Android-View宽高测量研究
2016-08-14 21:39
316 查看
前言
平时写自定义控件包括之前写下拉刷新库的时候,有时候都需要预先知道View的宽度或者高度,这样能够帮助我们很好地实现效果,但是我们都或多或少知道View的度量和绘制是立刻完成的操作,所以当我初始化一个View之后,是无法立刻拿到它的宽度和高度值的,这时候去google一下,网友就会告诉你,用measure()方法调用一下,就可以获取了,于是急急忙忙把代码段从其他地方copy来使用,就这样不知道解决了多少次我的问题。 但是,用了那么多次,我只是知道它是这么“救急”,却不知道它是如何工作的,现在趁着晚上有空,我研究了一下。View.measure() 方法测量宽高
先来了解View.MeasureSpec
Google官方对其解释:A MeasureSpec encapsulates the layout requirements passed from parent to child. Each MeasureSpec represents a requirement for either the width or the height. A MeasureSpec is comprised of a size and a mode. There are three possible modes: UNSPECIFIED The parent has not imposed any constraint on the child. It can be whatever size it wants. //父布局不对子View做任何约束,子View的大小能由自己决定。 EXACTLY The parent has determined an exact size for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless of how big it wants to be. //父布局对子View给出精确大小,子View将会被这些边界限制而不管它自己想要多大。 AT_MOST The child can be as large as it wants up to the specified size. MeasureSpecs are implemented as ints to reduce object allocation. This class is provided to pack and unpack the <size, mode> tuple into the int. //子View大小一般随着控件的子空间或内容进行变化,此时控件尺寸只要不超过父控件允许的最大尺寸即可。
我们知道MeasureSpec是Android中父布局传递给子View用来描述其对子View布局需求的数据类型,也就是说父布局把它希望子View的大小以及变化的尺度封装在这个类中。而子View的measure方法拿到这个数值,则会根据这个数值中的信息对自身进行度量。
进入源码查看:
/** * Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint * on the child. It can be whatever size it wants. */ public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT; /** * Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size * for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless * of how big it wants to be. */ public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT; /** * Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up * to the specified size. */ public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
从上面我们得出
MASK = 0x3 << 30 = 0xC0000000,前4位为 1100;
UNSPECTIFIED = 0 << 30 = 0x00000000,前4位为 0000;
EXACTLY = 1 << 30 = 0x40000000, 前4位为 0100;
AT_MOST = 2 << 30 = 0x80000000, 前4位为 1000;
继续查看MeasureSpec类的代码:
/**
* Creates a measure specification based on the supplied size and mode.
*
* The mode must always be one of the following:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED}</li>
* <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}</li>
* <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST}</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p><strong>Note:</strong> On API level 17 and lower, makeMeasureSpec's
* implementation was such that the order of arguments did not matter
* and overflow in either value could impact the resulting MeasureSpec.
* {@link android.widget.RelativeLayout} was affected by this bug.
* Apps targeting API levels greater than 17 will get the fixed, more strict
* behavior.</p>
*
* @param size the size of the measure specification
* @param mode the mode of the measure specification
* @return the measure specification based on size and mode
*/
public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}/**
* Extracts the mode from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the mode from
* @return {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED},
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST} or
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}
*/
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
/**
* Extracts the size from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the size from
* @return the size in pixels defined in the supplied measure specification
*/
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}measrureSpec 是由size和mode两个int数值做二进制运算,mode & MODE_MASK 即取mode的前2位,size & ~MODE_MASK 即取size的后30位,然后这两部分组成了我们想要的measureSpec的值,这样做不仅能够满足对于描述布局的需求,还节省的内存开支。
measure()方法测量流程
知识铺垫看完,看到measure()方法的属性为public,包括layout()方法,以及draw()方法,外部代码框架通过调用这几个方法,来实现View的测量,定位,以及绘制。/**
* <p>
* This is called to find out how big a view should be. The parent
* supplies constraint information in the width and height parameters.
* </p>
*
* <p>
* The actual measurement work of a view is performed in
* {@link #onMeasure(int, int)}, called by this method. Therefore, only
* {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} can and must be overridden by subclasses.
