POJ 1149-PIGS(Ford-Fulkerson 标号法求网络最大流)
2016-08-15 16:17
597 查看
PIGS
Description
Mirko works on a pig farm that consists of M locked pig-houses and Mirko can't unlock any pighouse because he doesn't have the keys. Customers come to the farm one after another. Each of them has keys to some pig-houses and wants to buy a certain number of
pigs.
All data concerning customers planning to visit the farm on that particular day are available to Mirko early in the morning so that he can make a sales-plan in order to maximize the number of pigs sold.
More precisely, the procedure is as following: the customer arrives, opens all pig-houses to which he has the key, Mirko sells a certain number of pigs from all the unlocked pig-houses to him, and, if Mirko wants, he can redistribute the remaining pigs across
the unlocked pig-houses.
An unlimited number of pigs can be placed in every pig-house.
Write a program that will find the maximum number of pigs that he can sell on that day.
Input
The first line of input contains two integers M and N, 1 <= M <= 1000, 1 <= N <= 100, number of pighouses and number of customers. Pig houses are numbered from 1 to M and customers are numbered from 1 to N.
The next line contains M integeres, for each pig-house initial number of pigs. The number of pigs in each pig-house is greater or equal to 0 and less or equal to 1000.
The next N lines contains records about the customers in the following form ( record about the i-th customer is written in the (i+2)-th line):
A K1 K2 ... KA B It means that this customer has key to the pig-houses marked with the numbers K1, K2, ..., KA (sorted nondecreasingly ) and that he wants to buy B pigs. Numbers A and B can be equal to 0.
Output
The first and only line of the output should contain the number of sold pigs.
Sample Input
Sample Output
Source
Croatia OI 2002 Final Exam - First day
每个顾客有A把钥匙,对应A个猪圈的编号,每个顾客会买B头猪。
Mark木有猪圈的钥匙,每个顾客来的时候把他们有钥匙的猪圈全部打开;而且Mark可以重新分配被打开的猪圈里面的猪。
顾客离开后,猪圈再次被锁上。
求Mark能卖出的猪的最大值。
除了顾客的N个顶点外,自己增加源点和汇点这两个点。
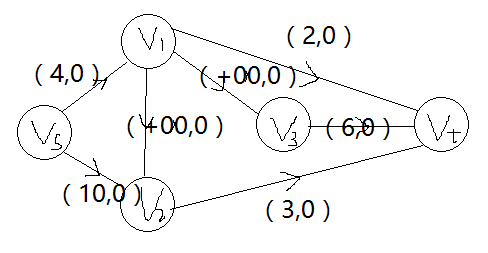
每个顾客购买的数目是连接到汇点上的容量;
源点与每个猪圈的第一个顾客连边,边的容量是开始时猪圈中猪的数目;
若源点与某个结点之间有重边,将权合并(如上图中Vs~V1,4就是合并了1和3);
若顾客j紧跟i后面打开猪圈,那么<i,j>容量为正无穷(因为此时可以随意调整猪圈中的猪的数量)。
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 20029 | Accepted: 9178 |
Mirko works on a pig farm that consists of M locked pig-houses and Mirko can't unlock any pighouse because he doesn't have the keys. Customers come to the farm one after another. Each of them has keys to some pig-houses and wants to buy a certain number of
pigs.
All data concerning customers planning to visit the farm on that particular day are available to Mirko early in the morning so that he can make a sales-plan in order to maximize the number of pigs sold.
More precisely, the procedure is as following: the customer arrives, opens all pig-houses to which he has the key, Mirko sells a certain number of pigs from all the unlocked pig-houses to him, and, if Mirko wants, he can redistribute the remaining pigs across
the unlocked pig-houses.
An unlimited number of pigs can be placed in every pig-house.
Write a program that will find the maximum number of pigs that he can sell on that day.
Input
The first line of input contains two integers M and N, 1 <= M <= 1000, 1 <= N <= 100, number of pighouses and number of customers. Pig houses are numbered from 1 to M and customers are numbered from 1 to N.
The next line contains M integeres, for each pig-house initial number of pigs. The number of pigs in each pig-house is greater or equal to 0 and less or equal to 1000.
The next N lines contains records about the customers in the following form ( record about the i-th customer is written in the (i+2)-th line):
A K1 K2 ... KA B It means that this customer has key to the pig-houses marked with the numbers K1, K2, ..., KA (sorted nondecreasingly ) and that he wants to buy B pigs. Numbers A and B can be equal to 0.
Output
The first and only line of the output should contain the number of sold pigs.
