弱引用weak_ptr 解决shared_ptr的循环引用
2016-11-07 10:39
615 查看
循环引用:
引用计数是一种便利的内存管理机制,但它有一个很大的缺点,那就是不能管理循环引用的对象。一个简单的例子如下:
parent 类中有指向children 类的shared_ptr智能指针,children 类中有指向parent类的shared_ptr 智能指针,他们相互指向会构成shared_ptr 的循环引用。
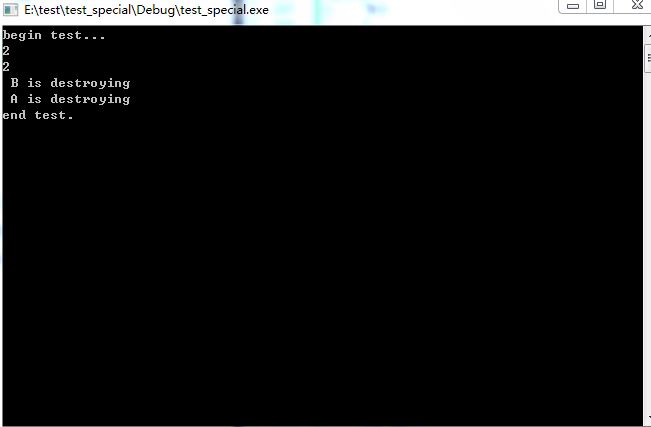
运行该程序可以看到,即使退出了test函数后,由于parent和children对象互相引用,它们的引用计数都是1,不能自动释放,并且此时这两个对象再无法访问到。这就引起了c++中那臭名昭著的内存泄漏。
利用weak_ptr来解决此问题:
- 强引用和弱引用
一个强引用当被引用的对象活着的时候,这个引用也存在。(就是说,当至少有一个强引用,那么这个对象就不能被释放)。boost::share_ptr就是强引用。
相对而言,弱引用当引用的对象活的时候不一定存在 。仅仅是当它存在的时候的一个引用。弱引用并不修改该对象的引用技术,这意味这弱引用它并不对对象的内存进行管理,在功能上类似普通的指针,然而一个比较大的区别是:弱引用能检测到所管理的对象是否已经被释放,从而避免访问非法内存。
- boost::weak_ptr
boost::weak_ptr是boost提供的一个弱引用的智能指针,它的声明可以简化如下:
可以看到,weak_ptr 必须从一个share_ptr或者另一个weak_ptr转换而来,不能使用new 对象进行构造。这也说明,进行该对象的内存管理的是那个强引用的shared_ptr。weak_ptr只是提供了对管理对象一个访问手段。
-方法 1
-方法2
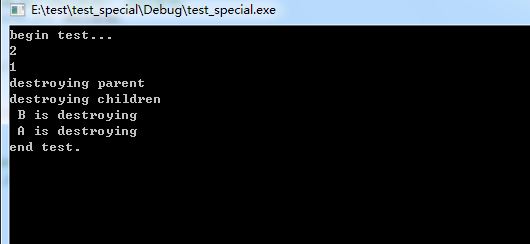
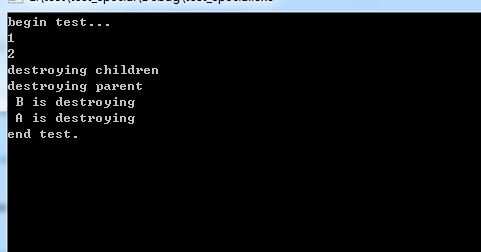
由于弱引用不更改引用计数,类似普通指针,只要把循环引用的一方使用弱引用,即可解除循环引用。
注意:
最后值得一提的是,虽然通过弱引用指针可以有效的解除循环引用,但这种方式必须在程序员能预见会出现循环引用的情况下才能使用,也可以是说这个仅仅是一种编译期的解决方案,如果程序在运行过程中出现了循环引用,还是会造成内存泄漏的。因此,不要认为只要使用了智能指针便能杜绝内存泄漏。毕竟,对于C++来说,由于没有垃圾回收机制,内存泄漏对每一个程序员来说都是一个非常头痛的问题。
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/TianFang/archive/2008/09/20/1294590.html
shared_ptr 的参考文件:
http://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_62_0/libs/smart_ptr/shared_ptr.htm#comparison
引用计数是一种便利的内存管理机制,但它有一个很大的缺点,那就是不能管理循环引用的对象。一个简单的例子如下:
class parent;
class children;
typedef shared_ptr<parent> parent_ptr;
typedef shared_ptr<children> children_ptr;
class parent
{
public:
~parent() { std::cout << "destroying parent\n"; }
public:
//weak_ptr<children> children;
children_ptr children;
};
class children
{
public:
~children() { std::cout << "destroying children\n"; }
public:
parent_ptr parent;
//weak_ptr<parent> parent;
};
class A
{
public:
~A()
{
cout << " A is destroying" << endl;
}
};
class B
{
public:
~B()
{
cout << " B is destroying" << endl;
}
};
void test()
{
A a;
B b;
parent_ptr father(new parent());
children_ptr son(new children);
father->children = son;
cout << son.use_count() << endl;
son->parent = father;
cout << father.use_count() << endl;
}
void main()
{
std::cout << "begin test...\n";
test();
std::cout << "end test.\n";
cin.get();
}parent 类中有指向children 类的shared_ptr智能指针,children 类中有指向parent类的shared_ptr 智能指针,他们相互指向会构成shared_ptr 的循环引用。

