Spring Boot系列 - 2. Spring Boot提供的特性
2016-11-18 15:31
399 查看
一、导览
本文主要按以下模块介绍spring Boot(1.4.2.RELEASE)提供的特性。SpringApplication类
外部化配置
Profiles
日志
开发WEB应用
Security
使用SQL
使用NoSQL
缓存
消息
发送邮件
JTA处理分布式事务
Spring Session
测试
Actuator
部署
二、SpringApplication类
在主类——即带有@SpringBootApplication注解类,的main方法里调用SpringApplication.run(应用的Configration配置类.class,参数列表) 会启动spring应用。默认log级别是INFO,会显示一些相关的启动详情,比如启动应用的用户等。
1. 使用SpringApplicationBuilder类可以创建分层的 ApplicationContext
new SpringApplicationBuilder() .bannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF) .sources(Parent.class) .child(Application.class) .run(args);1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
2. Application事件和监听器
除了常用的Spring framework事件,例如ContextRefreshedEvent等,SpringApplication也会发送一些其他的应用事件。 一些事件在ApplicationContext被创建之前就被触发,因此无法将监听器注册为bean来监听。但是可以使用SpringApplication.addListeners(…) 或SpringApplicationBuilder.listeners(…)来注册监听器。也可以在META-INF/spring.factories文件定义监听器:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=com.example.project.MyListener
应用运行时,应用事件发送顺序如下:
① 在监听器和初始化器被初始化之后,任何其他应用之前,应用刚开始运行时会发送一个ApplicationStartedEvent。
② 在context被创建之前,context中要使用的Environment被知道时,一个ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent被发送。
③ 在bean定义被加载之后,refresh启动之前,一个ApplicationPreparedEvent被发送。
④ 在refresh以及任何相关的回调被处理之后,一个ApplicationReadyEvent被发送,表明应用已准备好服务requests。
⑤ 启动时如果发生异常,一个ApplicationFailedEvent被发送。
3. web环境
SpringApplication会根据应用是否为web来创建不同的ApplicationContext: AnnotationConfigApplicationContext或AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext。 可以调用setWebEnvironment(boolean webEnvironment)复写默认实现(在junit测试时置为false最好),更可以使用setApplicationContextClass(…).完全控制ApplicationContext的创建。
4. 在SpringApplication.run完成前执行特定代码
使用ApplicationRunner或CommandLineRunner,并配合Order注解指定调用顺序。 CommandLineRunner的run(String …args)方法直接访问SpringApplication.run传递的参数,ApplicationRunner的run方法则使用ApplicationArguments访问参数。例如:
import org.springframework.boot.*
import org.springframework.stereotype.*
@Component
public class MyBean implements CommandLineRunner {
public void run(String... args) {
// Do something...
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
三、外部化配置
1. 如何引用配置的属性
可使用properties文件,YAML文件,环境变量,命令行参数(如 –name=”fuck”)来外部化配置。属性值可以使用@Value注解直接注入到bean中,并通过Spring的Environment抽象或经过@ ConfigurationProperties 注解绑定到结构化对象来访问。 示例:
YAML文件:

或者等效的properties文件:

使用@Value注入单个属性:
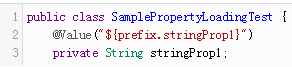
使用@ ConfigurationProperties注入属性族:

※ 注意里面使用了JSR-303注解来校验属性值。
@ ConfigurationProperties还可以用到@Bean注解的方法上。
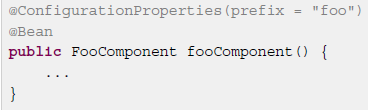
2. 属性加载顺序
Spring按照如下顺序设置properties: (一) 命令行参数。如:Java -jar app.jar –name=”Spring”
(二) SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON。如java -Dspring.application.json=’{“foo”:”bar”, “hehe”:”fuck”}’ -jar fuckapp.jar
(三) 来自于java:comp/env的JNDI属性
(四) Java System properties (System.getProperties()).
(五) OS环境变量
(六) 只有在random.*里包含的属性会产生一个RandomValuePropertySource
(七) jar包外部的,由profile指定的application properties文件(application-{profile}.properties或YAML文件)
(八) jar包内部的,由profile指定的application properties文件(application-{profile}.properties或YAML文件)
(九) jar包外部的application properties(application.properties和YAML)。
(十) jar包内部的application properties(application.properties和YAML)。
(十一) @Configuration注解类内部的@PropertySource注解
(十二) 由SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties设置的默认属性
YAML是JSON的超集,非常适合定义层级化配置数据。引入SnakeYAML库会使SpringApplication类自动支持YAML。使用spring-boot-starter会自动引入YAML。
四、Profiles
Spring Profiles提供了一种隔离应用程序配置的方式,并让这些配置只能在特定的环境下生效。
1. 如何配置profile
任何@Component或@Configuration都能被@Profile标记,从而限制加载它的时机。 例如:
@Configuration
@Profile("production")
public class ProductionConfiguration {
// ...
