javascript对象---10 继承
2016-11-28 00:00
537 查看
摘要: 一、继承的概念
二、原型继承方式
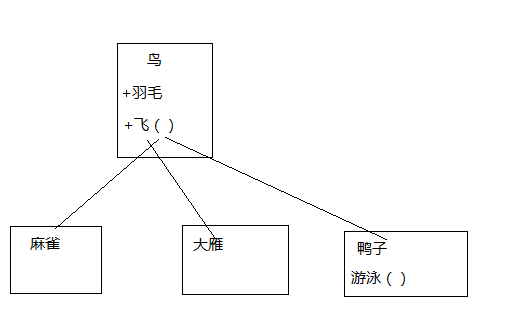
JS中继承的特点:
1.子类对象 拥有 父类对象 的 属性和方法; (把构造函数称为一个类,使用构造函数为当前对象初始化属性)
2.子类对象可以有自己的新属性和方法;
3.子类对象可以重写父类对象的方法;
4.JS中并没有专门的继承语法,但可以通过原型链机制实现。
把共有的属性封装在父类,子类继承
继承的优点
1.提供了一种优良的代码组合方式,提高了代码的重用性。
2.子类可以灵活调用父类的属性,同时可以扩展覆盖父类的属性,体现灵活性。
3.提供了代码的可维护性
正常声明两个构造函数 ---人类 和学生
//人类 : 性别年龄-说话、跑跳
//人类中包括学生 --有学校 考试
//注意父类并不是专门为子类服务的,父类也会有相关的事例
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log("名字:" +this.name);
}
//创建学生构造函数
function Student( name ,age ,school){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.school = school;
}
Student.prototype.gotoSchool=function(){
console.log("去"+this.school+"上学")
}
让学生继承人类的 sayhello( ) ;方法
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log("名字:" +this.name);
}
//创建学生构造函数
function Student( name ,age ,school){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.school = school;
}
//修改了
Student.prototype = new Person(); //必须在添加方法前面
//new Person 没有创建对象引用他,所以栈内存中没有值
//Student的原型对象指针指向了 new Person 对象
Student.prototype.gotoSchool=function(){
console.log("去"+this.school+"上学");
}
//当前student1具备Person对象里面属性方法---任何Student实例具备 person里的方法
var student1 = new Student("Shixin",18, "天津理工大学");
student1.gotoSchool();
student1.sayHello();
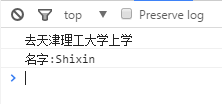
Person.prototype.category="哺乳类";
console.log(student1.category); //哺乳类
student1.category = "灵长类"; //
console.log(student1.category); //灵长类
var student2 = new Student("lis",20, "天津理工大学");
console.log(student2.category); //哺乳类
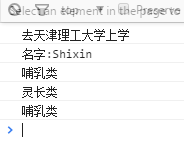
//添加设置,返回方法
Person.prototype.setCategory = function( val){
this.category = val;
}
person.prototype.getCategory = function(){
return this.category;
}
student1.setCategory("灵长类");
console.log(student1.getCategory()); ----------//灵长类
var student2 = new Student("lis",20, "天津理工大学");
console.log(student2.getCategory()); ----------------//哺乳类
缺点:
1.原型对象中数据发生变化,会导致多有对象数据都变化
2.无法向父类·对象·传递参数。
三、构造函数继承方式
通过构造函数完成继承
缺点:只能继承父类构造函数中执行的赋值的属性,无法对原型对象的属性进行继承,因此很少单独使用
//构造函数的应用场景,只能继承基本属性,无法继承方法;
function Person( name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//子类
function Student( name,age,schoolName){
this.schoolName = schoolName;
Person.call(this,name,age); //继承基本属性 ---赋值 name age
}
Student.prototype.goToSchool = function(){
console.log("去"+this.schoolName+"上学");
}
var st = new Student('张三',18,"理工大学");
st.goToSchool();
结果:----去理工大学上学
function Person( name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log("我叫"+this.name);
}
function Student ( name, age,schoolName){
this.schoolName = schoolName;
Person.call(this,name,age); //构造函数继承方式--this值加到 创建的对象上,student
相当于进行了 this.name=name,this.age=age;
}
Student.prototype = new Person(); //重置原型链可以使用Person()的方法
Student.prototype.gotoSchool = function(){
console.log("我去"+this.schoolName+"上学");
}