运行该程序可以看到,即使退出了test函数后,由于parent和children对象互相引用,它们的引用计数都是1,不能自动释放,并且此时这两个对象再无法访问到。这就引起了c++中那臭名昭著的内存泄漏。
利用weak_ptr来解决此问题:
- 强引用和弱引用
一个强引用当被引用的对象活着的时候,这个引用也存在。(就是说,当至少有一个强引用,那么这个对象就不能被释放)。boost::share_ptr就是强引用。
相对而言,弱引用当引用的对象活的时候不一定存在 。仅仅是当它存在的时候的一个引用。弱引用并不修改该对象的引用技术,这意味这弱引用它并不对对象的内存进行管理,在功能上类似普通的指针,然而一个比较大的区别是:弱引用能检测到所管理的对象是否已经被释放,从而避免访问非法内存。
- boost::weak_ptr
boost::weak_ptr是boost提供的一个弱引用的智能指针,它的声明可以简化如下:
namespace boost {
template<typename T>class weak_ptr {
public:
template <typename Y>
weak_ptr(const shared_ptr<Y>& r);
weak_ptr(const weak_ptr& r);
~weak_ptr();
T* get() const;
bool expired() const;
shared_ptr<T> lock() const;
};
}可以看到,weak_ptr 必须从一个share_ptr或者另一个weak_ptr转换而来,不能使用new 对象进行构造。这也说明,进行该对象的内存管理的是那个强引用的shared_ptr。weak_ptr只是提供了对管理对象一个访问手段。
-方法 1
class parent
{
public:
~parent() { std::cout << "destroying parent\n"; }
public:
weak_ptr<children> children;//将shared_ptr替换成 weak_ptr
//children_ptr children;
};
-方法2
class children
{
public:
~children() { std::cout << "destroying children\n"; }
public:
// parent_ptr parent;
weak_ptr<parent> parent;
};
由于弱引用不更改引用计数,类似普通指针,只要把循环引用的一方使用弱引用,即可解除循环引用。
注意:
最后值得一提的是,虽然通过弱引用指针可以有效的解除循环引用,但这种方式必须在程序员能预见会出现循环引用的情况下才能使用,也可以是说这个仅仅是一种编译期的解决方案,如果程序在运行过程中出现了循环引用,还是会造成内存泄漏的。因此,不要认为只要使用了智能指针便能杜绝内存泄漏。毕竟,对于C++来说,由于没有垃圾回收机制,内存泄漏对每一个程序员来说都是一个非常头痛的问题。
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/TianFang/archive/2008/09/20/1294590.html
shared_ptr 的参考文件:
http://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_62_0/libs/smart_ptr/shared_ptr.htm#comparison
相关文章推荐
- C++智能指针(三):weak_ptr--解决shared_ptr循环引用问题
- 弱引用weak_ptr解决shared_ptr的循环引用
- std::shared_ptr 和 std::weak_ptr的用法以及引用计数的循环引用问题
- shared_ptr造成的循环引用&&解决方法和原理(弱引用&&强引用)
- 使用weak_ptr打破shared_ptr循环引用
- std::shared_ptr 和 std::weak_ptr的用法以及引用计数的循环引用问题
- weak_ptr解决shared_ptr环状引用所引起的内存泄漏
- weak_ptr解决shared_ptr环状引用所引起的内存泄漏
- weak_ptr shared_ptr与循环引用
- std::shared_ptr 和 std::weak_ptr的用法以及引用计数的循环引用问题
- std::shared_ptr 和 std::weak_ptr的用法以及引用计数的循环引用问题
- C++11智能指针(五):shared_ptr的循环引用的问题及weak_ptr
- std::shared_ptr 和 std::weak_ptr的用法以及引用计数的循环引用问题
- 标准库里的weak_ptr如何解决循环引用所带来的问题
- weak_ptr解决shared_ptr环状引用所引起的内存泄漏
- weak_ptr解决shared_ptr环状引用所引起的内存泄漏
- weak_ptr的作用及应用场景——shared_ptr的循环引用问题
- [转] weak_ptr解决shared_ptr环状引用所引起的内存泄漏
- weak_ptr解决循环引用问题demo
- 用weak_ptr解决shared_ptr的环形引用问题
