(十) 编写LED驱动程序
2016-09-29 21:17
127 查看
结合前面介绍的linux字符驱动编写的流程(申请设备号-设备注册-生成设备节点),开始对LED驱动进行编写。编写驱动的流程:查看原理图以及数据手册-内核寻找相似驱动进行开发,有时从零开始-字符驱动编写以及实现功能,方便调用-编译内核或者insmod加载-测试驱动。
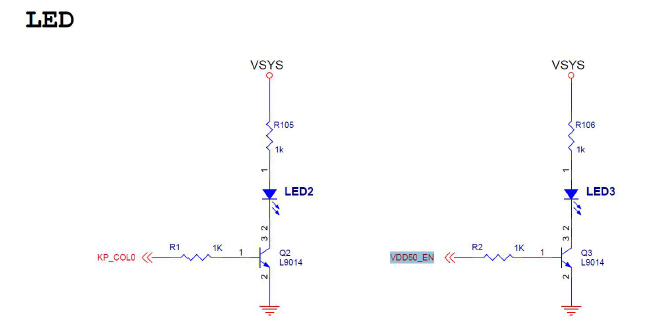
当KP_COL0 和VDD50_EN 网络时高电平的时候,三极管L9014 的BE 导通,CE 导通,相当于5V 的VSYS 电压加到1K 和Led 小灯上,小灯就会亮;当KP_COL0 和VDD50_EN 网络时低电平的时候,三极管L9014 的BE 会截止,CE 截止,相当于5V 的VSYS 电压加到1K、Led 小灯和一个无限大的电阻上,电流为零,小灯就会灭。
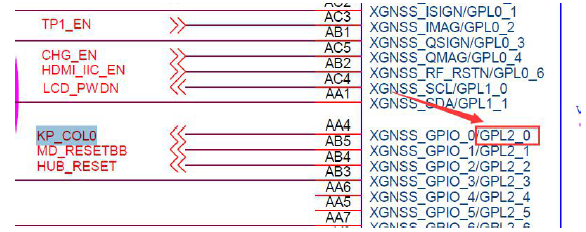
从上图可以看出led宏定义为EXYNOS4_GPL2(0),EXYNOS4_GPK1(1)。
头文件char_driver.h
驱动程序char_driver.c
1.LED原理图
查看原理图以及数据手册(如下图),从图中可以看出KP_COL0和VDD50_EN控制Led的点亮。
当KP_COL0 和VDD50_EN 网络时高电平的时候,三极管L9014 的BE 导通,CE 导通,相当于5V 的VSYS 电压加到1K 和Led 小灯上,小灯就会亮;当KP_COL0 和VDD50_EN 网络时低电平的时候,三极管L9014 的BE 会截止,CE 截止,相当于5V 的VSYS 电压加到1K、Led 小灯和一个无限大的电阻上,电流为零,小灯就会灭。

从上图可以看出led宏定义为EXYNOS4_GPL2(0),EXYNOS4_GPK1(1)。
2.驱动程序编写
头文件char_driver.h
#ifndef _CHAR_DRIVER_LEDS_H_
#define _CHAR_DRIVER_LEDS_H_
#ifndef DEVICE_NAME
#define DEVICE_NAME "chdriver"
#endif
#ifndef DEVICE_MINOR_NUM
#define DEVICE_MINOR_NUM 2
#endif
#ifndef DEV_MAJOR
#define DEV_MAJOR 0
#endif
#ifndef DEV_MINOR
#define DEV_MINOR 0
#endif
#ifndef REGDEV_SIZE
#define REGDEV_SIZE 3000
#endif
struct reg_dev
{
char *data;
unsigned long size;
struct cdev cdev;
};
#endif驱动程序char_driver.c
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/kdev_t.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <plat/gpio-cfg.h>
#include <mach/gpio-exynos4.h>
#include "char_driver.h"
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("flywang");
static int led_gpios[] = {
EXYNOS4_GPL2(0),EXYNOS4_GPK1(1),
};
#define LED_NUM ARRAY_SIZE(led_gpios)
int numdev_major = DEV_MAJOR;
int numdev_minor = DEV_MINOR;
module_param(numdev_major,int,S_IRUSR);
module_param(numdev_minor,int,S_IRUSR);
static struct class *myclass;
struct reg_dev *my_devices;
static int chardevnode_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){
printk(KERN_EMERG "chardevnode_open is success!\n");
return 0;
}
/*关闭操作*/
static int chardevnode_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){
printk(KERN_EMERG "chardevnode_release is success!\n");
return 0;
}
/*IO操作*/
static long chardevnode_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg){
switch(cmd)
{
case 0:
case 1:
if (arg > LED_NUM) {
return -EINVAL;
}
gpio_set_value(led_gpios[arg], cmd);
break;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
printk(KERN_EMERG "chardevnode_ioctl is success! cmd is %d,arg is %d \n",cmd,arg);
return 0;
}
ssize_t chardevnode_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_ops){
return 0;
}
ssize_t chardevnode_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_ops){
return 0;
}
loff_t chardevnode_llseek(struct file *file, loff_t offset, int ence){
return 0;
}
struct file_operations my_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = chardevnode_open,
.release = chardevnode_release,
.unlocked_ioctl = chardevnode_ioctl,
.read = chardevnode_read,
.write = chardevnode_write,
.llseek = chardevnode_llseek,
};
/*设备注册到系统*/
static void reg_init_cdev(struct reg_dev *dev,int index){
int err;
int devno = MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor+index);
cdev_init(&dev->cdev,&my_fops);
dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
dev->cdev.ops = &my_fops;
err = cdev_add(&dev->cdev,devno,1);
if(err){
printk(KERN_EMERG "cdev_add %d is fail! %d\n",index,err);
