C++ STL——hash/unordered_set/c++11关键字decltype
2016-09-01 11:43
573 查看
摘自MSDN,以VS2012版为主
1、hash类模板
定义如下:
[cpp] view
plain copy


template<class Ty>
struct hash
: public unary_function<Ty, size_t> {
size_t operator()(Ty _Val) const;
};
并给出一个例子:
[cpp] view
plain copy


// std_tr1__functional__hash.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
int main()
{
std::unordered_set<int, std::hash<int> > c0;
c0.insert(3);
std::cout << *c0.find(3) << std::endl;
return (0);
}
输出结果3
2.unordered_set类模板
定义:
[cpp] view
plain copy


template<class Key,
class Hash = std::hash<Key>,
class Pred = std::equal_to<Key>,
class Alloc = std::allocator<Key> >
class unordered_set;
结合第一个例子说明一下,
unordered_set是c++11引入的散列容器,在没有冲突的情况下,时间复杂度是常数时间。内部通过hash函数进行弱排序。
在说明unordered_set之前,先说明hash函数。
hash,百度百科中翻译为"散列"或者”哈希“,其通过一个hash函数,建立一个散列表,举个例子:
假设 (员工 工资); zhao 3550;qian 4600;sun 4300;zhai 5210
设计一个hash函数,姓对应其首字母的ascii码,即zhao(Z)-90,qian(Q)-81,sun(S)-83,zhai(Z)-90
这就是所谓的 h(key)=value,h表示hash函数
这里第一个和第四个冲突,把第四个存在第一个旁边
开辟一个大小为200的数组H,H[90]=3550;H[81]=4600;H[83]=4300;H[91]=5210;
这种做法效率极其低下,但在没有冲突情况下是常数运行时间。
实际中,内存中是这么存储的,separate chaining:
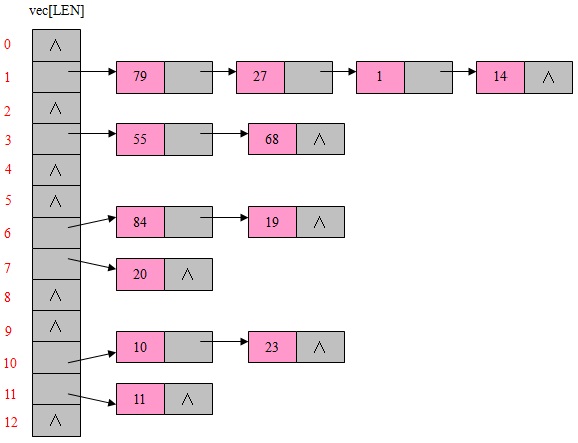
LEN表示这个vec长度,可以看出一个vector,每个vec[i]暂且称为一个node,每个node后面一串叫做buckets,每个buckets是可变大小。
在回过头,讲unordered_set
[cpp] view
plain copy


std::unordered_set<int, std::hash<int> > c0;
hash<int>是一个实例化后的函数类
文章开头,
[cpp] view
plain copy


