Android中的IPC——AIDL方式
2016-08-09 22:35
411 查看
AIDL是实现Android中IPC的一种方式。
通过AIDL我们将各种通信操作以接口方式进行定义,Android SDK则会按照AIDL的规则将AIDL编码成java类嵌入到应用中,然后我们就可以在APP运行时以调用函数的形式来进行IPC了。
通过图片来展现这种关系,大致为:
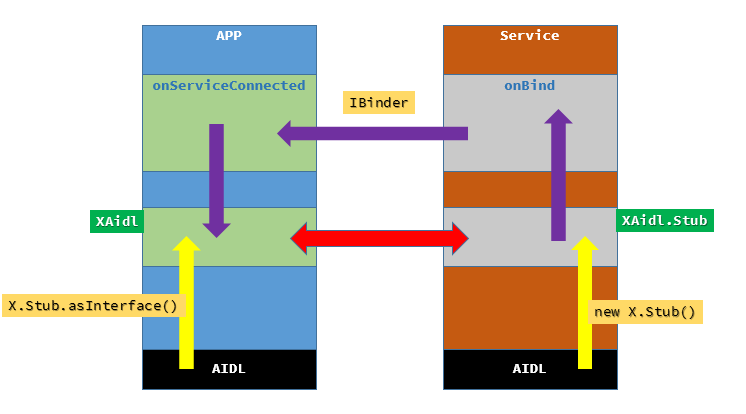
1.在Service及APP工程中创建相同的AIDL文件,并定义相同接口。
2.在Service的onBind中返回AIDL的Stub
3.在APP中实现ServiceConnection,在onServiceConnected函数中调用Stub.asInterface获取到AIDL对象。
4.在事件响应中按需调用AIDL接口
首先,我们再App与Service工程中建立相同的AIDL接口:
App中——
Service中——
创建好AIDL接口后,在其中添加一个简单的函数,接收两个int值,返回两者相加:
Android Studio默认添加了一个函数说明在AIDL中可接受的参数类型。
在定义完
接下来,在Service工程中创建一个Service,在其中实现AIDL的接口:
然后在App工程中,启动Service,并通过
安装两个APP后,无需启动Service,直接运行TestAidlApp。
此时含有AIDL的Service尚未启动,因此第一次点击按钮,会触发启动Service,这时Service会直接在另一个进程中启动;
然后再次点击按钮,就可以通过获取到的AIDL对象直接运行Service中方法,并拿到返回结果显示在界面上了。
通过AIDL我们将各种通信操作以接口方式进行定义,Android SDK则会按照AIDL的规则将AIDL编码成java类嵌入到应用中,然后我们就可以在APP运行时以调用函数的形式来进行IPC了。
与Messenger的区别
实际Messenger进行IPC本质也是以AIDL方式实现的,只不过通过上层接口封装我们不用自己实现AIDL的接口定义。Messenger与AIDL的区别在于——由于Messenger使用Handler处理消息序列,因此Service一次仅接受一个请求,适用于单线程的IPC通讯;AIDL则可以同时处理多个请求,不过这也要求我们的Service具备多线程处理能力。构成
以下表格是APP与Service中组件及说明:| 备注 | APP | 类型 | Service | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 在Service绑定回调中获取到AIDL对象 | onServiceConnected | Connection | onBind | onBind声明周期调用时返回AIDL Stub |
| 获取到AIDL对象,以调用接口 | AIDL | Variable | AIDL Stub | 实现AIDL定义的接口 |
| 需要与Service中定义相同 | AIDL定义文件 | AIDL | AIDL定义文件 | 需要与APP中定义相同 |

实现步骤
使用AIDL大致需要一下步骤:1.在Service及APP工程中创建相同的AIDL文件,并定义相同接口。
2.在Service的onBind中返回AIDL的Stub
3.在APP中实现ServiceConnection,在onServiceConnected函数中调用Stub.asInterface获取到AIDL对象。
4.在事件响应中按需调用AIDL接口
首先,我们再App与Service工程中建立相同的AIDL接口:
App中——

