struts2学习三(OGNL和ValueStack值栈)
2016-10-02 15:42
323 查看
1、OGNL
OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language),它是一种功能强大的表达式语言,比EL更强大的表达式语言(开源)。struts整合OGNL表达式。使用OGNL作为默认的表达式语言。主要功能:
1、存取对象的属性,调用对象的方法
2、操作集合
3、直接new对象
4、访问OGNL上下文(OGNL context和ActionContext);
1、在root中的示例
public class TestOGNL {
@Test
public void test1() throws OgnlException {
// 1、执行对象的方法
Object o = Ognl.getValue("'abc'.toUpperCase()", null);
System.out.println(o);
// 输出结果:ABC
}
@Test
public void test2() throws OgnlException {
// 2、静态资源的访问
Ognl.getValue("@System@out.println(@Math@PI)", new HashMap(),
new Object());
System.out.println(Math.PI);
// 输出结果:3.141592653589793
}
@Test
public void test3() throws OgnlException{
//1、获取root属性值,直接使用对象的名称获取
User user =new User("abc","123");
Object o=Ognl.getValue("username", new HashMap(),user);
System.out.println(o);
//输出结果:abc
}
@Test
public void test4() throws OgnlException{
//2、获取root属性值,如果存放的是map,直接通过key获取
Map<String,String> map =new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("a", "aaaaa");
map.put("b", "bbbbb");
map.put("c", "ccccc");
Object o=Ognl.getValue("a",new HashMap(),map);
System.out.println(o);
//运行结果:aaaaa
}2、在context中的操作
@Test
public void test1() throws OgnlException {
//1、获取contxt中的值
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("a", "aaa");
Object o=Ognl.getValue("#a", map,new Object());
System.out.println(o);
//运行结果:aaa
}3、赋值
@Test
public void test2() throws OgnlException {
// 赋值
User user = new User();
Ognl.getValue("username='tom'", new HashMap(), user);
System.out.println(user);
//运行结果:User [username=tom, password=null]
}4、投影(过滤)
OGNL中的投影说的通俗一点就是过滤,目的就是在结果中选择满族条件的结果显示出来@Test
public void demo4() throws OgnlException{
// #12过滤:对集合,进一步的操作,可以给遍历的集合添加过滤条件
// 语法:集合.{符号 过滤表达式}
// 符号:? 所有, ^ 第一个 , $ 最后一个
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list.add(new User("jack","1"));
list.add(new User("rose","2"));
list.add(new User("tom","3"));
list.add(new User("cat","4"));
// 当前对象
Object val = Ognl.getValue("#this", new HashMap(), list);
System.out.println(val);
// 当前对象 -- 第一个
Object val2 = Ognl.getValue("#this.{^#this}", new HashMap(), list);
System.out.println(val2);
// 当前对象 -- 所有内容,添加条件
Object val3 = Ognl.getValue("#this.{?#this.userPwd > 2}", new HashMap(), list);
System.out.println(val3);
}2、ValueStack值栈
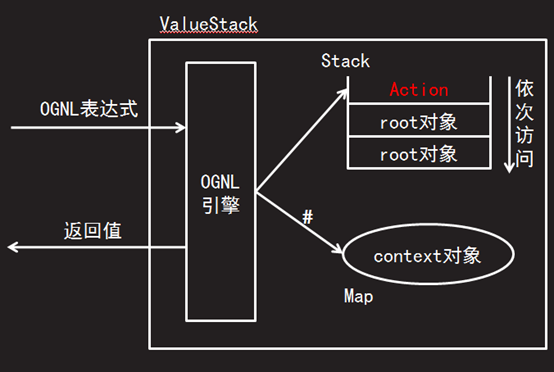
1、struts在action中存放数据,在jsp中显示数据。struts有两个地方存储数据:root和context;
root:底层是ArrayList,用于存放没有名称的数据。也称为值栈
context:底层是Map,给存放在map中每一个对象进行命名。
2、ValueStack(值栈): 贯穿整个 Action 的生命周期(每个 Action 类的对象实例都拥有一个ValueStack 对象,每次请求都会创建一个Action类)。请求完成后ValueStack与request将一起消失。
ValueStack相当于一个数据的中转站. 在其中保存当前Action 对象和其他相关对象.
