法性能比较及A*算法的应用
案例分析

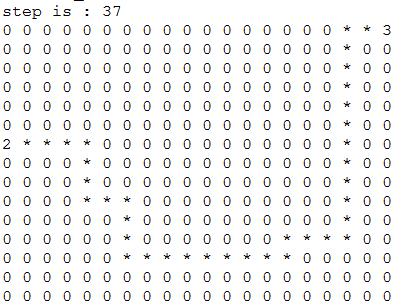
以上矩阵代表某地区的地形图,节点数字为0代表该节点可以通行,节点数字1代表此处有障碍物,节点数字2代表该节点为始发点,数字3代表终点,要求找到一条由始发点到终点的最短路径(曼哈顿距离最短)。
这里运用A*算法解决,程序如下:
公式表示为: f(n)=g(n)+h(n),
其中 f(n) 是从初始节点经由节点n到目标节点的代价估计,
g(n) 是在节点空间中从初始节点到节点n的实际代价,
h(n) 是从节点n到目标节点的最佳路径的估计代价。
帮助理解A*算法的文章:
A*算法原理图文详解
A*算法之寻路初探
A*搜索算法
A*,Dijkstra,BFS算法性能比较及A*算法的应用
案例分析

以上矩阵代表某地区的地形图,节点数字为0代表该节点可以通行,节点数字1代表此处有障碍物,节点数字2代表该节点为始发点,数字3代表终点,要求找到一条由始发点到终点的最短路径(曼哈顿距离最短)。
这里运用A*算法解决,程序如下:
package AStar;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class AStar {
// 开始节点
private Point startPoint = null;
// 当前节点
private Point endPoint = null;
// 结束节点
private Point currentPoint = null;
// 最短距离坐标节点
private Point shortestFPoint = null;
//数组地图
private static final int[][] mazeArray = {
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,3 },
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1 },
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1 },
{ 1,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1 },
{ 0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1 },
{ 0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1 },
{ 2,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1 },
{ 0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1 },
{ 0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0 },
{ 0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1 },
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1 }
};
// 地图坐标对象
private Point[][] mazePoint = null;
// 开启队列,用于存放待处理的节点
Queue<Point> openQueue = null;
// 关闭队列,用于存放已经处理过的节点
Queue<Point> closedQueue = null;
// 起始节点到某个节点的距离
int[][] GList = null;
// 某个节点到目的节点的距离
int[][] HList = null;
// 起始节点经过某个节点到目的节点的距离
int[][] FList = null;
public AStar(Point[][] mazePoint, Point startPoint, Point endPoint) {
this.mazePoint = mazePoint;
this.startPoint = startPoint;
this.endPoint = endPoint;
openQueue = new LinkedList<Point>();
//将元素添加到列表的末尾
openQueue.offer(startPoint);
closedQueue = new LinkedList<Point>();
FList = new int[mazePoint.length][mazePoint[0].length];
GList = new int[mazePoint.length][mazePoint[0].length];
HList = new int[mazePoint.length][mazePoint[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < mazePoint.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mazePoint[0].length; j++) {
FList[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
GList[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
HList[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
// 起始节点到当前节点的距离
GList[startPoint.getX()][startPoint.getY()] = 0;
// 当前节点到目的节点的距离
HList[startPoint.getX()][startPoint.getY()] = getPointDistance(
startPoint.getX(), startPoint.getY(), endPoint.getX(),
endPoint.getY());
// f(x) = g(x) + h(x)
FList[startPoint.getX()][startPoint.getY()] = GList[startPoint.getX()][startPoint
.getY()] + HList[startPoint.getX()][startPoint.getY()];
}
/**
* 计算当前坐标与结束坐标之间的距离
*
* 计算方法为每向相信坐标移动一次算作一个距离单位
*/
private int getPointDistance(int current_x, int current_y, int end_x,
int end_y) {
return Math.abs(current_x - end_x) + Math.abs(current_y - end_y);
}
/**
* 节点地图
*
* 0代表可通行 ,1代表障碍 ,2代表开始节点 ,3代表结束节点
*
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建节点地图
Point[][] mazePoint = new Point[mazeArray.length][mazeArray[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < mazePoint.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mazePoint[0].length; j++) {
