CodeForces 703B Mishka and trip
2016-08-11 11:33
393 查看
B. Mishka and trip
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Little Mishka is a great traveller and she visited many countries. After thinking about where to travel this time, she chose XXX — beautiful, but little-known northern country.
Here are some interesting facts about XXX:
XXX consists of n cities, k of
whose (just imagine!) are capital cities.
All of cities in the country are beautiful, but each is beautiful in its own way. Beauty value of i-th city equals to ci.
All the cities are consecutively connected by the roads, including 1-st and n-th
city, forming a cyclic route 1 — 2 — ... — n — 1. Formally, for every 1 ≤ i < n there
is a road between i-th and i + 1-th
city, and another one between 1-st and n-th
city.
Each capital city is connected with each other city directly by the roads. Formally, if city x is a capital city, then for every1 ≤ i ≤ n, i ≠ x,
there is a road between cities x and i.
There is at most one road between any two cities.
Price of passing a road directly depends on beauty values of cities it connects. Thus if there is a road between cities i and j,
price of passing it equals ci·cj.
Mishka started to gather her things for a trip, but didn't still decide which route to follow and thus she asked you to help her determine summary price of passing each of the roads in XXX. Formally,
for every pair of cities a and b (a < b),
such that there is a road betweena and b you
are to find sum of products ca·cb.
Will you help her?
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and k (3 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) —
the number of cities in XXX and the number of capital cities among them.
The second line of the input contains n integers c1, c2, ..., cn (1 ≤ ci ≤ 10 000) —
beauty values of the cities.
The third line of the input contains k distinct integers id1, id2, ..., idk (1 ≤ idi ≤ n) —
indices of capital cities. Indices are given in ascending order.
Output
Print the only integer — summary price of passing each of the roads in XXX.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
This image describes first sample case:
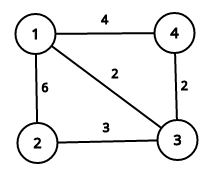
It is easy to see that summary price is equal to 17.
This image describes second sample case:
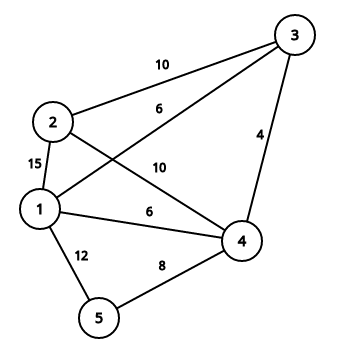
It is easy to see that summary price is equal to 71.
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Little Mishka is a great traveller and she visited many countries. After thinking about where to travel this time, she chose XXX — beautiful, but little-known northern country.
Here are some interesting facts about XXX:
XXX consists of n cities, k of
whose (just imagine!) are capital cities.
All of cities in the country are beautiful, but each is beautiful in its own way. Beauty value of i-th city equals to ci.
All the cities are consecutively connected by the roads, including 1-st and n-th
city, forming a cyclic route 1 — 2 — ... — n — 1. Formally, for every 1 ≤ i < n there
is a road between i-th and i + 1-th
city, and another one between 1-st and n-th
city.
Each capital city is connected with each other city directly by the roads. Formally, if city x is a capital city, then for every1 ≤ i ≤ n, i ≠ x,
there is a road between cities x and i.
There is at most one road between any two cities.
Price of passing a road directly depends on beauty values of cities it connects. Thus if there is a road between cities i and j,
price of passing it equals ci·cj.
Mishka started to gather her things for a trip, but didn't still decide which route to follow and thus she asked you to help her determine summary price of passing each of the roads in XXX. Formally,
for every pair of cities a and b (a < b),
such that there is a road betweena and b you
are to find sum of products ca·cb.
Will you help her?
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and k (3 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) —
the number of cities in XXX and the number of capital cities among them.
The second line of the input contains n integers c1, c2, ..., cn (1 ≤ ci ≤ 10 000) —
beauty values of the cities.
The third line of the input contains k distinct integers id1, id2, ..., idk (1 ≤ idi ≤ n) —
indices of capital cities. Indices are given in ascending order.
Output
Print the only integer — summary price of passing each of the roads in XXX.
Examples
input
4 1 2 3 1 2 3
output
17
input
5 2 3 5 2 2 4 1 4
output
71
Note
This image describes first sample case:

It is easy to see that summary price is equal to 17.
This image describes second sample case:

It is easy to see that summary price is equal to 71.
题意:给出每个城市的美丽值,在两个相连的城市的道路上走时,获得的美丽值是这两个城市美丽值之积,把所有城市相连的道路全部走一遍,
问得到的所有美丽值。其中 n个城市(编号为1---n)中道路相连规则如下:1.每个城市都与他相邻编号的城市相连,1-2 ,2-3,n-1; 2:有k个首都,首都与每个城市都相连。 思路:刚开始按所说的一个个算的,用了两层循环,超时了,给出的数据太大。转化为一层循环。先把所有城市的美丽值加起来
,然后再判断是否是首都,已经前一个是否是首都,注意1,和n, 要特判一下。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
__int64 b,a[100000+10],vis[100000+10];
int main()
{
int n,k,i,j;
__int64 sum,ans;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&k)!=EOF)
{
sum=0,ans=0;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sum+=a[i];
}
for(i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&b);
vis[b]=1;
}
if(vis[1])
{
ans+=(sum-a[1])*a[1];
sum=sum-a[1];
}
else if(!vis
)
{
ans=a[1]*a
;
}
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(vis[i])
{
ans+=(sum-a[i])*a[i];
sum=sum-a[i];
}
else if(!vis[i-1])
{
ans+=a[i-1]*a[i];
}
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- CodeForces 703B Mishka and trip(图论)
- CodeForces 703B Mishka and trip(城市省会修路,待AC)
- CodeForces 703B Mishka and trip
- CodeForces 703B Mishka and trip
- 【打CF,学算法——二星级】Codeforces 703B Mishka and trip (统计)
- codeforces 703B Mishka and trip
- CodeForces 703B Mishka and trip【水题】
- (模拟+数学)codeforces - 703B Mishka and trip
- Codeforces-703B Mishka and trip
- codeforces B. Mishka and trip
- Codeforces Round #365 (Div. 2) 703B Mishka and trip 水题
- Mishka and trip(CF 703B)
- codeforces - 703B - Mishka and trip(数学)
- codeforces 703B B. Mishka and trip(数学)
- cf703B Mishka and trip
- Codeforces Round #365 (Div. 2) B. Mishka and trip
- Coderforces 703B Mishka and trip
- Codeforces 703E Mishka and Divisors 离散化+DP
- CodeForces 703D Mishka and Interesting sum(树状数组 区间异或)
- Codeforces-703D Mishka and Interesting sum