3、ValueStack实际是一个接口,在Struts2中利用OGNL时,实际上使用的是实现了该接口的OgnlValueStack类,这个类是Struts2利用OGNL的基础
Struts 框架把 ValueStack 对象保存在名为 “struts.valueStack” 的请求属性中,request中
ServletActionContext类中提供了一个常量
public static final String STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY = “struts.valueStack”;
4、在 ValueStack 对象的内部有两个逻辑部分:
ObjectStack: Struts 把动作和相关对象压入 ObjectStack中,底层实现对象为CompoundRoot, CompoundRoot是一个ArrayList
ContextMap: Struts 把各种各样的映射关系(一些 Map 类型的对象) 压入 ContextMap 中。底层为Map
对值栈的操作,默认都是Root对象的操作,访问数据时不需要使用#号
源码如下:
public class CompoundRoot extends ArrayList {
public CompoundRoot() {
}
public CompoundRoot(List list) {
super(list);
}
public CompoundRoot cutStack(int index) {
return new CompoundRoot(subList(index, size()));
}
public Object peek() {
return get(0);
}
public Object pop() {
return remove(0);
}
public void push(Object o) {
add(0, o);
}
}5、Struts 会把下面这些映射压入 ContextMap 中,获取时间是需要使用#号
parameters: 该 Map 中包含当前请求的请求参数
request: 该 Map 中包含当前 request 对象中的所有属性
session: 该 Map 中包含当前 session 对象中的所有属性
application:该 Map 中包含当前 application 对象中的所有属性
attr: 该 Map 按如下顺序来检索某个属性: request, session, application
demo1
1、bean类和action类
package com.example.stack;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
public User(String username, String password) {
super();
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public User() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}action类
package com.example.stack;
import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack;
public class ActionValueStack1 extends ActionSupport {
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
// 1 获得值栈(root)
// 方式1: 从request作用域获得
ValueStack valueStack = (ValueStack) ServletActionContext.getRequest()
.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
// 方式2:通过context获得
ValueStack valueStack2 = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
valueStack2.getContext();
// 2 获得context
ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext();
// 3 root操作
// 3将指定的数据压入到栈顶,注意:一般情压入的javabean对象。jsp页面通过“属性”获得
valueStack2.push(new User("tom", "1234"));
return SUCCESS;
}
}2、struts.xml文件配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> <struts> <!-- 开发模式 --> <constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" /> <!-- 包 --> <package name="day03" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="actionValueStack1" class="com.example.stack.ActionValueStack1"> <result name="success">/a/success.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
3、访问form.jsp和success.jsp
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/actionValueStack1">使用值栈</a><br/>
</body><%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <s:property value="username"/> </body> </html>
4、struts中的#,$,%
“#”:表示从context中获取灵气%{}:表示使用ONGL解析
%{”}不使用ONGL解析,只是普通字符串
相关文章推荐
- struts2系列学习笔记(12)---------------OGNL
- Struts2中OGNL,valueStack,stackContext的学习
- Struts2深入学习----OGNL表达式原理
- struts2学习笔记----OGNL
- Struts2深入学习:OGNL表达式原理
- struts2 - ognl表达式 学习笔记
- Struts2学习6—OGNL (1)
- ognl学习(二)---struts2标签库与OGNL表达式的使用
- Struts2深入学习----OGNL表达式原理(转)
- Struts2深入学习:OGNL表达式原理
- struts2的ognl学习
- Struts2 OGNL学习知识
- Struts2深入学习----OGNL表达式原理
- Struts2深入学习----OGNL表达式原理
- Struts2深入学习----OGNL表达式原理
- struts2系列学习笔记(12)---------------Struts2在OGNL基础上的增强
- Struts2深入学习----OGNL表达式原理
- Struts2中OGNL,valueStack,stackContext的学习
- Struts2深入学习:OGNL表达式原理
- struts2学习(15)——ognl表达式