}12
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
2. 如何在构建时指定profile
以正常的Spring方式,你可以使用一个spring.profiles.active的Environment属性来指定哪个配置生效。你可以使用平常的任 何方式来指定该属性,例如,可以将它包含到你的application.properties中:
spring.profiles.active=dev,hsqldb1
1
或使用命令行开关:
--spring.profiles.active=dev,hsqldb1
1
2.1 添加激活的配置(profiles)
spring.profiles.active属性和其他属性一样都遵循上文中提到属性加载规则,优先级最高的PropertySource获胜。也就是说,你可以在application.properties中指定生效的配置,然后在命令行中设置同名属性的不同值来替换它们。有些时候,将profile特定的属性增加到active profile中,而不是直接替换会更有用。spring.profiles.include属性就可以用来无条件增加active profiles。SpringApplication类也提供api设置额外的profile(setAdditionalProfiles())
例如,按照下面的配置:
--- my.property: fromyamlfile --- spring.profiles: prod spring.profiles.include: proddb,prodmq1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
如果应用启动时打开选项–spring.profiles.active=prod,则proddb和prodmq也会被激活。
2.2 编程方式设置profile
在调用SpringApplication.run之前调用SpringApplication.setAdditionalProfiles(…)即可。实现ConfigurableEnvironment接口也可行。
2.3 profile特定的配置文件
除了application.properties文件,profile特定的属性也能通过application-{profile}.properties来定义。Spring boot提供了默认的application-default.properties文件,在没有定义任何profile时会加载。profile特定的属性从跟标准application.properties相同的路径加载,并且特定profile文件会覆盖默认的配置。如果声明了不止一个profile,则最后声明的被采用。
2.4 属性中的占位符(placeholders)
application.properties中的值会将由Environment过滤,所以你可以直接饮用之前定义的值:app.name=MyApp
app.description=${app.name} is a Spring Boot application12
1
2
五、日志
Spring Boot内部日志使用Commons Logging,但是开发底层日志实现。会为Java Util Logging, Log4j, Log4j2和Logback提供默认配置。不论哪种配置,loggers都被预配置为使用console输出,并提供一个可选的文件输出。默认情况下,如果是使用’Starter POMs’,Logback将被用作日志实现。
1. Log 格式
Spring Boot默认的log格式如下:2016-07-14 17:27:33.212 INFO 13092 --- [ost-startStop-1] o.s.web.context.ContextLoader : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 3832 ms 2016-07-14 17:27:33.668 WARN 13092 --- [ost-startStop-1] .s.b.d.a.RemoteDevToolsAutoConfiguration : Listening for remote debug traffic on /.~~spring-boot!~/debug1
2
3
1
2
3
显示以下内容:
日期和时间—毫秒精度,利于排序
Log级别—ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG or TRACE.
PID.
一个— 分隔符,表明实际log消息的开始
线程名—方括号中显示(控制台输出时可能会被省略)
Logger名—一般是类名的缩写格式
log消息
2. 控制台输出
默认,log信息被原样输出到控制台,输出ERROR, WARN, INFO级别。可以通过以下手段激活debug模式,输出更多的信息:在命令行使用 –debug 选项
在application.properties中添加debug=true
开启debug模式后,一些核心的loggers(如嵌入的servlet容器,hibernate和Spring)被配置输出更多的信息。
请注意
此处开启的debug模式,并非将你应用的日志级别修改为DEBUG级别。
Spring Boot输出日志到控制台时,会检测console是否支持ansi,如果支持,会显示彩色的日志。可以停止这种检测,或更改检测策略:
将 spring.output.ansi.enabled 改为其他值即可(默认是detect)。
3. 文件输出
默认,Spring Boot只输出日志到console。如果还想输出到文件,需要设置logging.file或logging.path属性。 它们的组合如下:
| logging.file | logging.path | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 无 | 无 | 只输出到console | |
| 具体文件名 | 无 | my.log | console和日志文件。文件名还可以带路径 |
| 无 | 具体路径 | /var/log | console和路径下的spring.log。路径可绝对可相对 |
4. 日志级别
所有支持的日志系统在Spring的Environment(例如在application.properties里)都可以通过’logging.level.*=LEVEL’(’LEVEL’是TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN,ERROR, FATAL, OFF中的一个)来设置日志级别。root logger可以通过logging.level.root来配置。 示例:application.properties
logging.level.root=WARN logging.level.org.springframework.web=DEBUG logging.level.org.hibernate=ERROR1
2
3
1
2
3
5. 自定义日志配置
将相应jar包放到依赖中,即可激活对应的日志框架。将日志的配置文件放到classpath的根目录下,或者放到logging.config指定路径下,就可以自定义日志的输出。注意
因为logging实在ApplicationContext被创建之前就初始化的,因此无法通过@Configuration注解类的@PropertySources来控制日志。而只能通过系统属性,环境变量和Spring Boot的外部配置文件等来配置
与日志系统相对应的文件会被自动加载:
| 日志系统 | 配置文件 |
|---|---|
| logback | logback-spring.xml, logback-spring.groovy, logback.xml,logback.groovy |
| Log4j | log4j-spring.properties, log4j-spring.xml, log4j.properties,log4j.xml |
| Log4j2 | log4j2-spring.xml, log4j2.xml |
| JDK (Java Util Logging) | logging.properties |
推荐使用-spring后缀的配置文件,例如logback-spring.xml,而非logback.xml。否则Spring可能无法完全控制log的初始化。
注意
Java Util Logging可能会导致类加载问题,不推荐使用。
6. Logback扩展
Spring Boot为Logback提供了一些高级配置属性。可以在logback-spring.xml中使用。注意
不能再logback.xml中使用,因为此文件加载的太早。要么在logback-spring.xml中使用,要么定义logging.confi属性。
6.1 Profile特定的配置
<springProfile> 标签允许你基于Spring profiles加入或者排除一些配置。 例如:
<springProfile name="staging"> <!-- configuration to be enabled when the "staging" profile is active --> </springProfile> <springProfile name="dev, staging"> <!-- configuration to be enabled when the "dev" or "staging" profiles are active --> </springProfile> <springProfile name="!production"> <!-- configuration to be enabled when the "production" profile is not active --> </springProfile>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
6.2 Environment属性
<springProperty> 标签允许你在logback配置文件中使用Spring Environment的属性。这可以让你在logback配置中使用application.properties中的值。 例如:
<springProperty scope="context" name="fluentHost" source="myapp.fluentd.host"/>
<appender name="FLUENT" class="ch.qos.logback.more.appenders.DataFluentAppender">
<remoteHost>${fluentHost}</remoteHost>
...
