拉普拉斯图像融合
2016-09-26 11:31
399 查看
转载来自:https://www.baidu.com/link?url=WKY64Yy9miikawY0DJMDZGoasUqAVgn072ozE3otWuCkz0GMSmoCMYIIlA2_FK11LwSiIydyBz41sA0x87FLvq&wd=&eqid=a85685090006802a0000000657e891a2
图像金字塔是一个图像集合,集合中所有的图像都来源于同一个原始图像,而且是通过对原始图像的连续降采样获得,直到达到某个终止条件才停止降采样。
常见的两种图像金字塔:
高斯金字塔(Gaussian pyramid): 向下采样图像
拉普拉斯金字塔(Laplacian pyramid):用来从金字塔低层图像中向上采样重建一个图像。
下采样使得图像金字塔的层级越高,图像越小。假设每一层都按从下到上的次序编号,层级(i + 1) 的尺寸表示为Gi+1。则由第i层图像获得第i+1层图像的步骤为:
1)将Gi与高斯内核卷积:
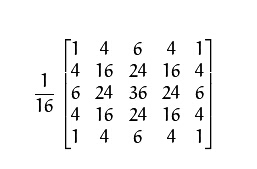
2)将所有偶数行和列去除。
经过上诉处理后,获得的结果图像为原来原图的1/4。不断对迭代上诉步骤就可以得到整个图像金字塔。
Mat格式的:
pyrDown( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 )
函数 pyrDown 接受3个参数:
tmp: 当前图像, 初始化为原图像 src 。
dst: 目的图像( 显示图像,为输入图像的一半)
Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ) :目的图像大小, 既然我们是向下采样, pyrDown 期待一个一半于输入图像( tmp)的大小。
注意输入图像的大小(在两个方向)必须是2的冥,否则,将会显示错误。
上采样使得图像变大。步骤:
1)将图像在每个方向扩大为原来的两倍,新增的行与列以0填充
2)使用先前同样的内核(乘以4)与放大后的图像卷积,获得新增像素的近似值。
注意上采样不是下采样的逆操作。因为下采样是一个丢失图像信息的处理过程。
Mat格式:
pyrUp( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 )
函数 pyrUp 接受了3个参数:
tmp: 当前图像, 初始化为原图像 src 。
dst: 目的图像( 显示图像,为输入图像的两倍)
Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 ) : 目的图像大小, 既然我们是向上采样, pyrUp 期待一个两倍于输入图像( tmp )的大小。
降采样操作丢失的信息数据形成了拉普拉斯金字塔。拉普拉斯金字塔的第i层定义为:
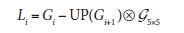
借助于opencv,PyrUp()函数实现的功能就是
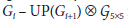
所定义的,所以,可以使用opencv直接进行拉普拉运算:
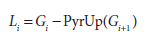
拉普拉斯金字塔与高斯金字塔如下图所示:
利用高斯金字塔与拉普拉斯金字塔,可以将两幅图像进行融合。具体实现步骤为:
1)每个源图像先被分解成拉普拉斯金字塔(左边列和右边列)
2)建立高斯金字塔。(二值掩膜)
3)每个拉普拉斯金字塔图像乘以相应的高斯掩膜(卷积)
4)进行拼接blendLapPyrs() ; 在每一层上将左右laplacian图像直接拼起来得结果金字塔resultLapPyr。
5)重建图像: 从最高层结果图
//将左右laplacian图像拼成的resultLapPyr金字塔中每一层,从上到下插值放大并和下一层相加,即得blend图像结果(reconstructImgFromLapPyramid)
具体代码:
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace cv;
/************************************************************************/
/* 说明:
*金字塔从下到上依次为 [0,1,...,level-1] 层
*blendMask 为图像的掩模
*maskGaussianPyramid为金字塔每一层的掩模
*resultLapPyr 存放每层金字塔中直接用左右两图Laplacian变换拼成的图像
*/
/************************************************************************/
class LaplacianBlending {
private:
Mat_<Vec3f> left;
Mat_<Vec3f> right;
Mat_<float> blendMask;
vector<Mat_<Vec3f> > leftLapPyr,rightLapPyr,resultLapPyr;//Laplacian Pyramids
Mat leftHighestLevel, rightHighestLevel, resultHighestLevel;
vector<Mat_<Vec3f> > maskGaussianPyramid; //masks are 3-channels for easier multiplication with RGB
int levels;
void buildPyramids() {
buildLaplacianPyramid(left,leftLapPyr,leftHighestLevel);
buildLaplacianPyramid(right,rightLapPyr,rightHighestLevel);
buildGaussianPyramid();
}
void buildGaussianPyramid() {//金字塔内容为每一层的掩模
assert(leftLapPyr.size()>0);
maskGaussianPyramid.clear();
Mat currentImg;
cvtColor(blendMask, currentImg, CV_GRAY2BGR);//store color img of blend mask into maskGaussianPyramid