* </p>
*
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec Horizontal space requirements as imposed by the
* parent
* @param heightMeasureSpec Vertical space requirements as imposed by the
* parent
*
* @see #onMeasure(int, int)
*/
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {measure()方法中会再调用onMeasure()方法
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}通过在onMeasure方法中对View自身的宽高进行测量,这里先看View的onMeasure()方法,查看View类的onMeasure()方法,这里调用setMeasuredDimension()来设置测量的宽度和高度。
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}而测量的高度和宽度则是根据MeasureSpec计算出来的,我们可以看下面的getDefaultSize()方法
/**
* Utility to return a default size. Uses the supplied size if the
* MeasureSpec imposed no constraints. Will get larger if allowed
* by the MeasureSpec.
*
* @param size Default size for this view
* @param measureSpec Constraints imposed by the parent
* @return The size this view should be.
*/
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}这里通过解析MeasureSpec获取specMode(父布局传递进来的度量模式),specSize(父布局传递进来的尺寸数值)
当值为MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED,result 直接赋值为View自身的实际尺寸
当值为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST 或者 MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,result 赋值为父布局传递进来的尺寸数值。
看过了View类的onMeasure()如何对自身进行测量,再看ImageView的onMeasure()如何对自身进行测量。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
resolveUri();
int w;
int h;
...
w += pleft + pright;
h += ptop + pbottom;
w = Math.max(w, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
h = Math.max(h, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
widthSize = resolveSizeAndState(w, widthMeasureSpec, 0);
heightSize = resolveSizeAndState(h, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
...
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
}继续查看resolveSizeAndState()方法,根据父类传递的MeasureSpec测量自身的逻辑
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}这里通过解析MeasureSpec获取specMode(父布局传递进来的度量模式),specSize(父布局传递进来的尺寸数值)
当值为MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED,result 直接赋值为View自身的实际尺寸
当值为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,当实际尺寸不超过specSize的时候,result赋值为View自身实际尺寸,当实际尺寸超过specSize的时候,result赋值为specSize.
当值为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,result 赋值为父布局传递进来的尺寸数值,即赋值为specSize.
综上,一个View(or ImageView or TextView ext)测量自身的流程是:
调用measure(),并且传递相关的测量参数MeasureSpec
measure()方法内部继续调用onMeasure()方法,继续把MeasureSpec传递下去
onMeasure()方法中,根据自身View类型的不同(ImageView,TexView),以及传递进来的MeasureSpec,设置测量的尺寸变量mMeasuredWidth, mMeasureHeight.
MeasureSpec在measure过程中的传递
上面我们知道了measure()方法如何根据MeasureSpec来对自身进行度量,但是还有一个疑问,MeasureSpec这么重要,它似乎就是度量的关键,那么它又从哪里来?我们以LinearLayout为例,都知道LinearLayout是继承自ViewGroup,当我们调用ViewGroup.measure(),它会继续调用子View的measure()方法,只要我们其中的MeasureSpec是如何从父View传递给子View,那么MeasureSpec如何创建以及由什么决定就可以找到了。
当调用LinearLayout的measure()去度量,会再自动调用onMeasure()来测量(已经被LinearLayout类重写),如下:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}再进入measureHorizontal()方法
/**
* Measures the children when the orientation of this LinearLayout is set
* to {@link #HORIZONTAL}.
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec Horizontal space requirements as imposed by the parent.
* @param heightMeasureSpec Vertical space requirements as imposed by the parent.
*
* @see #getOrientation()
* @see #setOrientation(int)
* @see #onMeasure(int, int)
*/
void measureHorizontal(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
// Determine how big this child would like to be. If this or
// previous children have given a weight, then we allow it to
// use all available space (and we will shrink things later
// if needed).
measureChildBeforeLayout(child, i, widthMeasureSpec,
totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0,
heightMeasureSpec, 0);
...