</appender>12
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
六、开发web应用
Spring Boot非常适合开发web应用。你可以使用内嵌的Tomcat,Jetty或Undertow轻松创建一个HTTP服务器。大多数的web应用都使用spring-boot-starter-web模块进行快速搭建和运行。
1. Spring MVC
Spring Web MVC框架是一个富”模型,视图,控制器”的web框架。 允许你创建特定的@Controller或@RestController beans来处理传入的HTTP请求。 使用@RequestMapping注解可以将控制器中的方法映射到相应的HTTP请求。 Spring Boot为MVC提供了如自动配置,模板引擎等很多特性。
1.1 自动配置
Sprint boot为mvc增加如下自动配置:引入ContentNegotiatingViewResolver和BeanNameViewResolver beans。
① ContentNegotiatingViewResolver是ViewResolver的一种实现,其根据请求的media type来为请求选择一个合适的View。请求的mediatype由ContentNegotiationManager决定。一旦请求的media type被决定,这个resolver查询所有的view resolver,并返回最匹配的。可以指定ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 的defaultViews属性,在mediatype匹配时将使用此defaultViews指定的viewResolver。
例如,一个/view.html的请求会去寻找content type为text/html的viewresolver;一个路径为/view,并且header中Accept为text/html的请求也同理。
② BeanNameViewResolver也是一种viewresolver,简单的将view name解释成bean
name。如controller中返回”view”,会去找id为view的bean。
对静态资源的支持,包括对WebJars的支持。
自动注册Converter,GenericConverter,Formatter beans
Converter<S,T>用来将S转换成T
对HttpMessageConverters的支持。
可将对象转换成Http request/response,或者相反。Spring MVC中,object可以自动转换成Json(Jackson库)或XML(Jacksonxml或者jaxb)。String使用utf-8编码。
自动注册MessageCodesResolver。
对静态index.html的支持。
对自定义Favicon的支持。
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean的自动使用。
※ 若要完全掌控springmvc,应添加自己的@Configuration和@EnableWebMVC注解的类。若想保留Spring boot mvc的特性,同时添加额外的mvc配置(如拦截器,formatters,view controllers等),你可以添加自己的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类型的@Bean(不使用@EnableWebMVC注解)。
1.2 静态内容
默认情况下,Spring Boot从classpath的/static(/public,/resources或/META-INF/resources)的文件夹或从ServletContext根目录提供静态内容。 这使用了Spring MVC的ResourceHttpRequestHandler,所以你可以通过添加自己的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter并覆写addResourceHandlers方法来改变这个行为(加载静态文件)。
如果你的应用将被打包成jar,那就不要使用src/main/webapp文件夹。尽管该文件夹是一个共同的标准,但它仅在打包成war的情况下起作用,并且如果产生一个jar,多数构建工具都会静悄悄的忽略它。
1.3 模板引擎
Spring boot支持以下模板引擎的自动配置:freemarker, groovy, thymeleaf, velocity, mustache。 Boot自动从src/main/resources/templates中搜索模板。
使用内置servlet容器时要避免使用jsp,原因如下:
内置tomcat不支持执行jar里的jsp。
Jetty在jsp时不支持内置容器个格式。
Undertow不支持jsp。
1.4 Error Handling
Spring Boot默认提供一个/error映射用来以合适的方式处理所有的错误,并且它在servlet容器中注册了一个全局的 错误页面。 想要完全替换默认行为,可以实现ErrorController接口,或者实现BasicErrorController类,由自定义的Controller处理错误。
也可以通过@ContorllerAdavice注解+@ExceptionHandler注解定制某个controller或exception类别要返回的JSON文档。如:
@ControllerAdvice(basePackageClasses = FooController.class)
public class FooControllerAdvice extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(YourException.class)
@ResponseBody
ResponseEntity<?> handleControllerException(HttpServletRequest request, Throwable ex) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<>(new CustomErrorType(status.value(), ex.getMessage()), status);
}
private HttpStatus getStatus(HttpServletRequest request) {
Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
if (statusCode == null) {
return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
return HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode);
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2. 嵌入的servlet容器
Spring Boot支持内嵌的Tomcat, Jetty和Undertow服务器。多数开发者只需要使用合适的’Starter POM’来获取一个完全配置好的实例即可。默认情况下,内嵌的服务器会在8080端口监听HTTP请求。
2.1 将Servlets, filters, listeners注册为bean
所有定义为bean的servlets,filters,listeners都将被嵌入的容器注册。如果只有一个servlet,它将被map到/,否则bean的名字会作为path前缀。Filters都将map到/*。 也可以使用ServletRegistrationBean,FilterRegistrationBean and ServletListenerRegistrationBean更完整的控制。
2.2 通过注解扫描servlet, filter listener
使用嵌入式容器时,要实现@WebServlet,@WebFilter, @Weblistener的自动注册,需要使用@ServletComponentScan。使用独立容器时此注解无用。
2.3 Servlet Context 初始化
嵌入的servlet容器不会直接执行Servlet3.0+的javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口,或者Spring的 org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer接口。这是为了避免有些被设计为运行在war内的第三方库会破坏sprint boot应用。独立httpserver下实现WebApplicationInitializer即可在代码中配置ServletContext,代替web.xml。 若需要在spring boot应用中进行servlet context 初始化,你应该注册一个实现了org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.ServletContextInitializer接口。