maskGaussianPyramid.push_back(currentImg); //0-level
currentImg = blendMask;
for (int l=1; l<levels+1; l++) {
Mat _down;
if (leftLapPyr.size() > l)
pyrDown(currentImg, _down, leftLapPyr[l].size());
else
pyrDown(currentImg, _down, leftHighestLevel.size()); //lowest level
Mat down;
cvtColor(_down, down, CV_GRAY2BGR);
maskGaussianPyramid.push_back(down);//add color blend mask into mask Pyramid
currentImg = _down;
}
}
void buildLaplacianPyramid(const Mat& img, vector<Mat_<Vec3f> >& lapPyr, Mat& HighestLevel) {
lapPyr.clear();
Mat currentImg = img;
for (int l=0; l<levels; l++) {
Mat down,up;
pyrDown(currentImg, down);
pyrUp(down, up,currentImg.size());
Mat lap = currentImg - up;
lapPyr.push_back(lap);
currentImg = down;
}
currentImg.copyTo(HighestLevel);
}
Mat_<Vec3f> reconstructImgFromLapPyramid() {
//将左右laplacian图像拼成的resultLapPyr金字塔中每一层
//从上到下插值放大并相加,即得blend图像结果
Mat currentImg = resultHighestLevel;
for (int l=levels-1; l>=0; l--) {
Mat up;
pyrUp(currentImg, up, resultLapPyr[l].size());
currentImg = up + resultLapPyr[l];
}
return currentImg;
}
//Mat::mul执行两个矩阵按元素相乘或这两个矩阵的除法。该方法返回一个用可选的缩放比率编码了每个元素的数组乘法的临时的对象。
void blendLapPyrs() {
//获得每层金字塔中直接用左右两图Laplacian变换拼成的图像resultLapPyr
resultHighestLevel = leftHighestLevel.mul(maskGaussianPyramid.back()) +
rightHighestLevel.mul(Scalar(1.0,1.0,1.0) - maskGaussianPyramid.back());
for (int l=0; l<levels; l++) {
Mat A = leftLapPyr[l].mul(maskGaussianPyramid[l]);
Mat antiMask = Scalar(1.0,1.0,1.0) - maskGaussianPyramid[l];
Mat B = rightLapPyr[l].mul(antiMask);
Mat_<Vec3f> blendedLevel = A + B;
resultLapPyr.push_back(blendedLevel);
}
}
public:
LaplacianBlending(const Mat_<Vec3f>& _left, const Mat_<Vec3f>& _right, const Mat_<float>& _blendMask, int _levels)://construct function, used in LaplacianBlending lb(l,r,m,4);
left(_left),right(_right),blendMask(_blendMask),levels(_levels)
{
assert(_left.size() == _right.size());
assert(_left.size() == _blendMask.size());
buildPyramids(); //construct Laplacian Pyramid and Gaussian Pyramid
blendLapPyrs(); //blend left & right Pyramids into one Pyramid
};
Mat_<Vec3f> blend() {
return reconstructImgFromLapPyramid();//reconstruct Image from Laplacian Pyramid
}
};
Mat_<Vec3f> LaplacianBlend(const Mat_<Vec3f>& l, const Mat_<Vec3f>& r, const Mat_<float>& m) {
LaplacianBlending lb(l,r,m,4);
return lb.blend();
}
int main()
{
Mat l8u = imread("e:\\testvideo\\left.jpg");
Mat r8u = imread("e:\\testvideo\\right.jpg");
imshow("left",l8u);
imshow("right",r8u);
Mat_<Vec3f> l; l8u.convertTo(l,CV_32F,1.0/255.0);//Vec3f表示有三个通道,即 l[row][column][depth]
Mat_<Vec3f> r; r8u.convertTo(r,CV_32F,1.0/255.0);
/***************** void convertTo( OutputArray m, int rtype, double alpha=1, double beta=0 ) const;******************/
/* Performs linear transformation on every source array element:
dst(x,y,c) = scale*src(x,y,alpha)+beta.