Sample Input
3 3 3 1 10 2 1 2 2 2 1 3 3 1 2 6
Sample Output
7
Source
Croatia OI 2002 Final Exam - First day
题目意思:
有M个猪圈,N个顾客,给出每个猪圈中猪的数目。每个顾客有A把钥匙,对应A个猪圈的编号,每个顾客会买B头猪。
Mark木有猪圈的钥匙,每个顾客来的时候把他们有钥匙的猪圈全部打开;而且Mark可以重新分配被打开的猪圈里面的猪。
顾客离开后,猪圈再次被锁上。
求Mark能卖出的猪的最大值。
解题思路:
Ford-Fulkerson 标号法求网络最大流。除了顾客的N个顶点外,自己增加源点和汇点这两个点。

每个顾客购买的数目是连接到汇点上的容量;
源点与每个猪圈的第一个顾客连边,边的容量是开始时猪圈中猪的数目;
若源点与某个结点之间有重边,将权合并(如上图中Vs~V1,4就是合并了1和3);
若顾客j紧跟i后面打开猪圈,那么<i,j>容量为正无穷(因为此时可以随意调整猪圈中的猪的数量)。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#define maxn 1010
#define INF 0xfffffff
using namespace std;
struct ArcType
{
int c,f;//容量、流量
};
ArcType edge[maxn][maxn];
int n,m;//顶点数、弧数
int s,t;
int flag[maxn];//顶点状态:-1——未标号;0——已标号未检查;1——已标号已检查
int prev[maxn];//标号的第一个分量:指明标号从哪个顶点而来,以便找出可改进量
int alpha[maxn];//标号的第二个分量:可改进量α
int que[maxn];//相当于BFS中的队列
int v;//队列头元素
int qs,qe;//队首队尾的位置
int i,j;
void ford()//标号法求网络最大流
{
int flow[maxn][maxn];//节点之间的流量Fij
int prev[maxn];//可改进路径上前一个节点的标号,相当于标号的第一个分量
int minflow[maxn];//每个顶点的可改进量α,相当于标号的第二个分量
int que[maxn];
int qs,qe;//队列首尾位置坐标
int v,p;//当前顶点、保存Cij-Fij
for(i=0; i<maxn; ++i)
for(j=0; j<maxn; ++j)
flow[i][j]=0;
minflow[0]=INF;//源点标号的第二分量为无穷大
while(1)//标号法
{
for(i=0; i<maxn; ++i)//每次标号前,每个顶点重新回到未标号状态
prev[i]=-2;
prev[0]=-1;
qs=0;
que[qs]=0;//源点入队
qe=1;
while(qs<qe&&prev[t]==-2)
{
v=que[qs];//取队列头节点
++qs;
for(i=0; i<t+1; ++i)//prev[i]==-2表示顶点i未标号
if(prev[i]==-2&&(p=edge[v][i].c-flow[v][i]))//edge[v][i].c-flow[v][i]!=0能保证i是v邻接顶点且能进行标号
{
prev[i]=v;
que[qe]=i;
++qe;
minflow[i]=(minflow[v]<p)?minflow[v]:p;
}
}
if(prev[t]==-2) break;//汇点t无标号,标号法结束
for(i=prev[t],j=t; i!=-1; j=i,i=prev[i])//调整过程
{
flow[i][j]+=minflow[t];
flow[j][i]=-flow[i][j];
}
}
for(i=0,p=0; i<t; ++i)//统计进入汇点的流量即最大流的流量
p+=flow[i][t];
cout<<p<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin>>m>>n;//顶点个数、弧数
s=0,t=n+1;//源点和汇点
int pig[maxn],last[maxn];//每个猪圈中猪的数量、每个猪圈前一个顾客的序号
memset(last,0,sizeof(last));
for(i=1; i<=m; ++i)
cin>>pig[i];//输入每个猪圈中猪的数量
for(i=1; i<=n; ++i)
{
int num;
cin>>num;//拥有的猪圈钥匙数量
for(j=0; j<num; ++j)
{
int k;
cin>>k;//钥匙编号
if(last[k]==0)
edge[s][i].c+=pig[k];
else edge[last[k]][i].c=INF;
last[k]=i;
}
cin>>edge[i][t].c;
edge[i][t].f=0;
}
n+=2;//加上源点和汇点
ford();
return 0;
}
/*
3 3 3 1 10 2 1 2 2 2 1 3 3 1 2 6
*/
相关文章推荐
- [笔记] 网络流-最大流 POJ-1273\HDU-4240
- Ford-Fulkerson 标号法求网络最大流
- Poj 1149 PIGS【最大流Dinic+建图】
- 网络最大流中一般增广路算法(标号法)
- POJ-1149 PIGS
- 【POJ 1149 PIGS】网络流 & 合并节点简化构图 & Dinic算法
- POJ1149_PIGS_网络流
- Http报文头部
- tcp_tw_reuse、tcp_tw_recycle 使用场景及注意事项
- 使用libpcap获取http报文
- https://github.com/chenghuige/tensorflow-exp/blob/master/examples/sparse-tensor-classification/
- CentOS 配置网络yum源
- linux上安装apache以及httpd.conf基本配置
- 内网和外网
- Little Endian, Big Endian, 网络字节序
- 使用Java发送HTTP发送POST、GET请求
- 美军网络司令部未来六年之六大预测
- Wireshark基本介绍和学习TCP三次握手
- SDN的今生与未来: 10年发展看10大趋势
- Theano入门神经网络(四)