Service中——

创建好AIDL接口后,在其中添加一个简单的函数,接收两个int值,返回两者相加:
interface TestAidlInterface {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
//String basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat,
// double aDouble, String aString);
int add(int alpha, int beta);
}Android Studio默认添加了一个函数说明在AIDL中可接受的参数类型。
在定义完
add接口后,Android Studio会触发Gradle自动生成interface的实现类,可以在build文件夹中找到:
package com.example.testaidlservice;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
public interface TestAidlInterface extends android.os.IInterface
{
/** Local-side IPC implementation stub class. */
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.example.testaidlservice.TestAidlInterface
{
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.example.testaidlservice.TestAidlInterface";
/** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */
public Stub()
{
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.example.testaidlservice.TestAidlInterface interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.example.testaidlservice.TestAidlInterface asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj)
{
if ((obj==null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin!=null)&&(iin instanceof com.example.testaidlservice.TestAidlInterface))) {
return ((com.example.testaidlservice.TestAidlInterface)iin);
}
return new com.example.testaidlservice.TestAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
// 余下略
}asInterface即为在App中获取实现AIDL接口的Service的方法。
接下来,在Service工程中创建一个Service,在其中实现AIDL的接口:
public class TestService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = TestService.class.getSimpleName();
public TestService() {
}
// 实现AIDL接口,并在onBind中返回给App
TestAidlInterface.Stub mStub = new TestAidlInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public int add(int alpha, int beta) throws RemoteException {
return alpha + beta;
}
};
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
Log.i(TAG, "testService onBind");
// 返回AIDL接口的对象
return mStub;
}
}然后在App工程中,启动Service,并通过
asInterface接口获取到AIDL的实现,进一步调用:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Context mContext;
private TextView resultText;
private Button testAddButton;
// 定义AIDL接口实现类的对象
private TestAidlInterface testAidl;
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// onBind对象返回了AIDL的实现类,调用其中的asInterface方法来获取到可调用对象
testAidl = TestAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mContext = this;
resultText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.result_text);
testAddButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.test_add);
testAddButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 判断是否需要启动Service
if (testAidl == null) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("android.intent.action.TestAidlService");
intent.setPackage("com.example.testaidlservice");
bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
} else {
try {
// 调用AIDL接口获取返回值
String result = "result: " + testAidl.add(5, 8);
resultText.setText(result);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "RemoteException", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
});
}
@Override
public void onBackPressed() {
super.onBackPressed();
unbindService(conn);
}
}安装两个APP后,无需启动Service,直接运行TestAidlApp。
此时含有AIDL的Service尚未启动,因此第一次点击按钮,会触发启动Service,这时Service会直接在另一个进程中启动;
然后再次点击按钮,就可以通过获取到的AIDL对象直接运行Service中方法,并拿到返回结果显示在界面上了。
相关文章推荐
- Android中的IPC方式(二)—— AIDL
- Android中的IPC方式——使用AIDL
- 9.Android中的IPC方式——Bundle、文件共享、Messenger、AIDL、Content-Provider
- Android中进程间通讯(IPC)方式之一AIDL机制
- IPC机制系列之三 Android中的IPC方式 (AIDL)
- Android中的IPC方式AIDL
- Android ipc数据传输方式之一 AIDL
- Android进程间通信方式总结(IPC)
- Android实战技术:IPC方式简介教程
- Android开源项目之Music (二)--- AIDL实现IPC进程间通讯
- Android IPC的6种方式
- Android IPC 系列(2.1):AIDL
- Android IPC进程通信——Messager方式
- [转]Android IPC进程通信——Messager方式
- android跨进程通信(IPC):使用AIDL
- Using self-defined Parcelable objects during an Android AIDL RPC / IPC call
- android跨进程通信(IPC):使用AIDL
- Android实战技术:IPC方式简介教程
- Android IPC 系列(2.2):AIDL
- Android两种IPC通信方式之Messager