2.4 EmbeddedWebApplicationContext
此类是一种特殊的WebApplicationContext,启动时会搜索一个EmbeddedServletContainerFactory,例如TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory, JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory, or UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory。Spring boot会自动配置这些。
2.5 配置嵌入式servlet容器
2.5.1 可以在如application.properties文件中配置servlet容器所用的属性
包括:server.port:http监听端口
server.address: 要绑定的接口地址
server.session.persistence: session持久化
server.session.timeout:session超时时间
server.session.store-dir:session数据的location
server.session.cookie.*: session-cookie配置。
server.error.path:error page的地址
server.ssl.key-store, server.ssl.key-store-password, server.ssl.key-password: ssl的配置
server.compression.enabled: http response压缩
server.compression.min-response-size:压缩所需的最小size,默认时2048字节
server.compression.mime-types:要压缩的response content 类型。默认时text/html, text/xml, text/plain, text/css
2.5.2 也可通过实现EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer接口在代码中修改属性
2.5.3 也可直接实现TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory bean来配置
七、Security
1. 启用Security
当spring security在classpath中(即引入spring-boot-starter-security pom),web应用将自动启用安全限制,并且默认启用basic认证。 也可通过@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注解添加方法级别的安全限制。
2. 配置Security
默认的AuthenticationManager有一个用户,名为user, 密码会打印在log中,也可设置security.user.password属性修改密码。 默认的security配置由SecurityAutoConfiguration配置类及其导入的配置类(SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration配置web security, AuthenticationManagerConfiguration配置认证,此类在非web应用也适用)实现。
若要完全关闭默认的web security配置,可以添加一个带有@EnableWebSecurity的bean,这样并不会关闭authentication manager配置。
@EnableWebSecurity注解使用方法
将此注解添加到带有@Configuration注解,并且实现了WebSecurityConfigurer接口或继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类的类上面,即可用此类替代xml设置web
security。同时还可将配置内容放到外部属性文件中。
若也想关闭authentication manager配置,你可以增加一个AuthenticationManager的bean,或者通过将AuthenticationManagerBuilder注入到@Configuration类的一个方法中来配置全局的AuthenticationManager。
3. Security带来的特性
Web应用中使用Spring Security以后,你可以获得如下基本特性:一个带有in-memory store的AuthenticationManager,和一个user(查看SecurityProperties.User获取user的属性)。
通用静态资源路径不会被安全限制:css/, /js/, /images/* and */favicon.ico
其他部分都会应用Http Basic安全保护。
安全事件都会被发布到spring的ApplicationEventPublisher(包括认证成功,认证失败以及拒绝访问等)
Spring Security提供的常见底层特性(HSTS, XSS, CSRF, 缓存)默认都被开启。
HSTS是什么
HTTP Strict Transport Security,HTTP严格传输安全。HSTS的作用是强制客户端(如浏览器)使用HTTPS与服务器创建连接。服务器开启HSTS的方法是,当客户端通过HTTPS发出请求时,在服务器返回的超文本传输协议响应头中包含Strict-Transport-Security字段。非加密传输时设置的HSTS字段无效。
参考: http://www.chinaz.com/program/2015/0511/405146.shtml
所有上面的配置都可以通过外部属性文件修改。想要在不改变任何其他自动配置特性的前提下覆盖访问规则,可以增加一个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类型的bean。
如果开启了spring-boot-actuator,会有如下特性:
- 即使应用路径不受保护,被管理的路径也会受到保护。
- 安全相关的事件被转换为AuditEvents(审计事件),并发布给AuditService。
- 默认的用户有ADMIN和USER的角色。
使用外部属性能够修改Actuator(执行器)的安全特性(management.security.*)。为了覆盖应用程序的访问规则,你可以添加一个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类型的@Bean。同时,如果不想覆盖执行器的访问规则,你可以使用@Order(SecurityProperties.ACCESS_OVERRIDE_ORDER)注解该bean,否则使用@Order(ManagementServerProperties.ACCESS_OVERRIDE_ORDER)注解该bean。
八、使用SQL数据库
Spring Boot项目引入spring-boot-starter-data-jpa等即可使用Spring Data与DB交互。除了spring框架提供的JdbcTemplate以及ORM,Spring Data还提供了其他级别的功能,如创建Repository接口的实现,然后基于方法名产生queries。
1. 配置数据源
Java的javax.sql.DataSource接口提供了一个标准的使用数据库连接的方法。传统做法是,一个DataSource使用一个URL和用户名/密码去初始化一个数据库连接。
1.1 内嵌数据库
Spring boot支持自动配置三种in-memory的嵌入式DB:H2, HSQL,Derby。 无需提供URL,引入如下依赖即可使用。例如,典型的pom如下:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hsqldb</groupId> <artifactId>hsqldb</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
上文可以使Spring Boot自动为应用配置in-memory的hsqldb数据库,并建立连接。
1.2 连接到一个生产环境数据库