Arbitrary combination of input and output array depths are allowed
(number of channels must be the same), thus the function can be used
for type conversion */
//create blend mask matrix m
Mat_<float> m(l.rows,l.cols,0.0); //将m全部赋值为0
m(Range::all(),Range(0,m.cols/2)) = 1.0; //取m全部行&[0,m.cols/2]列,赋值为1.0
Mat_<Vec3f> blend = LaplacianBlend(l, r, m);
imshow("blended",blend);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
1.图像金字塔
图像金字塔是一个图像集合,集合中所有的图像都来源于同一个原始图像,而且是通过对原始图像的连续降采样获得,直到达到某个终止条件才停止降采样。 常见的两种图像金字塔:
高斯金字塔(Gaussian pyramid): 向下采样图像
拉普拉斯金字塔(Laplacian pyramid):用来从金字塔低层图像中向上采样重建一个图像。
2.图像的向上、向下采样
2.1下采样
下采样使得图像金字塔的层级越高,图像越小。假设每一层都按从下到上的次序编号,层级(i + 1) 的尺寸表示为Gi+1。则由第i层图像获得第i+1层图像的步骤为: 1)将Gi与高斯内核卷积:

2)将所有偶数行和列去除。
经过上诉处理后,获得的结果图像为原来原图的1/4。不断对迭代上诉步骤就可以得到整个图像金字塔。
Mat格式的:
pyrDown( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 )
函数 pyrDown 接受3个参数:
tmp: 当前图像, 初始化为原图像 src 。
dst: 目的图像( 显示图像,为输入图像的一半)
Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ) :目的图像大小, 既然我们是向下采样, pyrDown 期待一个一半于输入图像( tmp)的大小。
注意输入图像的大小(在两个方向)必须是2的冥,否则,将会显示错误。
2.2上采样
上采样使得图像变大。步骤: 1)将图像在每个方向扩大为原来的两倍,新增的行与列以0填充
2)使用先前同样的内核(乘以4)与放大后的图像卷积,获得新增像素的近似值。
注意上采样不是下采样的逆操作。因为下采样是一个丢失图像信息的处理过程。
Mat格式:
pyrUp( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 )
函数 pyrUp 接受了3个参数:
tmp: 当前图像, 初始化为原图像 src 。
dst: 目的图像( 显示图像,为输入图像的两倍)
Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 ) : 目的图像大小, 既然我们是向上采样, pyrUp 期待一个两倍于输入图像( tmp )的大小。
3.拉普拉斯金字塔
降采样操作丢失的信息数据形成了拉普拉斯金字塔。拉普拉斯金字塔的第i层定义为: 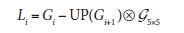
借助于opencv,PyrUp()函数实现的功能就是
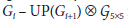
所定义的,所以,可以使用opencv直接进行拉普拉运算:
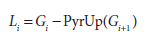
拉普拉斯金字塔与高斯金字塔如下图所示:
4.图像融合
利用高斯金字塔与拉普拉斯金字塔,可以将两幅图像进行融合。具体实现步骤为: 1)每个源图像先被分解成拉普拉斯金字塔(左边列和右边列)
2)建立高斯金字塔。(二值掩膜)
3)每个拉普拉斯金字塔图像乘以相应的高斯掩膜(卷积)
4)进行拼接blendLapPyrs() ; 在每一层上将左右laplacian图像直接拼起来得结果金字塔resultLapPyr。
5)重建图像: 从最高层结果图
//将左右laplacian图像拼成的resultLapPyr金字塔中每一层,从上到下插值放大并和下一层相加,即得blend图像结果(reconstructImgFromLapPyramid)
具体代码:
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace cv;
/************************************************************************/
/* 说明:
*金字塔从下到上依次为 [0,1,...,level-1] 层
*blendMask 为图像的掩模
*maskGaussianPyramid为金字塔每一层的掩模
*resultLapPyr 存放每层金字塔中直接用左右两图Laplacian变换拼成的图像
*/