var student = new Student("张三",18,"理工大学");
student.sayHello();
student.gotoSchool();
我叫张三
我去理工大学上学
缺点: 调用两次Person构造函数
1次-Student.prototype = new Person(); 只是原型链改变
2次-- Person.call(this,name,age);
为了解决这个弊端采用下种方法
通过自己构建一个prototype --- 替换 Student.prototype = new Person();
Student.prototype = new Person(); // 只需要借用原型链不需要执行代码
new person()的过程
1.创建内存空间
2.改变this指向
3.原型链指定
4.执行函数体
前3步需要,最后一步不需要
1. var ob = new Object();
2. ob.constructor = Student;
3 .ob.prototype = Person; 原型链指向Person
为了不打乱原型链 --提出一个公用方法
function inherit( parent, child){ //父亲孩子
}
//寄生组合方式
function inherit( parent,child){
//创建一个深度克隆 父类 prototype对象
var prototype = Object( parent.prototype); //相当于又复制了一个内存空间
//改变这个protityoe对象的 构造指针constructor指针指向子类的构造函数。
prototype.constructor = child;
//修改child的指针
child.prototype = prototype
}
function Person( name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
Console.log("名字:" +this.name);
}
function Student(name,age,schoolName){
this.schoolName = schoolName;
Person.call(this,name,age);
}
inherit(Person,Student);
Student.prototype.gotoSchool = function(){
console.log("去" + this.schoolName +"上学");
}
二、原型继承方式
一、继承的概念
继承是面向对象的重要特征。继承是指子类对象拥有父类对象的属性与方法,同时子类对象可以覆盖扩展父类对象的属性和方法。
JS中继承的特点:
1.子类对象 拥有 父类对象 的 属性和方法; (把构造函数称为一个类,使用构造函数为当前对象初始化属性)
2.子类对象可以有自己的新属性和方法;
3.子类对象可以重写父类对象的方法;
4.JS中并没有专门的继承语法,但可以通过原型链机制实现。
把共有的属性封装在父类,子类继承
继承的优点
1.提供了一种优良的代码组合方式,提高了代码的重用性。
2.子类可以灵活调用父类的属性,同时可以扩展覆盖父类的属性,体现灵活性。
3.提供了代码的可维护性
二、原型继承方式
原型继承方式:通过原型链完成继承。任何对象都会通过原型链继承Oject函数的 prototype对象中的属性和方法正常声明两个构造函数 ---人类 和学生
//人类 : 性别年龄-说话、跑跳
//人类中包括学生 --有学校 考试
//注意父类并不是专门为子类服务的,父类也会有相关的事例
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log("名字:" +this.name);
}
//创建学生构造函数
function Student( name ,age ,school){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.school = school;
}
Student.prototype.gotoSchool=function(){
console.log("去"+this.school+"上学")
}
让学生继承人类的 sayhello( ) ;方法
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log("名字:" +this.name);
}
//创建学生构造函数
function Student( name ,age ,school){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.school = school;
}
//修改了
Student.prototype = new Person(); //必须在添加方法前面
//new Person 没有创建对象引用他,所以栈内存中没有值
//Student的原型对象指针指向了 new Person 对象
Student.prototype.gotoSchool=function(){
console.log("去"+this.school+"上学");
}
//当前student1具备Person对象里面属性方法---任何Student实例具备 person里的方法
var student1 = new Student("Shixin",18, "天津理工大学");
student1.gotoSchool();
student1.sayHello();

Person.prototype.category="哺乳类";
console.log(student1.category); //哺乳类
student1.category = "灵长类"; //
console.log(student1.category); //灵长类
var student2 = new Student("lis",20, "天津理工大学");
console.log(student2.category); //哺乳类

//添加设置,返回方法
Person.prototype.setCategory = function( val){
this.category = val;
}
person.prototype.getCategory = function(){
return this.category;
}
student1.setCategory("灵长类");
