ADB常用命令
2016-09-22 16:29
204 查看
ADB是一个 客户端-服务器端程序, 其中客户端是你用来操作的电脑, 服务器端就是你的android设备。
安卓设备连接pc端,设置模式为USB调试模式,连接成功后cmd下打开adb.exe进行客户端-服务器端的
相关调试。ADB的官方文档的说明信息如下所示:
其中ADB常用命令已经在网上有人总结过,如下所示
以下进行部分测试
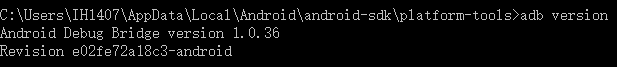
adb verson显示adb版本
安卓设备连接pc端,设置模式为USB调试模式,连接成功后cmd下打开adb.exe进行客户端-服务器端的
相关调试。ADB的官方文档的说明信息如下所示:
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.36
Revision e02fe72a18c3-android
-a - directs adb to listen on all interfaces for a connection
-d - directs command to the only connected USB device
returns an error if more than one USB device is present.
-e - directs command to the only running emulator.
returns an error if more than one emulator is running.
-s <specific device> - directs command to the device or emulator with the given
serial number or qualifier. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL
environment variable.
-p <product name or path> - simple product name like 'sooner', or
a relative/absolute path to a product
out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'.
If -p is not specified, the ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT
environment variable is used, which must
be an absolute path.
-H - Name of adb server host (default: localhost)
-P - Port of adb server (default: 5037)
devices [-l] - list all connected devices
('-l' will also list device qualifiers)
connect <host>[:<port>] - connect to a device via TCP/IP
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
disconnect [<host>[:<port>]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device.
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
Using this command with no additional arguments
will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices.
device commands:
adb push <local>... <remote>
- copy files/dirs to device
adb pull [-a] <remote>... <local>
- copy files/dirs from device
(-a preserves file timestamp and mode)
adb sync [ <directory> ] - copy host->device only if changed
(-l means list but don't copy)
adb shell [-e escape] [-n] [-Tt] [-x] [command]
- run remote shell command (interactive shell if no command given)
(-e: choose escape character, or "none"; default '~')
(-n: don't read from stdin)
(-T: disable PTY allocation)
(-t: force PTY allocation)
(-x: disable remote exit codes and stdout/stderr separation)
adb emu <command> - run emulator console command
adb logcat [ <filter-spec> ] - View device log
adb forward --list - list all forward socket connections.
the format is a list of lines with the following format:
<serial> " " <local> " " <remote> "\n"
adb forward <local> <remote> - forward socket connections
forward specs are one of:
tcp:<port>
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
dev:<character device name>
jdwp:<process pid> (remote only)
adb forward --no-rebind <local> <remote>
- same as 'adb forward <local> <remote>' but fails
if <local> is already forwarded
adb forward --remove <local> - remove a specific forward socket connection
adb forward --remove-all - remove all forward socket connections
adb reverse --list - list all reverse socket connections from device
adb reverse <remote> <local> - reverse socket connections
reverse specs are one of:
tcp:<port>
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
adb reverse --no-rebind <remote> <local>
- same as 'adb reverse <remote> <local>' but fails
if <remote> is already reversed.
adb reverse --remove <remote>
- remove a specific reversed socket connection
adb reverse --remove-all - remove all reversed socket connections from device
adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport
adb install [-lrtsdg] <file>
- push this package file to the device and install it
(-l: forward lock application)
(-r: replace existing application)
(-t: allow test packages)
(-s: install application on sdcard)
(-d: allow version code downgrade (debuggable packages only))
(-g: grant all runtime permissions)
adb install-multiple [-lrtsdpg] <file...>
- push this package file to the device and install it
(-l: forward lock application)
(-r: replace existing application)
(-t: allow test packages)
(-s: install application on sdcard)
(-d: allow version code downgrade (debuggable packages only))
(-p: partial application install)
(-g: grant all runtime permissions)
adb uninstall [-k] <package> - remove this app package from the device
('-k' means keep the data and cache directories)
adb bugreport [<zip_file>] - return all information from the device
that should be included in a bug report.
adb backup [-f <file>] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] [<packages...>]
- write an archive of the device's data to <file>.
If no -f option is supplied then the data is written
to "backup.ab" in the current directory.
(-apk|-noapk enable/disable backup of the .apks themselves
in the archive; the default is noapk.)
(-obb|-noobb enable/disable backup of any installed apk expansion
(aka .obb) files associated with each application; the default
is noobb.)
(-shared|-noshared enable/disable backup of the device's
shared storage / SD card contents; the default is noshared.)
(-all means to back up all installed applications)
(-system|-nosystem toggles whether -all automatically includes
system applications; the default is to include system apps)
(<packages...> is the list of applications to be backed up. If
the -all or -shared flags are passed, then the package
list is optional. Applications explicitly given on the
command line will be included even if -nosystem would
ordinarily cause them to be omitted.)
adb restore <file> - restore device contents from the <file> backup archive
adb disable-verity - disable dm-verity checking on USERDEBUG builds
adb enable-verity - re-enable dm-verity checking on USERDEBUG builds
adb keygen <file> - generate adb public/private key. The private key is stored in <file>,
and the public key is stored in <file>.pub. Any existing files
are overwritten.
adb help - show this help message
adb version - show version num
scripting:
adb wait-for[-<transport>]-<state>
- wait for device to be in the given state:
device, recovery, sideload, or bootloader
Transport is: usb, local or any [default=any]
adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - prints: <serial-number>
adb get-devpath - prints: <device-path>
adb remount - remounts the /system, /vendor (if present) and /oem (if present) partitions on the device read-write
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery]
- reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program.
adb reboot sideload - reboots the device into the sideload mode in recovery program (adb root required).
adb reboot sideload-auto-reboot
- reboots into the sideload mode, then reboots automatically after the sideload regardless of the result.
adb sideload <file> - sideloads the given package
adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions
adb unroot - restarts the adbd daemon without root permissions
adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB
adb tcpip <port> - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port
networking:
adb ppp <tty> [parameters] - Run PPP over USB.
Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection.
<tty> refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
adb sync notes: adb sync [ <directory> ]
<localdir> can be interpreted in several ways:
- If <directory> is not specified, /system, /vendor (if present), /oem (if present) and /data partitions will be updated.
- If it is "system", "vendor", "oem" or "data", only the corresponding partition
is updated.
internal debugging:
adb reconnect Kick current connection from host side and make it reconnect.
adb reconnect device Kick current connection from device side and make it reconnect.
environment variables:
ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values
1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given.
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed.其中ADB常用命令已经在网上有人总结过,如下所示
adb -d 当Android手机用USB连接计算机时可通过adb-d对该装置下命令 adb -e对正在运行的仿真器下指令 adb -s指定仿真器序号 adb dervices显示当前启动的仿真器装置序号 adb help显示adb指令用法 adb pull下载文件或目录(adb pull 文件所在手机的位置即文件名 目的位置) adb logcat监控仿真器运行记录 adb bugreport生成adb出错报告 adb start-server启动adb服务器 adb kill-server关闭adb服务器 adb get-state取得adb服务器运行状态 adb get-serialno获得仿真器运行序号 adb forward tcp:port更改仿真器的网络TCP通信端口
以下进行部分测试
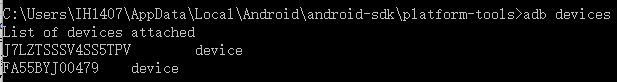
adb dervices显示当前启动的仿真器装置序号,下图中可以看到有两台手机设备。