/************************************************************************/
class LaplacianBlending {
private:
Mat_<Vec3f> left;
Mat_<Vec3f> right;
Mat_<float> blendMask;
vector<Mat_<Vec3f> > leftLapPyr,rightLapPyr,resultLapPyr;//Laplacian Pyramids
Mat leftHighestLevel, rightHighestLevel, resultHighestLevel;
vector<Mat_<Vec3f> > maskGaussianPyramid; //masks are 3-channels for easier multiplication with RGB
int levels;
void buildPyramids() {
buildLaplacianPyramid(left,leftLapPyr,leftHighestLevel);
buildLaplacianPyramid(right,rightLapPyr,rightHighestLevel);
buildGaussianPyramid();
}
void buildGaussianPyramid() {//金字塔内容为每一层的掩模
assert(leftLapPyr.size()>0);
maskGaussianPyramid.clear();
Mat currentImg;
cvtColor(blendMask, currentImg, CV_GRAY2BGR);//store color img of blend mask into maskGaussianPyramid
maskGaussianPyramid.push_back(currentImg); //0-level
currentImg = blendMask;
for (int l=1; l<levels+1; l++) {
Mat _down;
if (leftLapPyr.size() > l)
pyrDown(currentImg, _down, leftLapPyr[l].size());
else
pyrDown(currentImg, _down, leftHighestLevel.size()); //lowest level
Mat down;
cvtColor(_down, down, CV_GRAY2BGR);
maskGaussianPyramid.push_back(down);//add color blend mask into mask Pyramid
currentImg = _down;
}
}
void buildLaplacianPyramid(const Mat& img, vector<Mat_<Vec3f> >& lapPyr, Mat& HighestLevel) {
lapPyr.clear();
Mat currentImg = img;
for (int l=0; l<levels; l++) {
Mat down,up;
pyrDown(currentImg, down);
pyrUp(down, up,currentImg.size());
Mat lap = currentImg - up;
lapPyr.push_back(lap);
currentImg = down;
}
currentImg.copyTo(HighestLevel);
}
Mat_<Vec3f> reconstructImgFromLapPyramid() {
//将左右laplacian图像拼成的resultLapPyr金字塔中每一层
//从上到下插值放大并相加,即得blend图像结果
Mat currentImg = resultHighestLevel;
for (int l=levels-1; l>=0; l--) {
Mat up;
pyrUp(currentImg, up, resultLapPyr[l].size());
currentImg = up + resultLapPyr[l];
}
return currentImg;
}
//Mat::mul执行两个矩阵按元素相乘或这两个矩阵的除法。该方法返回一个用可选的缩放比率编码了每个元素的数组乘法的临时的对象。
void blendLapPyrs() {
//获得每层金字塔中直接用左右两图Laplacian变换拼成的图像resultLapPyr
resultHighestLevel = leftHighestLevel.mul(maskGaussianPyramid.back()) +
rightHighestLevel.mul(Scalar(1.0,1.0,1.0) - maskGaussianPyramid.back());
for (int l=0; l<levels; l++) {
Mat A = leftLapPyr[l].mul(maskGaussianPyramid[l]);
Mat antiMask = Scalar(1.0,1.0,1.0) - maskGaussianPyramid[l];