}发现在measureHorizontal()方法中最后会调用measureChildBeforeLayout()方法
/**
* <p>Measure the child according to the parent's measure specs. This
* method should be overriden by subclasses to force the sizing of
* children. This method is called by {@link #measureVertical(int, int)} and
* {@link #measureHorizontal(int, int)}.</p>
*
* @param child the child to measure
* @param childIndex the index of the child in this view
* @param widthMeasureSpec horizontal space requirements as imposed by the parent
* @param totalWidth extra space that has been used up by the parent horizontally
* @param heightMeasureSpec vertical space requirements as imposed by the parent
* @param totalHeight extra space that has been used up by the parent vertically
*/
void measureChildBeforeLayout(View child, int childIndex,
int widthMeasureSpec, int totalWidth, int heightMeasureSpec,
int totalHeight) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, totalWidth,
heightMeasureSpec, totalHeight);
}继续追踪measureChildBeforeLayout(),发现它又调用了ViewGroup.measureChildWithMargins()方法
/**
* Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into
* account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding
* and margins. The child must have MarginLayoutParams The heavy lifting is
* done in getChildMeasureSpec.
*
* @param child The child to measure
* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view
* @param widthUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* horizontally (possibly by other children of the parent)
* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view
* @param heightUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* vertically (possibly by other children of the parent)
*/
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}在measureChildWithMargins()方法中,很明显最后一行调用了子View的measure()方法测量子View的宽高,这里传递给子View的MeasureSpec数值又经过了一番计算,这里很明显,传递给子View的MeasureSpec数值是由于子View的LayoutParams和父View传下来的MeasureSpec共同决定的。
通过ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec()方法,根据父布局传入的MeasureSpec和view自身的LayoutParams计算出应该传递给view的MeasureSpec的数值
/**
* Does the hard part of measureChildren: figuring out the MeasureSpec to
* pass to a particular child. This method figures out the right MeasureSpec
* for one dimension (height or width) of one child view.
*
* The goal is to combine information from our MeasureSpec with the
* LayoutParams of the child to get the best possible results. For example,
* if the this view knows its size (because its MeasureSpec has a mode of
* EXACTLY), and the child has indicated in its LayoutParams that it wants
* to be the same size as the parent, the parent should ask the child to
* layout given an exact size.
*
* @param spec The requirements for this view
* @param padding The padding of this view for the current dimension and
* margins, if applicable
* @param childDimension How big the child wants to be in the current
* dimension
* @return a MeasureSpec integer for the child
*/
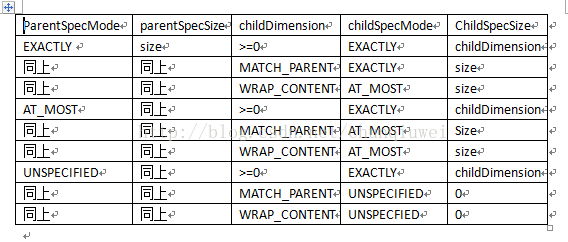
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}我们来看ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec()计算MeasureSpec的逻辑,由父View的MeasureSpec数值和自身的LayoutParams数值共同决定,具体的逻辑处理可见下表:
(图片来自网络)
测试例子
测量的开始是从调用measure()方法开始,而当我构造一个View的实例时,它的measure()并不会被马上调用,那么当我们想要预先知道一个View的宽高的时候,我们可以不需要等待View的测量绘制流程,直接手动调用measure(),测量View的尺寸数据。/**
* 测量view的尺寸,实际上view的最终尺寸会由于父布局传递来的MeasureSpec和view本身的LayoutParams共同决定
* 这里预先测量,由自己给出的MeasureSpec计算尺寸
* @param view
*/
public static void measure(View view) {
int sizeWidth, sizeHeight, modeWidth, modeHeight;
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = view.getLayoutParams();
if (layoutParams == null) {
layoutParams = new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
if (layoutParams.width == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
sizeWidth = 0;
modeWidth = View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else {
sizeWidth = layoutParams.width;