console.log(student1.getCategory()); ----------//灵长类
var student2 = new Student("lis",20, "天津理工大学");
console.log(student2.getCategory()); ----------------//哺乳类
缺点:
1.原型对象中数据发生变化,会导致多有对象数据都变化
2.无法向父类·对象·传递参数。
三、构造函数继承方式
通过构造函数完成继承
缺点:只能继承父类构造函数中执行的赋值的属性,无法对原型对象的属性进行继承,因此很少单独使用
//构造函数的应用场景,只能继承基本属性,无法继承方法;
function Person( name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//子类
function Student( name,age,schoolName){
this.schoolName = schoolName;
Person.call(this,name,age); //继承基本属性 ---赋值 name age
}
Student.prototype.goToSchool = function(){
console.log("去"+this.schoolName+"上学");
}
var st = new Student('张三',18,"理工大学");
st.goToSchool();
结果:----去理工大学上学
四、混合继承方式
通过构造函数,原型链共同完成继承,使用最多的方案function Person( name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log("我叫"+this.name);
}
function Student ( name, age,schoolName){
this.schoolName = schoolName;
Person.call(this,name,age); //构造函数继承方式--this值加到 创建的对象上,student
相当于进行了 this.name=name,this.age=age;
}
Student.prototype = new Person(); //重置原型链可以使用Person()的方法
Student.prototype.gotoSchool = function(){
console.log("我去"+this.schoolName+"上学");
}
var student = new Student("张三",18,"理工大学");
student.sayHello();
student.gotoSchool();
我叫张三
我去理工大学上学
缺点: 调用两次Person构造函数
1次-Student.prototype = new Person(); 只是原型链改变
2次-- Person.call(this,name,age);
为了解决这个弊端采用下种方法
五、寄生组合继承方法 --最优良
寄生组合继承方式:将子对象的prototype 设定为克隆出来的父类的 prototype 对象。最优的解决方案。通过自己构建一个prototype --- 替换 Student.prototype = new Person();
Student.prototype = new Person(); // 只需要借用原型链不需要执行代码
new person()的过程
1.创建内存空间
2.改变this指向
3.原型链指定
4.执行函数体
前3步需要,最后一步不需要
1. var ob = new Object();
2. ob.constructor = Student;
3 .ob.prototype = Person; 原型链指向Person
为了不打乱原型链 --提出一个公用方法
function inherit( parent, child){ //父亲孩子
}
//寄生组合方式
function inherit( parent,child){
//创建一个深度克隆 父类 prototype对象
var prototype = Object( parent.prototype); //相当于又复制了一个内存空间
//改变这个protityoe对象的 构造指针constructor指针指向子类的构造函数。
prototype.constructor = child;
//修改child的指针
child.prototype = prototype
}
function Person( name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
Console.log("名字:" +this.name);
}
function Student(name,age,schoolName){
this.schoolName = schoolName;
Person.call(this,name,age);
}
inherit(Person,Student);
Student.prototype.gotoSchool = function(){
console.log("去" + this.schoolName +"上学");
}
相关文章推荐
- JavaScript面向对象编程(10)快速构建继承关系之对象拷贝
- JavaScript面向对象编程(10)高速构建继承关系之对象拷贝
- javascript 中对象的继承〔转贴〕
- JavaScript 面向对象程序设计(下)——继承与多态(转)
- Javascript对象继承
- Javascript学习6 - 类、对象、继承
- JavaScript 面向对象程序设计(下)——继承与多态
- javascript 中对象的继承〔转贴〕
- javascript 面向对象继承
- JavaScript 的继承机制----对象冒充
- JavaScript 对象、函数和继承
- 关于javascript语言的继承、面向对象问题的文章
- (转)JavaScript 面向对象程序设计(下)——继承与多态
- javascript进阶之对象篇(5)继承
- JavaScript 面向对象程序设计(下)——继承与多态
- JavaScript 对象、函数和继承
- JavaScript的面向对象机理2)-继承
- JavaScript 面向对象程序设计(下)——继承与多态
- Javascript对象继承
- 【转】JavaScript中的对象、函数和继承
