Linux Linux程序练习四
2016-08-28 22:15
246 查看
编写两个不同的可执行程序,名称分别为a和b,b为a的子进程。 在a程序中调用open函数打开a.txt文件。 在b程序不可以调用open或者fopen,只允许调用read函数来实现读取a.txt文件。 (a程序中可以使用 fork与execve函数创建子进程)。
a程序
//fork共享文件标识符
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int arg, char * args[])
{
pid_t child=0;
int status;
child=fork();
if(child==-1)
{
printf("system is game over\n");
return -1;
}
//open the file in read mode
int fd=open("a.txt",O_RDONLY);
if(fd==-1)
{
printf("open the file failed ! \n error msg:%s",strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
if(child==0)
{
char buf[10]={0};
sprintf(buf,"%d",fd);
char * argv[]={"../2/tec",buf,NULL};
execve("../2/tec",argv,NULL);
}else
{
//父进程中关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
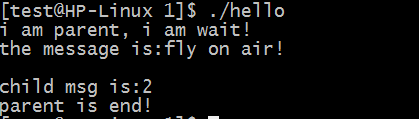
printf("i am parent, i am wait!\n");
wait(&status);
printf("child msg is:%d\n",WEXITSTATUS(status));
printf("parent is end!\n");
}
return 0;
}b程序
//execve共享文件标识符
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(int arg, char * args[])
{
if(arg<2)
{
printf("请输入一个参数!\n");
return -1;
}
int fd=atoi(args[1]);
if(fd<3)
{
printf("缺少文件标识符!\n");
return -1;
}
//read the file
char buf[50]={0};
read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("the message is:%s\n",buf);
//关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return 2;
}
相关文章推荐
- 随手写了一个linux服务端与window客户端的epoll程序,当做练习把。
- linux后台服务程序练习开发
- Linux练习(处理程序命令行参数)
- Linux_C练习:编写一个程序,求出满足下列条件的四位数:该数是个完全平方数,且第一、三位数字之和为10,第二、四位数字之积为12;
- Linux_C练习:设计一个洗牌发牌的程序;(随机产生52个不同的数)
- linux 每日一练习:父程序与子程序的概念
- Linux Linux程序练习十三(信号阻塞,捕获)
- Linux Linux程序练习十(网络编程大文件发送)
- linux的基本命令及vim程序编辑器的练习
- linux 练习五 如何生成库.so及被C和C++程序可用
- 随手写了一个linux服务端与window客户端的epoll程序,当做练习把。
- Linux Linux程序练习九
- Linux Linux程序练习十五(进程间的通信共享内存版)
- Linux C程序练习(4)进程通信之信号量、共享内存
- Linux Linux程序练习八
- Linux Linux程序练习十八
- 有时间练习下linux下的queue.h这个程序
- Linux Linux程序练习六
- Linux C程序练习(3)进程通信之pipe、fifo、消息队列
- Linux Linux程序练习十四(多进程压力测试)