在生产环境中,数据库连接可以使用DataSource池进行自动配置。Spring boot自动配置DataSource池时的选择顺序如下:由于Tomcat数据源连接池的性能和并发,在tomcat可用时,我们总是优先使用它。
如果HikariCP可用,我们将使用它。
如果Commons DBCP可用,我们将使用它,但在生产环境不推荐使用它。
最后,如果Commons DBCP2可用,我们将使用它。
如果使用了spring-boot-starter-jdbc或spring-boot-starter-data-jpa ‘starter POMs’,你将会自动获取对tomcat-jdbc的依赖。
若要修改默认的数据源类型,或者指定其他的数据源类型,可以在application.properties中指定。
例如:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost/test spring.datasource.username=dbuser spring.datasource.password=dbpass spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.type=xxxxxHikariCP1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
注:使用MySQL时要增加mysql connector的依赖。
2. 使用JdbcTemplate
Spring的JdbcTemplate和NamedParameterJdbcTemplate类将被自动配置,你可以在自己的beans中通过@Autowire直接注入它们。 例如:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyBean {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public MyBean(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
// ...
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
3. JPA和Spring Data
Spring-boot-starter-data-jpa提供如下依赖:Hibernate
Spring Data JPA
Spring ORMs
3.1 Entity类
传统上,JPA实体需要在persistence.xml中声明。Spring boot中无需这样,它可以自动搜索Entity。 默认在主配置类(标记有@EnableAutoConfiguration 或者 @SpringBootApplication)下的所有包会被搜索,并且会搜索带有@Entity, @Embeddable 或者 @MappedSuperclass的类。
3.2 Spring Data JPA Repositories
Spring Data JPA仓库(repositories)是用来定义访问数据的接口。JPA会根据你的方法名自动创建查询。比如,一个CityRepository接口可能声明一个findAllByState(String state)方法,用来查找给定状态的所有城市。 继承Repository 、CrudRepository或者PagingAndSortingRepository接口的接口即为Spring JPA的repositories。Spring Boot会自动搜索这些接口,并通过方法名自动生成JPA queries。更复杂的查询可借助Spring Data的Query注解。
3.3 创建和删除JPA db
默认情况下,只有使用嵌入式DB(H2, HSQL或Derby)时,jpa数据库才会被自动创建。 可以通过spring.jpa.*属性来配置jpa,例如:
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop可开启自动创建和删除表,并且默认情况下,ApplicationContext启动之后才会执行DDL。
spring.jpa.generate-ddl 也可以用来配置生成表,但是Hibernate自动配置下,该选项不会被激活,因为Hibernate的ddl-auto属性更适用。
九、使用NoSQL
Spring Data支持MongoDB, Neo4J, Elasticsearch, Solr, Redis,Gemfire, Couchbase 和Cassandra等NoSQL技术。
Spring Boot可以自动配置其中的Redis, MongoDB, Elasticsearch, Solr 和 Cassandra。其他需要手动配置。
1. Redis
spring-boot-starter-redis自动导入依赖。Spring boot会自动配置RedisConnectionFactory, StringRedisTemplate 或者RedisTemplate。默认,这些实例会连接localhost:6379。 例子:
@Component
public class MyBean {
private StringRedisTemplate template;
@Autowired
public MyBean(StringRedisTemplate template) {
this.template = template;
}
// ...
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
如果你添加一个自己的任何自动配置类型的@Bean,它将替换默认的(除了RedisTemplate的情况,它是根据bean的名称’redisTemplate’而不是它的类型进行排除的)。如果在classpath路径下存在commons-pool2,默认你会获得一个连接池工厂。
2. MongoDB
spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb导入依赖。 Spring boot自动配置MongoDbFactory和MongoTemplate。默认实例使用mongodb://localhost/test
可设置以下属性:
spring.data.mongodb.uri (mongodb3.0)
spring.data.mongodb.host (mongo 2.x)
spring.data.mongodb.port
Spring Data MongoDB也支持和Spring Data JPA一样的Repository接口,Spring Data会根据方法名自动生成queries。
3. Solr
Apache Solr是个搜索引擎。 Sprint Boot利用Spring Data Solr为Solr4客户端库提供基本的自动配置。spring-boot-starter-datasolr导入依赖。Solr5暂不支持。 Spring Boot自动配置SolrServer,默认连接localhost:8983/solr
Spring Data也为Solr提供与JPA一样的Repositories,只不过实体注解为@SolrDocument。
4. Elasticsearch
Elastic Search是一个开源的,分布式,实时搜索和分析引擎。Spring Boot利用Spring Data Elasticserach为Elasticsearch提供基本的自动配置。spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch导入依赖。 Spring boot自动配置ElasticsearchTemplate或Client实例,并且默认连接一个本地的内存服务器(即一个NodeClient),可设置spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-nodes连接到remote server(TransportClient)。
Spring Data也为Elasticsearch提供与JPA一样的Repositories,只不过实体注解为@Document。
十、缓存
Spring 框架支持透明地为应用添加缓存。其核心是抽象层将缓存应用到方法,减少执行次数。可以使用JSR-107(JCache)注解后者水平自己的缓存注解实现缓存。 JCache示例:
import javax.cache.annotation.CacheResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MathService {
@CacheResult
public int computePiDecimal(int i) {
// ...