modeWidth = View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
}
if (layoutParams.height == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
sizeHeight = 0;
modeHeight = View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else {
sizeHeight = layoutParams.height;
modeHeight = View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
}
view.measure(View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(sizeWidth, modeWidth),
View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(sizeHeight, modeHeight)
);
}我们来做一个测验:
TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text); Log.d(TAG, "Before Measure the view"); Log.d(TAG, "width = " + textView.getMeasuredWidth()); Log.d(TAG, "height = " + textView.getMeasuredHeight()); MeasureUtils.measure(textView); Log.d(TAG, "After Measure the view"); Log.d(TAG, "width = " + textView.getMeasuredWidth()); Log.d(TAG, "height = " + textView.getMeasuredHeight());
结果输出:
08-13 02:50:58.714 2548-2548/? D/Measure: Before Measure the view
08-13 02:50:58.714 2548-2548/? D/Measure: width = 0
08-13 02:50:58.714 2548-2548/? D/Measure: height = 0
08-13 02:50:58.715 2548-2548/? D/Measure: After Measure the view
08-13 02:50:58.715 2548-2548/? D/Measure: width = 24
08-13 02:50:58.715 2548-2548/? D/Measure: height = 19
从这个测试例子,我们也可以验证之前的说法,View的测量时从外部调用View的共有方法measure()开始的,但是调用的时机并不是我们一初始化View它就开始,所以一开始初始化之后,mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight的值都为默认的 0 , 但是当我们主动调用measure()方法之后,View就完成了对自身的尺寸的测量。
onSizeChange()方法获取宽高
先来看看View源码的onSizeChanged()/**
* This is called during layout when the size of this view has changed. If
* you were just added to the view hierarchy, you're called with the old
* values of 0.
*
* @param w Current width of this view.
* @param h Current height of this view.
* @param oldw Old width of this view.
* @param oldh Old height of this view.
*/
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
}通过代码查看,我们寻找View类中哪里调用了这个方法:
private void sizeChange(int newWidth, int newHeight, int oldWidth, int oldHeight) {
onSizeChanged(newWidth, newHeight, oldWidth, oldHeight);
if (mOverlay != null) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().setRight(newWidth);
mOverlay.getOverlayView().setBottom(newHeight);
}
rebuildOutline();
}继续查看,哪里调用了sizeChange():
/**
* Sets the top position of this view relative to its parent. This method is meant to be called
* by the layout system and should not generally be called otherwise, because the property
* may be changed at any time by the layout.
*
* @param top The top of this view, in pixels.
*/
public final void setTop(int top) {
...
sizeChange(width, mBottom - mTop, width, oldHeight);
...
}setTop()方法用来设置View的top position的值,它被layout system调用,当View的尺寸属性发生变化,会调用,同理我们也可以在setBottom(),setLeft(),setRight()方法中看到sizeChange()被调用。
因此,当onSizeChanged()调用的时候,我们可以从中获取到当前View的高度和宽度。
其他方法
其实通过在onSizeChanged()方法中获取width和height,就是等待View的度量和绘制工作完成,相比第一种方式,这种方式较为被动,但是获取的数值也较为准确。同理,我们也可以在onDraw()方法中获取width和height,这时候View的度量工作已经完成,我们能够获取到View已经测量好的宽度和高度。
另外在网上看到,我们还可以使用以下方式来获取宽高:
view.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(
new ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
view.getMeasuredWidth();
view.getMeasuredHeight();
}
});
相关文章推荐
- 简单研究Android View绘制一 测量过程
- Android的webview研究
- 最近研究有关Android中的TextView
- 【android】动画效果研究(View/PopupWindow)【2】
- Android自定义View研究(五)--View的大小
- Android自定义View研究(四) -- 在XML中定义View
- Android的webview研究
- Android自定义View研究(七)--XML中布局自定义View时View触摸原点问题
- Android自定义View研究:View的大小
- Android自定义View研究(八)--自定义View总结
- Android自定义View研究(七)--XML中布局自定义View时View触摸原点问题
- Android SurfaceView 绘图覆盖刷新及“.NET研究”脏矩形刷新方法
- Android中自定义View的研究(四) -- 在XML中定义View
- Android中自定义View的研究(三) -- 获得Bitmap的三种方法
- 【android】动画效果研究(View)【1】
- android view构造函数研究
- Android中继承View的研究(二) -- 绘图的基本知识
- Android自定义View研究(六)--View中的原点坐标相关问题
- Android自定义View研究(二) -- 绘图的基本知识
- Android自定义View研究(八)--自定义View总结