adb verson显示adb版本

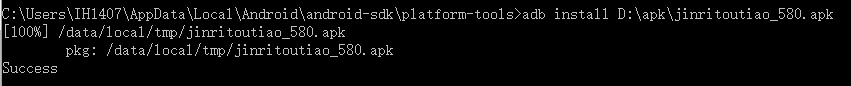
adb install安装APK应用程序组件

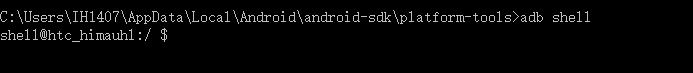
adb shell进入Android系统命令行模式,因为安卓的linux使用的shell与PC端linux系统的shell不同,所以大多数命令 也无法使用,如果手机root了可以使用的命令相对会多一些。


adb push上传文件或目录(adb push 文件所在PC的位置即文件名 目的位置)
相关文章推荐
- android 常用adb 及linux 命令
- Android常用的几个adb命令
- Android 中查看内存的使用情况集常用adb命令
- Android 常用adb命令及部分Linux命令2015.01.28
- Android adb 常用命令学习
- Android adb 常用命令
- adb 常用命令
- 常用的dos命令部分与android用的adb命令
- adb常用命令
- Android ADB常用命令整理
- adb 常用命令大全
- Ubuntu下adb环境配置及常用命令
- adb 常用命令
- adb的原理以及adb常用命令的介绍
- linux 常用命令adb
- Android常用ADB命令
- Android系统开发常用shell命令汇总+vim中复制操作+adb logcat过滤
- Android 常用的ADB 命令
- adb常用命令笔记
- android一些常用的adb命令