mazePoint[i][j] = new Point(i, j, mazeArray[i][j]);
}
}
Point start = mazePoint[6][0];
Point end = mazePoint[0][19];
AStar star = new AStar(mazePoint, start, end);
star.start();
System.out.println(mazeArray.length + "," + mazeArray[0].length);
star.printPath();
}
/**
* 开始地图节点搜索
*/
public void start() {
while ((currentPoint = findShortestFPoint()) != null) {
if (currentPoint.getX() == endPoint.getX()
&& currentPoint.getY() == endPoint.getY())
return;
updateNeighborPoints(currentPoint);
}
}
/**
* 获取距离最短的坐标点
*
*/
public Point findShortestFPoint() {
currentPoint = null;
//最短距离坐标节点
shortestFPoint = null;
int shortestFValue = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Iterator<Point> it = openQueue.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
currentPoint = it.next();
if (FList[currentPoint.getX()][currentPoint.getY()] <= shortestFValue) {
shortestFPoint = currentPoint;
shortestFValue = FList[currentPoint.getX()][currentPoint.getY()];
}
}
if (shortestFValue != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out
.println("【移除节点】:" + shortestFPoint.getValue() + "["
+ shortestFPoint.getX() + ","
+ shortestFPoint.getY() + "]");
openQueue.remove(shortestFPoint);
closedQueue.offer(shortestFPoint);
}
return shortestFPoint;
}
/**
* 更新临近节点
*
*/
private void updateNeighborPoints(Point currentPoint) {
int current_x = currentPoint.getX();
int current_y = currentPoint.getY();
System.out.println("当前节点:[" + current_x + "," + current_y + "]");
// 上
if (checkPosValid(current_x - 1, current_y)) {
System.out.print("上");
updatePoint(mazePoint[current_x][current_y],
mazePoint[current_x - 1][current_y]);
}
// 下
if (checkPosValid(current_x + 1, current_y)) {
System.out.print("下");
updatePoint(mazePoint[current_x][current_y],
mazePoint[current_x + 1][current_y]);
}
// 左
if (checkPosValid(current_x, current_y - 1)) {
System.out.print("左");
updatePoint(mazePoint[current_x][current_y],
mazePoint[current_x][current_y - 1]);
}
// 右
if (checkPosValid(current_x, current_y + 1)) {
System.out.print("右");
updatePoint(mazePoint[current_x][current_y],
mazePoint[current_x][current_y + 1]);
}
System.out.println("---------------");
}
/**
* 检查该节点是否有效
*
*/
private boolean checkPosValid(int x, int y) {
// 检查x,y是否越界, 并且当前节点不是墙
if ((x >= 0 && x < mazePoint.length)
&& (y >= 0 && y < mazePoint[0].length)
&& (mazePoint[x][y].getValue() != 1)) {
// 检查当前节点是否已在关闭队列中,若存在,则返回 "false"
Iterator<Point> it = closedQueue.iterator();
Point point = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
if ((point = it.next()) != null) {
if (point.getX() == x && point.getY() == y)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 更新当前节点
*/
private void updatePoint(Point lastPoint, Point currentPoint) {
int last_x = lastPoint.getX();
int last_y = lastPoint.getY();
int current_x = currentPoint.getX();
int current_y = currentPoint.getY();
// 起始节点到当前节点的距离
int temp_g = GList[last_x][last_y] + 1;
// 当前节点到目的位置的距离
System.out.print(" [" + current_x + "," + current_y + "]"
+ mazePoint[current_x][current_y].getValue());
int temp_h = getPointDistance(current_x, current_y, endPoint.getX(),
endPoint.getY());
System.out.println("到目的位置的距离 :" + temp_h);
// f(x) = g(x) + h(x)
