codeforces 257 C. View Angle (数学)
2016-10-23 17:51
239 查看
C. View Angle
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Flatland has recently introduced a new type of an eye check for the driver's licence. The check goes like that: there is a plane with mannequins standing on it. You should tell the value of the minimum angle with the vertex at the origin of coordinates and
with all mannequins standing inside or on the boarder of this angle.
As you spend lots of time "glued to the screen", your vision is impaired. So you have to write a program that will pass the check for you.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) —
the number of mannequins.
Next n lines contain two space-separated integers each: xi, yi (|xi|, |yi| ≤ 1000) —
the coordinates of the i-th mannequin. It is guaranteed that the origin of the coordinates has no mannequin. It is guaranteed that
no two mannequins are located in the same point on the plane.
Output
Print a single real number — the value of the sought angle in degrees. The answer will be considered valid if the relative or absolute error doesn't exceed 10 - 6.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
Solution for the first sample test is shown below:
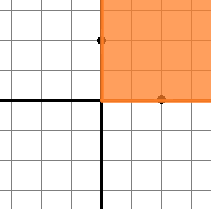
Solution for the second sample test is shown below:
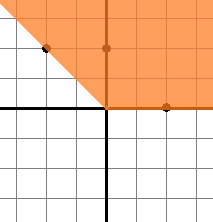
Solution for the third sample test is shown below:
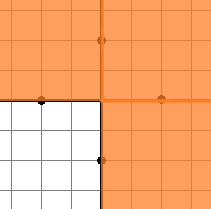
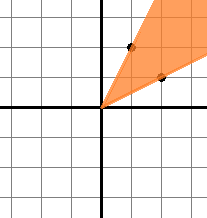
Solution for the fourth sample test is shown below:
包含所给所有点的最小的角度,利用反函数atan( )求与x正半轴夹角,360-相邻两边的最大角 就是解
代码:
一)
二)
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Flatland has recently introduced a new type of an eye check for the driver's licence. The check goes like that: there is a plane with mannequins standing on it. You should tell the value of the minimum angle with the vertex at the origin of coordinates and
with all mannequins standing inside or on the boarder of this angle.
As you spend lots of time "glued to the screen", your vision is impaired. So you have to write a program that will pass the check for you.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) —
the number of mannequins.
Next n lines contain two space-separated integers each: xi, yi (|xi|, |yi| ≤ 1000) —
the coordinates of the i-th mannequin. It is guaranteed that the origin of the coordinates has no mannequin. It is guaranteed that
no two mannequins are located in the same point on the plane.
Output
Print a single real number — the value of the sought angle in degrees. The answer will be considered valid if the relative or absolute error doesn't exceed 10 - 6.
Examples
input
2 2 0 0 2
output
90.0000000000
input
3 2 0 0 2 -2 2
output
135.0000000000
input
4 2 0 0 2 -2 0 0 -2
output
270.0000000000
input
2 2 1 1 2
output
36.8698976458
Note
Solution for the first sample test is shown below:

Solution for the second sample test is shown below:

Solution for the third sample test is shown below:

Solution for the fourth sample test is shown below:

包含所给所有点的最小的角度,利用反函数atan( )求与x正半轴夹角,360-相邻两边的最大角 就是解
代码:
一)
/*注意角度化成度数形式*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
double x,y;
double angle[100010];
scanf("%d",&n);
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y);
if(y==0)
{
if(x>0) angle[i]=0;
else angle[i]=180;
}
else if(x==0)
{
if(y>0) angle[i]=90;
else angle[i]=270;
}
else if(x>0&&y>0)
angle[i]=atan(y/x)*(180/PI);
else if(x<0&&y>0)
angle[i]=90+atan(-1*x/y)*(180/PI);
else if(x<0&&y<0)
angle[i]=180+atan(y/x)*(180/PI);
else
angle[i]=270+atan(-1*x/y)*(180/PI);
}
double maxn=0.0,minn;
sort(angle,angle+n);
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
maxn=max(maxn,angle[i+1]-angle[i]);
}
maxn=max(maxn,360-angle[n-1]+angle[0]);
minn=360-maxn;
printf("%.8lf\n",minn);
return 0;
}二)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
double x,y;
double angle;
}node[100000+10];
bool cmp(Node a,Node b)
{
return a.angle<b.angle;
}
double Angle(double x,double y)
{
if(y==0)
{
if(x>0) return 0;
else return 180;
}
else if(x==0)
{
if(y>0) return 90;
else return 270;
}
else if(x>0&&y>0)
return atan(y/x)*(180/PI);
else if(x<0&&y>0)
return 90+atan(-x/y)*(180/PI);
else if(x<0&&y<0)
return 180+atan(y/x)*(180/PI);
else
return 270+atan(-x/y)*(180/PI);
}
int main()
{
int n;
//double x,y;
//double angle[1010];
scanf("%d",&n);
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%lf %lf",&node[i].x,&node[i].y);
node[i].angle=Angle(node[i].x,node[i].y);
}
double maxn=0.0,minn;
sort(node,node+n,cmp);
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
maxn=max(maxn,node[i+1].angle-node[i].angle);
}
maxn=max(maxn,360-node[n-1].angle+node[0].angle);
minn=360-maxn;
printf("%.8lf\n",minn);
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces 257C:View Angle(思维+数学+atan2函数)
- 【CodeForces】257C - View Angle(计算几何)
- CodeForces 257C View Angle(求角度)
- codeforces - 257c View Angle 【数学】
- CodeForces 785 D.Anton and School - 2(组合数学)
- Codeforces 658D Bear and Polynomials【数学】
- CodeForces 589D Boulevard (数学,相遇)
- CodeForces 258C Little Elephant and LCM(数学推理)
- Codeforces 552B - Vanya and Books(数学)
- 数学 之 Codeforces 354A - Vasya and Robot
- CodeForces 173A Rock-Paper-Scissors 数学
- codeforces-755D-PolandBall and Polygon(数学题)
- Codeforces--614A--Link/Cut Tree(数学)(暴力求解)
- 【codeforces】数学
- [Codeforces 711E] ZS and The Birthday Paradox (数学+Legendre公式)
- CodeForces - 630D Hexagons! (数学规律)
- codeforces 257 div2 B
- Codeforces Div. 2 #257-B. Jzzhu and Sequences
- CodeForces - 611B 数学思维
- 简单数学题或者计算几何:Codeforces 659D-Bicycle Race