Mat B = rightLapPyr[l].mul(antiMask);
Mat_<Vec3f> blendedLevel = A + B;
resultLapPyr.push_back(blendedLevel);
}
}
public:
LaplacianBlending(const Mat_<Vec3f>& _left, const Mat_<Vec3f>& _right, const Mat_<float>& _blendMask, int _levels)://construct function, used in LaplacianBlending lb(l,r,m,4);
left(_left),right(_right),blendMask(_blendMask),levels(_levels)
{
assert(_left.size() == _right.size());
assert(_left.size() == _blendMask.size());
buildPyramids(); //construct Laplacian Pyramid and Gaussian Pyramid
blendLapPyrs(); //blend left & right Pyramids into one Pyramid
};
Mat_<Vec3f> blend() {
return reconstructImgFromLapPyramid();//reconstruct Image from Laplacian Pyramid
}
};
Mat_<Vec3f> LaplacianBlend(const Mat_<Vec3f>& l, const Mat_<Vec3f>& r, const Mat_<float>& m) {
LaplacianBlending lb(l,r,m,4);
return lb.blend();
}
int main()
{
Mat l8u = imread("e:\\testvideo\\left.jpg");
Mat r8u = imread("e:\\testvideo\\right.jpg");
imshow("left",l8u);
imshow("right",r8u);
Mat_<Vec3f> l; l8u.convertTo(l,CV_32F,1.0/255.0);//Vec3f表示有三个通道,即 l[row][column][depth]
Mat_<Vec3f> r; r8u.convertTo(r,CV_32F,1.0/255.0);
/***************** void convertTo( OutputArray m, int rtype, double alpha=1, double beta=0 ) const;******************/
/* Performs linear transformation on every source array element:
dst(x,y,c) = scale*src(x,y,alpha)+beta.
Arbitrary combination of input and output array depths are allowed
(number of channels must be the same), thus the function can be used
for type conversion */
//create blend mask matrix m
Mat_<float> m(l.rows,l.cols,0.0); //将m全部赋值为0
m(Range::all(),Range(0,m.cols/2)) = 1.0; //取m全部行&[0,m.cols/2]列,赋值为1.0
Mat_<Vec3f> blend = LaplacianBlend(l, r, m);
imshow("blended",blend);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 拉普拉斯图像融合
- 图像拉普拉斯融合原理
- 图像拉普拉斯金字塔融合(Laplacian Pyramid Blending)
- 图像拉普拉斯金字塔融合(Laplacian Pyramid Blending)
- 图像拉普拉斯金字塔融合(Laplacian Pyramid Blending)
- 图像拉普拉斯金字塔融合(Laplacian Pyramid Blending)
- 图像拉普拉斯金字塔融合(Laplacian Pyramid Blending)
- 图像融合之拉普拉斯融合(laplacian blending)
- 图像拉普拉斯金字塔融合(Laplacian Pyramid Blending)
- 图像拉普拉斯金字塔融合(Laplacian Pyramid Blending)
- (转)拉普拉斯滤波实现图像增强
- opencv 图像融合裁剪
- 图像融合(六)-- 小波融合
- 图像处理之基于高斯金字塔的图像融合
- 图像锐化拉普拉斯vc代码
- 图像处理27:图像融合
- ENVI下的图像融合方法
- 图像融合1
- OpenNI2显示深度、彩色及融合图像
- opencv图像融合c++代码实例及运行结果