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Cache抽象层并不提供真实的存储,它依赖于org.springframework.cache.Cache 和 org.springframework.cache.CacheManager提供的抽象。开启@EnableCaching之后,SpringBoot会根据实现自动配置一个合适的CacheManager。
spring-boot-starter-cache导入依赖。
Spring Boot会依如下顺序检测缓存provider。
Generic
JCache (JSR-107)
EhCache 2.x
Hazelcast
Infinispan
Redis
Guava
Simple
也可使用spring.cache.type指定使用哪一种缓存。
若由Spring Boot自动配置CacheManager, 你可以通过实现CacheManagerCustomizer接口在cachemanager在完全初始化以前调整其配置:
@Bean
public CacheManagerCustomizer<ConcurrentMapCacheManager> cacheManagerCustomizer() {
return new CacheManagerCustomizer<ConcurrentMapCacheManager>() {
@Override
public void customize(ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(Arrays.asList("one", "two"));
}
};
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1. Generic (自定义Cache)
当至少自定义了一个org.springframework.cache.Cache bean时,Generic caching会被启用,并且会配置一个CacheManager来包装它们。
2. JCache
当javax.cache.spi.CachingProvider(这是个JSR107兼容的缓存库)在classpath中时,JCache会被启动。当有多个provider时,必须通过spring.cache.jcache.provider明确指定一个。还可通过spring.cache.jcache.config来指定配置文件的位置。 有一些方法可以定制化javax.cache.cacheManager:
可以在启动时指定spring.cache.cache-names创建caches。也可定义javax.cache.configuration.Configuration bean去定制化。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheManagerCustomizer beans会被调用,并传入CacheManager来定制。
3. EhCache2.x
在classpath跟路径下如果发现了ehcache.xml,EhCache2.x会被使用。也可使用指定spring.cache.ehcache.config=classpath:config/another-config.xml其他文件。
4. Redis
若配置了Redis,RedisCacheManager会被自动配置。也可以由spring.cache.cache-names指定。 Hazelcast和Infinispan略。
5. Guava
如果Guava可用,GuavaCacheManager会被配置。也可通过spring.cache.cache-names指定。
6. Simple
如果上述选项都没成功,一个使用ConcurrentHashMap的简单实现会被配置为cache store.
十一、消息
Spring Framework框架为集成消息系统提供了扩展支持:从使用JmsTemplate简化JMS API,到实现一个完整异步消息接收的底层设施。 Spring AMQP提供一个相似的用于’Advanced Message Queuing Protocol’的特征集,并且Spring Boot也为RabbitTemplate和RabbitMQ提供了自动配置选项。
Spring WebSocket提供原生的STOMP消息支持,并且Spring Boot通过starters和一些自动配置也提供了对它的支持。
1. JMS
javax.jms.ConnectionFactory接口提供了一个标准的用于创建一个javax.jms.Connection的方法,javax.jms.Connection用于和JMS代理(broker)交互。Spring Boot为收发消息提供了自动配置。
1.1 ActiveMQ 支持
SpringBoot检测到ActiveMQ在classpath中可用时,会配置一个ConnectionFactory。可配置如下属性: spring.activemq.broker-url=tcp://192.168.1.210:9876
spring.activemq.user=admin
spring.activemq.password=secret
1.2 HornetQ支持
支持的属性有embedded,native。spring-boot-starter-hornetq导入依赖。
1.3 Artemis 支持
Apache Artemis是在2015年HornetQ被捐给Apache基金会以后建立的,所有特性和HornetQ一样。spring-boot-starter-artemis导入依赖
2. AMQP
AMQP是一个面向消息的,平台中立、wire-level(指的是并非定义api和库,而是定义会话字节流,类似http)的中间件协议。
2.1 RabbitMQ支持
RabbitMQ是轻量级,可靠的,可扩展的,轻便的基于AMQP协议的消息代理。Spring利用RabbitMQ实现AMQP协议。可通过spring.rabbitmq.*属性组来配置,如: spring.rabbitmq.host=localhost
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
spring.rabbitmq.password=secret
Spring boot会自动配置AmqpTemplate,AmqpAdmin,RabbitMessagingTemplate。
十二、发送邮件
Spring Boot自动配置JavaMailSender来发送邮件。spring-boot-starter-mail导入依赖。 可通过spring.mail.*属性组来配置。
十三、JTA处理分布式事务
Spring Boot使用一个Atomkos或Bitronix的内嵌事务管理器来支持跨多个XA资源的分布式JTA事务。当部署到一个恰当的J2EE应用服务器时也会支持JTA事务。 当发现一个JTA环境时,Spring Boot将使用Spring的JtaTransactionManager来管理事务。自动配置的JMS,DataSource和JPA beans将被升级以支持XA事务。
你可以使用标准的@ransactional来参与到一个分布式事务中。可设置ring.jta.enabled=alse来禁用JTA自动配置功能。
spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos和spring-boot-starter-jta-bitronix导入依赖。
十四、Spring Session
Spring Session为管理用户的session信息提供支持。若web应用的classpath中有spring session 和spring data redis,spring boot会通过@EnableRedisHttpSession自动配置Spring session。Session数据被存储在redis中,超时期限可通过server.session.timeout设置。
十五、测试
spring-boot-starter-test提供以下库: • spring-test提供集成测试支持
• JUnit
• Hamcrest—为JUnit提供assertThat支持
• Mockito
1. 测试Spring Boot应用
Spring Boot提供@SpringApplicationConfiguration替代spring-test标准的@ContextConfiguration注解。测试中使用@SpringApplicationConfiguration配置ApplicationContext,ApplicationContext会被SpringApplication创建,并且带有额外的Spring boot的特性。实例:@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringApplicationConfiguration(SampleDataJpaApplication.class)
public class CityRepositoryIntegrationTests {
@Autowired
CityRepository repository;
// ...