int temp_f = temp_g + temp_h;
System.out.println("f(x) = g(x) + h(x) :" + temp_f + "=" + temp_g + "+"
+ temp_h);
// 如果当前节点在开启列表中不存在,则:置入开启列表,并且“设置”
// 1) 起始节点到当前节点距离
// 2) 当前节点到目的节点的距离
// 3) 起始节点到目的节点距离
if (!openQueue.contains(currentPoint)) {
openQueue.offer(currentPoint);
currentPoint.setFather(lastPoint);
System.out.println("添加到开启列表:" + currentPoint.getValue() + "["
+ currentPoint.getX() + "," + currentPoint.getY() + "]");
// 起始节点到当前节点的距离
GList[current_x][current_y] = temp_g;
// 当前节点到目的节点的距离
HList[current_x][current_y] = temp_h;
// f(x) = g(x) + h(x)
FList[current_x][current_y] = temp_f;
} else {
// 如果当前节点在开启列表中存在,并且,
// 从起始节点、经过上一节点到当前节点、至目的地的距离 < 上一次记录的从起始节点、到当前节点、至目的地的距离,
// 则:“更新”
// 1) 起始节点到当前节点距离
// 2) 当前节点到目的节点的距离
// 3) 起始节点到目的节点距离
if (temp_f < FList[current_x][current_y]) {
// 起始节点到当前节点的距离
GList[current_x][current_y] = temp_g;
// 当前节点到目的位置的距离
HList[current_x][current_y] = temp_h;
// f(x) = g(x) + h(x)
FList[current_x][current_y] = temp_f;
// 更新当前节点的父节点
currentPoint.setFather(lastPoint);
}
System.out.println("currentPoint:" + currentPoint.getValue() + "["
+ currentPoint.getX() + "," + currentPoint.getY() + "]");
System.out.println("currentPoint.father:"
+ currentPoint.getFather().getValue() + "["
+ currentPoint.getFather().getX() + ","
+ currentPoint.getFather().getY() + "]");
}
}
/**
* 打印地铁路径
*/
public void printPath() {
System.out.println("================ 开始打印地铁路径【用 “*”表示】 ================");
Point father_point = null;
Object[][] result = new Object[mazeArray.length][mazeArray[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < mazeArray.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mazeArray[0].length; j++) {
result[i][j] = 0;
}
}
int step = 0;
father_point = mazePoint[endPoint.getX()][endPoint.getY()];
while (father_point != null) {
System.out.println("【father_point】" + father_point.getValue() + "["
+ father_point.getX() + "," + father_point.getY() + "]");
if (father_point.equals(startPoint))
result[father_point.getX()][father_point.getY()] = 2;
else if (father_point.equals(endPoint)) {
result[father_point.getX()][father_point.getY()] = 3;
step++;
} else {
result[father_point.getX()][father_point.getY()] = "*";
step++;
}
father_point = father_point.getFather();
}
// 打印行走步数
System.out.println("step is : " + step);
for (int i = 0; i < mazeArray.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mazeArray[0].length; j++) {
System.out.print(result[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class Point{
private int x;
private int y;
private int l;
private Point father;
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public int getValue(){
return l;
}
public Point(int x,int y,int l){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
this.l=l;
}
public Point getFather(){
return this.father;
}
public void setFather(Point Point){
this.father=Point;
}
}程序运行结果:
相关文章推荐
- 让孩子踏上阅读快车道
- 12种方法让你踏上晋升快车道。
- 12种方法让你踏上晋升快车道
- 很多时候,决定一切的是态度,有了正确的态度,就可以将压力转化为动力,踏上成功的舞台
- 踏上JAVA之路
- 步入事业发展快车道
- 踏上白盒测试迷茫之路(之一)
- 踏上Silverlight的征程 体验Silverlight之美
- 踏上Linux内核学习之旅
- 踏上编程之路的感言
- 写给即将踏上工作岗位的人
- 讲座:踏上快乐与激情的IT学习之旅
- 一个2013届毕业生(踏上IT行业)的迷茫(1)
- 踏上Oracle ebs的道路
- 从小白踏上程序员之路
- 开篇:勇敢踏上这第一步
- 踏上Cisco学习新征程
- 从今天起,我将踏上一条C语言的不归路。。
- 1月12日云栖精选夜读:阿里云新推出 HiTSDB + IoT套件 物联网设备上云步入快车道
- 2004.10.15,Fri - 再次踏上旅程?