}
else{
printk(KERN_EMERG "cdev_add %d is success!\n",numdev_minor+index);
}
}
static int gpio_init(void){
int i=0,ret;
for(i=0;i<LED_NUM;i++){
ret = gpio_request(led_gpios[i], "LED");
if (ret) {
printk("%s: request GPIO %d for LED failed, ret = %d\n", DEVICE_NAME,i,ret);
return -1;
}
else{
s3c_gpio_cfgpin(led_gpios[i], S3C_GPIO_OUTPUT);
gpio_set_value(led_gpios[i], 1);
}
}
return 0;
}
static int led_init(void)
{
int ret = 0,i;
dev_t num_dev;
printk(KERN_EMERG "numdev_major is %d!\n",numdev_major);
printk(KERN_EMERG "numdev_minor is %d!\n",numdev_minor);
if(numdev_major){
num_dev = MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor);
ret = register_chrdev_region(num_dev,DEVICE_MINOR_NUM,DEVICE_NAME);
}
else{
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&num_dev,numdev_minor,DEVICE_MINOR_NUM,DEVICE_NAME);
/*获得主设备号*/
numdev_major = MAJOR(num_dev);
printk(KERN_EMERG "adev_region req %d !\n",numdev_major);
}
if(ret<0){
printk(KERN_EMERG "register_chrdev_region req %d is failed!\n",numdev_major);
}
myclass = class_create(THIS_MODULE,DEVICE_NAME);
my_devices = kmalloc(DEVICE_MINOR_NUM * sizeof(struct reg_dev),GFP_KERNEL);
if(!my_devices){
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto fail;
}
memset(my_devices,0,DEVICE_MINOR_NUM * sizeof(struct reg_dev));
/*设备初始化*/
for(i=0;i<DEVICE_MINOR_NUM;i++){
my_devices[i].data=
kmalloc(REGDEV_SIZE,GFP_KERNEL);
memset(my_devices[i].data,0,REGDEV_SIZE);
/*设备注册到系统*/
reg_init_cdev(&my_devices[i],i);
device_create(myclass,NULL, MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor+i),
NULL,DEVICE_NAME"%d",i);
}
ret = gpio_init();
if(ret){
printk(KERN_EMERG "gpio_init failed!\n");
}
printk(KERN_EMERG "scdev_init!\n");
return 0;
fail:
/*注销设备号*/
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor),DEVICE_MINOR_NUM);
printk(KERN_EMERG "kmalloc is fail!\n");
return ret;
}
static void led_exit(void)
{
int i;
printk(KERN_EMERG "scdev_exit!\n");
for(i=0;i<DEVICE_MINOR_NUM;i++){
cdev_del(&(my_devices[i].cdev));
device_destroy(myclass,MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor+i));
}
class_destroy(myclass);
kfree(my_devices);
for(i=0;i<LED_NUM;i++){
gpio_free(led_gpios[i]);
}
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor),DEVICE_MINOR_NUM);
}
module_init(led_init);
module_exit(led_exit);3.测试程序编写
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
/*argv[1] is cmd , argv[2] is io_arg*/
int main(int argc , char **argv){
int fd;
char *lednode = "/dev/chdriver";
if((fd = open(lednode,O_RDWR|O_NDELAY))<0){
printf("APP open %s failed!\n",lednode);
}
else{
printf("APP open %s success!\n",lednode);
ioctl(fd,atoi(argv[1]),atoi(argv[2]));
printf("APP ioctl %s ,cmd is %s! io_arg is %s!\n",lednode,argv[1],argv[2]);
}
close(fd);
}
相关文章推荐
- 字符设备驱动程序的编写_点亮LED灯
- ARM-linux驱动学习:led驱动程序编写练习(2014-8-22)
- LED&KEYPAD驱动程序编写实验
- 嵌入式驱动编写-点亮LED驱动程序
- 第12课第2.1节 字符设备驱动程序之LED驱动程序_编写编译
- 11.ok6410之led驱动程序编写
- LED&KEYPAD驱动程序编写实验
- 在Ubuntu上为Android系统编写Linux内核驱动程序
- 编写LED混杂设备驱动:静态映射,如何用Linux内核里的gpio_request(),gpio_set_value()等函数,ioctl函数
- Linux操作系统网络驱动程序编写
- Ubuntu中为Android系统上编写Linux内核驱动程序实现方法
- 为多功能片上系统处理器编写 Linux 设备驱动程序
- 学习 1-在Ubuntu上为Android系统编写Linux内核驱动程序
- 用户空间编写S3c2440 lcd的驱动程序
- Tiny6410开发板下块设备驱动程序的编写驱动之用内存模拟磁盘(一)
- 如何编写Linux设备驱动程序 (转)
- FL2440无操作系统应用程序编写测试003——LED
- 驱动测试程序编写、驱动程序卸载与测试
- fl2440——驱动学习-LED驱动程序代码分析
- 基于spi总线驱动程序的编写