}12
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
另外加上@WebIntegrationTest 或 @WebAppConfiguration注解,会使得context loader认为你在测试web应用。例如,为测试类加上@WebIntegrationTest会以web应用方式启动测试:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringApplicationConfiguration(SampleDataJpaApplication.class)
@WebIntegrationTest
public class CityRepositoryIntegrationTests {
@Autowired
CityRepository repository;
RestTemplate restTemplate = new TestRestTemplate();
// ... interact with the running server
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
可以使用@WebIntegrationTest注解的server.port等属性修改端口。例如:@WebIntegrationTest(“server.port:9000”)。如果将server.port和management.port置为0,应用的集成测试将使用任意端口,例如:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringApplicationConfiguration(MyApplication.class)
@WebIntegrationTest({"server.port=0", "management.port=0"})
public class SomeIntegrationTests {
// ...
}12
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
十六、Actuator(促动器):: Production-ready features
Springboot提供一些特性帮你在应用部署到生产环境后监视和管理应用。可通过HTTP,JMX甚至remote shell(SSH,Telnet)来管理和监视。审计,健康和数据采集会自动应用到你的应用。 HTTP只有在基于Spring MVC的应用中才可用。
1. 开启production-ready 特性
spring-boot-actuator提供Spring boot的production ready特性。 Actuator是机器术语,指移动或控制其他东西的机械设备。Actuator通过微小的改变产生很大的移动。
spring-boot-starter-actuator导入依赖。
2. endpoints 端点
Actuator端点使你可以监视应用并与之交互。Spring boot包含一些内置的端点(例如health端点),你也可以自己增加。 端点被暴露的方式取决于选择的技术类型。大多应用选择HTTP监视,这样端点的ID被map到URL。如health端点被map到/health.
2.1 常用端点
| ID | 描述 | 是否敏感 |
|---|---|---|
| actuator | 为其他端点提供一个基于超媒体(hypermedia-based)的发现页面。需要Spring HATEOAS支持 | true |
| autoconfig | 显示一个auto-configuration的报告,该报告展示所有auto-configuration候选者及它们被应用或未被应用的原因 | true |
| beans | 显示一个应用中所有Spring Beans的完整列表 | true |
| health | 展示应用的健康信息(当使用一个未认证连接访问时显示一个简单的’status’,使用认证连接访问则显示全部信息详情) | false |
| info | 显示任意的应用信息 | false |
| dump | 执行一个线程转储 | true |
| mappings | 显示一个所有@RequestMapping路径的整理列表 | true |
| trace | 显示trace信息(默认为最新的一些HTTP请求) | true |
取决于你如何暴露端点,敏感性可以用作安全指示。例如,如果使用HTTP并且打开了Spring Security,那么访问敏感端点要求用户名和密码。
2.2 CORS跨域资源共享支持
Cross-origin resource sharing,是个W3C规格,它为Web服务器定义了一种方式,允许网页从不同的域访问其资源(如字体),简言之,CORS就是为了让AJAX可以实现可控的跨域访问而生的。Actuator的MVC端点可以配置支持该场景:endpoints.cors.allowed-origins=http://example.com endpoints.cors.allowed-methods=GET,POST1
2
1
2
3. 通过HTTP监控和管理
开发Spring MVC应用时,Spring Boot Actuator会自动配置所有打开的端点,并通过HTTP暴露。默认的约定是端点id被map到url,如health到/health。
3.1 保护敏感端点
如果应用了Spring security,所有通过HTTP暴露的敏感的端点都会被保护。默认会使用基本认证(basic authentication,用户名为user,密码为应用启动时在控制台打印的密码)。 你可以使用Spring属性改变用户名,密码和访问端点需要的安全角色。例如,在application.properties中添加下列配置:
security.user.name=admin security.user.password=secret management.security.role=SUPERUSER1
2
3
1
2
3
3.2 定制管理端点的路径
可通过如下设置为端点的url设置前缀:management.context-path=/manage1
1
也可修改端点的id或者path来达到修改path的目的:
endpoints.health.id = fuck endpoints.health.path = /fuck/damn1
2
1
2
3.3 定制管理服务器的端口
针对基于云的部署,使用默认HTTP端口暴露管理端点比较明智。如果应用运行在自己的数据中心,可以如下修改端口:management.port=80811