size_t operator()(Ty _Val) const;
实际上是对运算符()重载
[cpp] view
plain copy


*c0.find(3)
相当于
[cpp] view
plain copy


*(c0.find(3))
说明find()之前,需要了解equal_range;
equal_range:返回一个pair,即[X.first, X.second) ,其中X的是迭代器,限制了key的范围
[cpp] view
plain copy
std::pair<iterator, iterator>
equal_range(const Key& keyval);
std::pair<const_iterator, const_iterator>
equal_range(const Key& keyval) const;
[cpp] view
plain copy
// std_tr1__unordered_set__unordered_set_equal_range.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <unordered_set>
#include <iostream>
typedef std::unordered_set<char> Myset;
int main()
{
Myset c1;
c1.insert('a');
c1.insert('b');
c1.insert('c');
// display contents " [c] [a]"
for (Myset::const_iterator it = c1.begin();
it != c1.end(); ++it)
std::cout << " [" << *it << "]";
std::cout << std::endl;
// display results of failed search
std::pair<Myset::iterator, Myset::iterator> pair1 =
c1.equal_range('x');
std::cout << "equal_range('x'):";
for (; pair1.first != pair1.second; ++pair1.first)
std::cout << " [" << *pair1.first << "]";
std::cout << std::endl;
// display results of successful search
pair1 = c1.equal_range('b');
std::cout << "equal_range('b'):";
for (; pair1.first != pair1.second; ++pair1.first)
std::cout << " [" << *pair1.first << "]";
std::cout << std::endl;
return (0);
}
结果:
[a] [b] [c]
equal_range('x'):
equal_range('b'): [b]
再看一个find的例子
[b][cpp] view
plain copy
const_iterator find(const Key& keyval) const;
find返回 unordered_set::equal_range(keyval).first
[cpp] view
plain copy
// std_tr1__unordered_set__unordered_set_find.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <unordered_set>
#include <iostream>
typedef std::unordered_set<char> Myset;
int main()
{
Myset c1;
c1.insert('a');
c1.insert('b');
c1.insert('c');
// display contents " [c] [a]"
// 我用VS2012编译是" [a] [b] [c]"
for (Myset::const_iterator it = c1.begin();
it != c1.end(); ++it)
std::cout << " [" << *it << "]";
std::cout << std::endl;
// try to find and fail
std::cout << "find('A') == "
<< std::boolalpha << (c1.find('A') != c1.end()) << std::endl;
// try to find and succeed
Myset::iterator it = c1.find('b');
std::cout << "find('b') == "
<< std::boolalpha << (it != c1.end())
<< ": [" << *it << "]" << std::endl;
return (0);
}
结果:
[a] [b] [c]
find('A')==false
find('b')==true: [b]
要注意的是:
[b][cpp] view
plain copy
c1.end()
不指向最后一个元素,而指向最后一个元素再+1,当find不到输入的元素时候,返回迭代器就指向这个end()
更复杂的代码分析:
[cpp] view
plain copy


#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
size_t hash_function_pair_int(pair<int, int> p)
{
return hash<int>()(p.first - p.second);
}
typedef unordered_set < pair<int, int>, decltype(hash_function_pair_int)* > set_pair_int;
void main()
{
set_pair_int boundEdge(10,hash_function_pair_int);
pair<int,int> f0(4,3),f1(3,1),f2(3,2),f3(3,2);
boundEdge.insert(f0);
boundEdge.insert(f1);
boundEdge.insert(f2);
boundEdge.insert(f3);
}
关键字decltype自动推断表达式类型;
hash<int>()是一个匿名对象,
[cpp] view
plain copy


hash<int>()(p.first - p.second)
后面第二个()是操作符重载,输入参数是pair的first和second的差
1、hash类模板
定义如下:
[cpp] view
plain copy

template<class Ty>
struct hash
: public unary_function<Ty, size_t> {
size_t operator()(Ty _Val) const;
};
并给出一个例子:
[cpp] view
plain copy

// std_tr1__functional__hash.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
int main()
{
std::unordered_set<int, std::hash<int> > c0;
c0.insert(3);
std::cout << *c0.find(3) << std::endl;
return (0);
}
输出结果3
2.unordered_set类模板
定义:
[cpp] view
plain copy

template<class Key,
class Hash = std::hash<Key>,
class Pred = std::equal_to<Key>,
class Alloc = std::allocator<Key> >
class unordered_set;
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
| Key | The key type. |
| Hash | The hash function object type. |
| Pred | The equality comparison function object type. |
| Alloc | The allocator class. |
unordered_set是c++11引入的散列容器,在没有冲突的情况下,时间复杂度是常数时间。内部通过hash函数进行弱排序。
在说明unordered_set之前,先说明hash函数。
hash,百度百科中翻译为"散列"或者”哈希“,其通过一个hash函数,建立一个散列表,举个例子:
假设 (员工 工资); zhao 3550;qian 4600;sun 4300;zhai 5210
设计一个hash函数,姓对应其首字母的ascii码,即zhao(Z)-90,qian(Q)-81,sun(S)-83,zhai(Z)-90
这就是所谓的 h(key)=value,h表示hash函数
这里第一个和第四个冲突,把第四个存在第一个旁边
开辟一个大小为200的数组H,H[90]=3550;H[81]=4600;H[83]=4300;H[91]=5210;
这种做法效率极其低下,但在没有冲突情况下是常数运行时间。
实际中,内存中是这么存储的,separate chaining:

LEN表示这个vec长度,可以看出一个vector,每个vec[i]暂且称为一个node,每个node后面一串叫做buckets,每个buckets是可变大小。
在回过头,讲unordered_set
[cpp] view
plain copy

std::unordered_set<int, std::hash<int> > c0;
hash<int>是一个实例化后的函数类
文章开头,
[cpp] view
plain copy

size_t operator()(Ty _Val) const;
实际上是对运算符()重载
[cpp] view
plain copy

*c0.find(3)
相当于
[cpp] view
plain copy

*(c0.find(3))
说明find()之前,需要了解equal_range;
equal_range:返回一个pair,即[X.first, X.second) ,其中X的是迭代器,限制了key的范围
[cpp] view
plain copy
std::pair<iterator, iterator>
equal_range(const Key& keyval);
std::pair<const_iterator, const_iterator>
equal_range(const Key& keyval) const;
[cpp] view
plain copy
// std_tr1__unordered_set__unordered_set_equal_range.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <unordered_set>
#include <iostream>
typedef std::unordered_set<char> Myset;
int main()
{
Myset c1;
c1.insert('a');
c1.insert('b');
c1.insert('c');
// display contents " [c] [a]"
for (Myset::const_iterator it = c1.begin();
it != c1.end(); ++it)
std::cout << " [" << *it << "]";
std::cout << std::endl;
// display results of failed search
std::pair<Myset::iterator, Myset::iterator> pair1 =
c1.equal_range('x');
std::cout << "equal_range('x'):";
for (; pair1.first != pair1.second; ++pair1.first)
std::cout << " [" << *pair1.first << "]";
std::cout << std::endl;
// display results of successful search
pair1 = c1.equal_range('b');
std::cout << "equal_range('b'):";
for (; pair1.first != pair1.second; ++pair1.first)
std::cout << " [" << *pair1.first << "]";
std::cout << std::endl;
return (0);
}
结果:
[a] [b] [c]
equal_range('x'):
equal_range('b'): [b]
再看一个find的例子
[b][cpp] view
plain copy
const_iterator find(const Key& keyval) const;
find返回 unordered_set::equal_range(keyval).first
[cpp] view
plain copy
// std_tr1__unordered_set__unordered_set_find.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <unordered_set>
#include <iostream>
typedef std::unordered_set<char> Myset;
int main()
{
Myset c1;
c1.insert('a');
c1.insert('b');
c1.insert('c');
// display contents " [c] [a]"
// 我用VS2012编译是" [a] [b] [c]"
for (Myset::const_iterator it = c1.begin();
it != c1.end(); ++it)
std::cout << " [" << *it << "]";
std::cout << std::endl;
// try to find and fail
std::cout << "find('A') == "
<< std::boolalpha << (c1.find('A') != c1.end()) << std::endl;
// try to find and succeed
Myset::iterator it = c1.find('b');
std::cout << "find('b') == "
<< std::boolalpha << (it != c1.end())
<< ": [" << *it << "]" << std::endl;
return (0);
}
结果:
[a] [b] [c]
find('A')==false
find('b')==true: [b]
要注意的是:
[b][cpp] view
plain copy
c1.end()
不指向最后一个元素,而指向最后一个元素再+1,当find不到输入的元素时候,返回迭代器就指向这个end()
更复杂的代码分析:
[cpp] view
plain copy

#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
size_t hash_function_pair_int(pair<int, int> p)
{
return hash<int>()(p.first - p.second);
}
typedef unordered_set < pair<int, int>, decltype(hash_function_pair_int)* > set_pair_int;
void main()
{
set_pair_int boundEdge(10,hash_function_pair_int);
pair<int,int> f0(4,3),f1(3,1),f2(3,2),f3(3,2);
boundEdge.insert(f0);
boundEdge.insert(f1);
boundEdge.insert(f2);
boundEdge.insert(f3);
}
关键字decltype自动推断表达式类型;
hash<int>()是一个匿名对象,
[cpp] view
plain copy

hash<int>()(p.first - p.second)
后面第二个()是操作符重载,输入参数是pair的first和second的差
相关文章推荐
- C++ STL 之 unordered_set 介绍
- C++ STL 之 unordered_set 介绍
- STL unordered_map(hash_map)详解
- 例说数据结构&STL(十)——hash_set/unordered_set
- C++ STL unordered_map介绍与使用方法
- 例说数据结构&STL(十一)——hash_map/unordered_map
- c++ unordered_map/set自定义对象的hash
- C++ STL 之 unordered_set 介绍
- STL hash table, Unordered Contains
- STL容器分析--unordered_map/unordered_set(C++11)
- C++ STL hash_map
- C++ STL中哈希表 hash_map介绍
- Linux下map、hash_map和unordered_map效率比较
- Linux下map hash_map和unordered_map效率比较
- C++ STL中哈希表 hash_map介绍
- c++ unordered_map compiling issue with g++
- C++ unordered_map
- C++ unordered Associative Containers(C++11)
- STL set multiset map multimap unordered_set unordered_map example
- STL set multiset map multimap unordered_set unordered_map example
