Codeforces 403B Upgrading Array [贪心] [数论]
2016-10-11 11:46
447 查看
B. Upgrading Array
time limit per test 1 second
memory limit per test 256 megabytes
input standard input
output standard output
You have an array of positive integers a[1], a[2], …, a
and a set of bad prime numbers b1, b2, …, bm. The prime numbers that do not occur in the set b are considered good. The beauty of array a is the sum
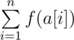
, where function f(s) is determined as follows:
f(1) = 0;
Let’s assume that p is the minimum prime divisor of s. If p is a good prime, then
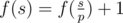
, otherwise
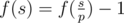
.
You are allowed to perform an arbitrary (probably zero) number of operations to improve array a. The operation of improvement is the following sequence of actions:
Choose some number r (1 ≤ r ≤ n) and calculate the value g = GCD(a[1], a[2], …, a[r]).
Apply the assignments:
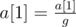
,
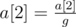
, …,
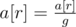
.
What is the maximum beauty of the array you can get?
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 5000) showing how many numbers are in the array and how many bad prime numbers there are.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a[1], a[2], …, a
(1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — array a. The third line contains m space-separated integers b1, b2, …, bm (2 ≤ b1 < b2 < … < bm ≤ 109) — the set of bad prime numbers.
Output
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem.
Examples
input
5 2
4 20 34 10 10
2 5
output
-2
input
4 5
2 4 8 16
3 5 7 11 17
output
10
Note
Note that the answer to the problem can be negative.
The GCD(x1, x2, …, xk) is the maximum positive integer that divides each xi.
从a[1]…a[r]同时除以最大公因数,当i < j时,GCD(j) | GCD(i) ,那么如果在i处进行操作,那么 j 操作将无法执行。
所以应该倒着考虑,如果当前 r 处不执行操作,那么如果在后面执行操作,(i,j] 这部分的GCD没有对答案进行贡献,所以倒着考虑时如果可以操作,并且操作后对答案有贡献那么就在当前位置进行操作,这样可以保证答案不会更劣。
time limit per test 1 second
memory limit per test 256 megabytes
input standard input
output standard output
You have an array of positive integers a[1], a[2], …, a
and a set of bad prime numbers b1, b2, …, bm. The prime numbers that do not occur in the set b are considered good. The beauty of array a is the sum
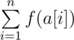
, where function f(s) is determined as follows:
f(1) = 0;
Let’s assume that p is the minimum prime divisor of s. If p is a good prime, then
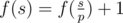
, otherwise
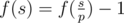
.
You are allowed to perform an arbitrary (probably zero) number of operations to improve array a. The operation of improvement is the following sequence of actions:
Choose some number r (1 ≤ r ≤ n) and calculate the value g = GCD(a[1], a[2], …, a[r]).
Apply the assignments:
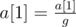
,
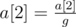
, …,
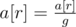
.
What is the maximum beauty of the array you can get?
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 5000) showing how many numbers are in the array and how many bad prime numbers there are.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a[1], a[2], …, a
(1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — array a. The third line contains m space-separated integers b1, b2, …, bm (2 ≤ b1 < b2 < … < bm ≤ 109) — the set of bad prime numbers.
Output
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem.
Examples
input
5 2
4 20 34 10 10
2 5
output
-2
input
4 5
2 4 8 16
3 5 7 11 17
output
10
Note
Note that the answer to the problem can be negative.
The GCD(x1, x2, …, xk) is the maximum positive integer that divides each xi.
从a[1]…a[r]同时除以最大公因数,当i < j时,GCD(j) | GCD(i) ,那么如果在i处进行操作,那么 j 操作将无法执行。
所以应该倒着考虑,如果当前 r 处不执行操作,那么如果在后面执行操作,(i,j] 这部分的GCD没有对答案进行贡献,所以倒着考虑时如果可以操作,并且操作后对答案有贡献那么就在当前位置进行操作,这样可以保证答案不会更劣。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
#include<ctime>
#include<climits>
#include<cctype>
#include<algorithm>
#define AUTO "%I64d"
using namespace std;
#define smax(x,tmp) x=max((x),(tmp))
#define smin(x,tmp) x=min((x),(tmp))
#define maxx(x1,x2,x3) max(max(x1,x2),x3)
#define minn(x1,x2,x3) min(min(x1,x2),x3)
typedef long long LL;
LL gcd(LL a,LL b) { return !b?a:gcd(b,a%b); }
const int N = sqrt(1e9)+1;
const int maxp = 100000;
const int maxpp = 10000;
int prime[maxpp],tot;
bool no[maxp];
void get_prime()
{
no[1]=true;
for(int i=2;i<=N;i++)
{
if(!no[i]) prime[++tot] = i;
int j=1;
LL to = (LL)i*prime[j];
while(j<=tot && to<=N)
{
no[to] = true;
if(i%prime[j]==0) break;
to = (LL) i * prime[++j];
}
}
}
set <int> bad;
int f(int num)
{
int ret = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=tot&&num^1;i++) if(num%prime[i]==0)
while(num%prime[i]==0)
{
num /= prime[i];
if(bad.find(prime[i]) == bad.end()) ret++;
else ret--;
}
if(num^1)
if(bad.find(num) == bad.end()) ret++;
else ret--;
return ret;
}
const int maxn = 5005;
int a[maxn],GCD[maxn];
int n,m;
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("array.in","r",stdin);
freopen("array.out","w",stdout);
#endif
get_prime();
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",a+i),GCD[i]=gcd(GCD[i-1],a[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int tmp;
scanf("%d",&tmp);
bad.insert(tmp);
}
int div=1;
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--)
{
int tmp=f(GCD[i]/div);
if(tmp<0) div = GCD[i];
a[i] /= div; // everyone is supposed to be divided once!!
}
LL ans = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
ans += f(a[i]);
printf(AUTO,ans);
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- codeforces 337E E. Divisor Tree(数论+贪心)
- codeforces 225B B. Well-known Numbers(数论+二分+贪心+构造)
- CodeForces 124C Prime Permutation (数论+贪心)
- Codeforces-798C-Mike and gcd problem(贪心+数论)
- Codeforces 798C:Mike and gcd problem【数论+贪心】
- !codeforces 399C Cards-数论&贪心-(暴力枚举)
- codeforces 276D D. Little Girl and Maximum XOR(贪心+dp+数论)
- codeforces 303C. Minimum Modular(数论+暴力+剪枝+贪心)
- CodeForces 432C - Prime Swaps (数论 + 贪心)
- [Codeforces 814D] An overnight dance in discotheque 树形dp,贪心
- 【CodeForces - 839B】Game of the Rows(贪心+暴力)(有点坑)
- CodeForces 703 C.Chris and Road(贪心)
- CodeForces 215D Hot Days(贪心)
- Codeforces 384B Multitasking(贪心)
- CodeForces 707B Bakery (水题,暴力,贪心)
- codeforces 474F F. Ant colony(线段树+数论)
- CodeForces 431# div.2 A Odds and Ends 暴力 贪心
- Codeforces_394C_Dominoes(贪心构造)
- 【数论】【扩展欧几里得】Codeforces 710D Two Arithmetic Progressions
- Codeforces 675C Money Transfers【贪心】