1
一般情况下内部应用的管理端口都被防火墙保护,不对外开放,因此可以如下关掉保护:
management.security.enabled=false1
1
※ 只有在启用Spring security才有必要明显的关闭,否则反而可能破坏应用。
3.4 定制管理服务器地址:
management.port=8081 management.address=127.0.0.11
2
1
2
3.5 关掉http端点
management.port=-11
1
4. 度量指标Metrics
Spring Boot Actuator包括一个支持’gauge’和’counter’级别的度量指标服务。’gauge’记录一个单一值;’counter’记录一个增量(增加或减少)。 所有HTTP请求的度量指标都会被自动记录,通过metrics端点(/metrics)即可访问。
4.1 系统度量指标
Spring Boot暴露以下系统指标: 系统内存总量(mem),单位:Kb
空闲内存数量(mem.free),单位:Kb
处理器数量(processors)
系统正常运行时间(uptime),单位:毫秒
应用上下文(就是一个应用实例)正常运行时间(instance.uptime),单位:毫秒
系统平均负载(systemload.average)
堆信息(heap,heap.committed,heap.init,heap.used),单位:Kb
线程信息(threads,thread.peak,thead.daemon)
类加载信息(classes,classes.loaded,classes.unloaded)
垃圾收集信息(gc.xxx.count, gc.xxx.time)
4.2 数据源指标
以下指标会被暴露(前缀都是datasource.): 活跃连接数(datasource.xxx.active)
当前连接池使用率(datasource.xxx.usage)
4.3 缓存指标
以下指标会被暴露: 当前cache大小(cache.xxx.size)
命中率(cache.xxx.hit.ratio)
未命中率(cache.xxx.miss.ratio)
4.4 tomcat session指标
若使用tomcat做嵌入的servlet容器,session指标会被暴露: 活跃session数:httpsessions.active
最大session数:httpsessions.max
十七、部署SpringBoot应用
Spring Boot灵活的打包选项帮你更容易的将Spring Boot 应用部署到云平台,容器镜像,虚拟机或者实体机。
1. 部署到云
Spring Boot的可执行jar包可以部署到大多数流行的PaaS(Platform as a service)云提供者。这些云提供者要求使用者“带好自己的容器”;而它们管理应用进程。所以它们需要一些中间层来将你的应用适配到云概念中的一个运行进程。 两个流行的云提供者,Heroku和Cloud Foundry,采取一种“buildpack”方式。Buildpack将你部署的代码打包进任何启动应用所需的包里:可能是个JDK和一个java调用,可能是一个嵌入式web服务器,也可能是一个完整的应用服务器。一个buildpack是可插拔的,但你最好尽可能少的对它进行自定义设置。这可以减少不受你控制的功能范围,并最小化开发和生产环境的差别。
理想情况下,你的应用比如一个Spring boot可执行jar包,应含有它运行所需的一切。
还有OpenShift, Boxfuse和Amazon Web Service也支持Spring boot jar的部署
Goole App Engine只支持Servlet 2.5,要部署Springboot应用需要做修改。
2. 安装Spring Boot 应用。
除了使用jar –jar运行可执行jar包,还可以编译成Unix上的完全可执行应用:<plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <executable>true</executable> </configuration> </plugin>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
CentOS和Ubuntu上都已支持此功能。这样就可将应用以unix/Linux service的方式启动。
参考链接
http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current-SNAPSHOT/reference/htmlsingle/
相关文章推荐
- [Spring Boot 系列] 集成maven和Spring boot的profile功能
- Spring Boot学习第二篇:Spring Boot特性
- Spring Boot系列六 Spring boot集成mybatis、分页插件pagehelper
- Spring Boot系列(六)Spring Boot 连接MySql数据库
- Spring Boot系列(二) Spring Boot 构建框架
- C#温故而知新学习系列之.NET框架高级特性—.NET框架中自身提供的属性(二)
- Spring boot-(3) Spring Boot特性1
- Spring Boot系列一----使用idea快速构建Spring boot项目
- 【Spring Boot&&Spring Cloud系列】Spring Boot配置文件
- Spring Boot系列(八) Spring Boot中使用MongoDB数据库
- [Spring Boot 系列] 集成maven和Spring boot的profile 专题
- Spring Boot系列(三):Spring Boot转化为json数据格式
- spring boot学习系列:spring boot与jdbcTemplate的整合案例
- 【Spring Boot && Spring Cloud系列】Spring Boot的启动器Starter
- Spring Boot 系列(六)web开发-Spring Boot 热部署
- SpringBoot入门系列:第七篇 Spring Boot的测试
- Spring Boot系列一 spring boot 集成 slf4j 和 logback
- Spring Boot系列<二>:SpringBoot完美配置Mybatis
- Spring Boot系列八 spring boot集成jsp、restful接口、springmvc基本功能
- Spring Boot系列(十一) Spring Boot 日志控制
