Java中的动态接口实现
2016-08-16 19:56
344 查看
应用场景举例:
我们有这样的应用场景, 我们有个接口, 接口中有若干方法, 然而我们并不行让这若干方法在同一个线程中执行 , 或者说, 只有在我们具体去实现这个接口的时候才去判断我们具体的哪个方法在哪个线程中使用
(这个案例, 说得是判断我们的接口方法在哪个线程中使用, 当然我们不一定只能解决这一个问题, 这种类似的问题, 都可以使用动态接口来实现)
简单分析
我们需要用到注解和反射机制, 自定义两个注解, 用来分别标示我们的方法(具体实现接口的方法) 是在哪个线程中运行.例如标示当前线程和子线程
实现接口, 并用1中自定义的注解去表示每个方法该在哪个线程中使用
新建工具类Util用反射机制获取到, 方法上的注解, 然后具体让每个方法如何如何执行……
上代码
两个注解类
接口
具体实现类
动态接口工具类
测试类
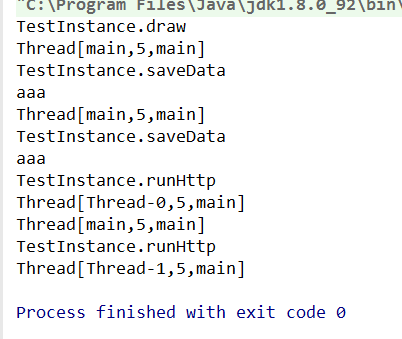
执行结果
我们有这样的应用场景, 我们有个接口, 接口中有若干方法, 然而我们并不行让这若干方法在同一个线程中执行 , 或者说, 只有在我们具体去实现这个接口的时候才去判断我们具体的哪个方法在哪个线程中使用
(这个案例, 说得是判断我们的接口方法在哪个线程中使用, 当然我们不一定只能解决这一个问题, 这种类似的问题, 都可以使用动态接口来实现)
简单分析
我们需要用到注解和反射机制, 自定义两个注解, 用来分别标示我们的方法(具体实现接口的方法) 是在哪个线程中运行.例如标示当前线程和子线程
实现接口, 并用1中自定义的注解去表示每个方法该在哪个线程中使用
新建工具类Util用反射机制获取到, 方法上的注解, 然后具体让每个方法如何如何执行……
上代码
两个注解类
/**
* Project: Day13
* Created: Lulu
* Date: 2016/8/12
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface CurrentThread {
}/**
* Project: Day13
* Created: Lulu
* Date: 2016/8/12
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SubThread {
}接口
/**
* Project: Day13
* Created: Lulu
* Date: 2016/8/12
*/
public interface TestInter {
void runHttp();
void saveData(String data);
void draw();
}具体实现类
/**
* Project: Day13
* Created: Lulu
* Date: 2016/8/12
*/
public class TestInstance implements TestInter {
@Override
@SubThread
public void runHttp() {
System.out.println("TestInstance.runHttp");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
}
@Override
@SubThread
public void saveData(String data) {
System.out.println("TestInstance.saveData");
System.out.println(data);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
}
@Override
@CurrentThread
public void draw() {
System.out.println("TestInstance.draw");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
}
}动态接口工具类
/**
* Project: Day13
* Created: Lulu
* Date: 2016/8/12
*/
/*
动态接口实现
*/
public class Util {
public static <T> T getInstance(Class<T> cl, Object instance) {
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(),
new Class[]{cl},
new MyHandler(instance)
);
return (T) o;
}
private static class MyHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object instance;
public MyHandler(Object instance) {
this.instance = instance;
}
/*
无论调用动态接口的任何方法都会调用invoke方法
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Method method1 = instance.getClass().getMethod(method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes());
CurrentThread currentThread = method1.getAnnotation(CurrentThread.class);
if (currentThread != null) {
method1.invoke(instance, args);
}
SubThread subThread = method1.getAnnotation(SubThread.class);
if (subThread != null) {
method1.invoke(instance, args);
}
if (subThread != null) {
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
try {
method1.invoke(instance, args);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
}
return null;
}
}
}测试类
/**
* Project: Day13
* Created: Lulu
* Date: 2016/8/12
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestInter instance = Util.getInstance(
TestInter.class , new TestInstance());
instance.draw();
instance.saveData("aaa");
instance.runHttp();
}
}执行结果

相关文章推荐
- java动态代理--代理接口无实现类
- java动态代理--代理接口无实现类
- Java动态代理实现接口方法
- Java动态获取某个接口下所有的实现类对象集合
- java反射和动态代理实现接口记录
- 【Java接口实现动态加载不同的类】
- Java中如何动态创建接口的实现方法
- java中通过接口实现自定义事件,动态设定行为
- java动态代理--代理接口无实现类
- JAVA学习笔记Day25——动态接口的实现
- Java中如何动态创建接口的实现
- Java动态获取某个接口下所有的实现类对象集合
- Java动态获取某个接口下所有的实现类对象集合
- java 动态实现接口
- Java中如何动态创建接口的实现
- Java动态代理实现接口invocationHandler
- java动态代理--代理接口无实现类
- Java中如何动态创建接口的实现
- java动态代理2 (cglib 不用实现接口)
