我的python学习--第五天
2016-08-01 15:49
337 查看
一、函数的定义:
def 函数名(name,age=20,*params):
函数体
return 返回值
示例:
二、模块
简单的理解,模块就是文件,我们可以使用import,把其他文件的内容引入,进行使用
模块整体分为三种:
1、python自带的模块,比如sys、math、random、os、time等
2、第三方的开发者开发的模块,可以通过pip install安装,然后用import导入,比如flask requests,pyquery,psutil等
3、自己开发的模块
import的模块查找路径:
1、当前目录
2、pythonpath全局路径
注:自己创建的文件名不要与模块名相同,不然导入时,导入的将是创建的文件而不是模块
三、Flask
Flask是一个使用Python编写的轻量级Web应用框架。其WSGI工具箱采用Werkzeug,模板引擎则使用Jinja2。
1、安装flask框架
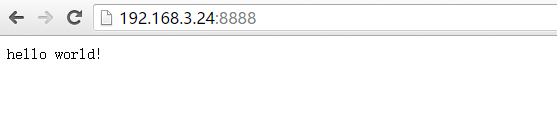
2、写一个hello world
运行结果
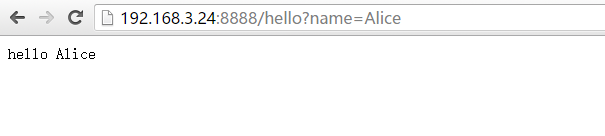
3、使用request
request里面包含一次网络请求所有的内容,所有get的url参数都在request.args这个变量里,request.args是一个类似字典的数据,flask通过request.args.get获取前端url给的参数
在url中通过name=Alice传入参数
4、使用模板
模板文件hello.html
运行结果
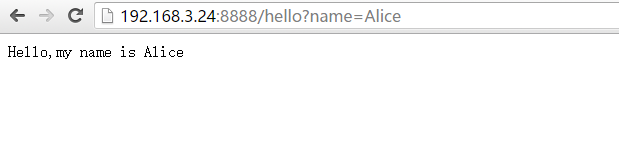
当使用模板时,render_template会自动到当前目录下的templates目录下去查找请求的html文件,并将参数替换
flask使用的是jinja2模板语言:
``.``.``.``包裹的表示变量
{%...%}包裹的是python的语句
循环语法:
{% for x in arr%}
...
{%endfor%}
循环结束,if同理
5、redirect跳转
user.html文件
显示结果:
非admin用户
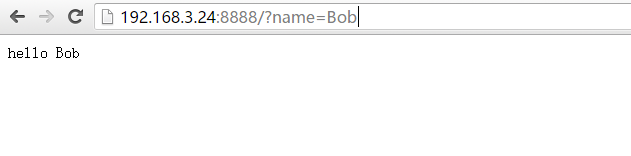
admin用户和密码

跳转后
6、在5的基础上将添加用户功能进行美化
user.html代码为:
运行结果:

7、html常见标签
table:后端向前端展示数据
form:前段向后端提交数据
action:提交的地址(url)
input:输入框
type:输入类型
text:文本
submit:提交按钮
value:按钮上的文字
password:密码已点或星显示
checkbox:多选框
radio:单选框
name:字段名
8、其他常见标签:
p:一段话
br:换行
hr:一个横线
a herf="":锚点(超链接)
img:图片标签
widh:宽度
height:高度
def 函数名(name,age=20,*params):
函数体
return 返回值
示例:
def hello(): print 'hello world' # print表示要表达的一段话 return 'hello' # return表示函数的返回值 def dosth(fn): print fn+' everyone' # 函数中还可以调用函数 hello() dosth(hello()) [root@test1 python]# python hello.py hello world hello world hello everyone
二、模块
简单的理解,模块就是文件,我们可以使用import,把其他文件的内容引入,进行使用
模块整体分为三种:
1、python自带的模块,比如sys、math、random、os、time等
2、第三方的开发者开发的模块,可以通过pip install安装,然后用import导入,比如flask requests,pyquery,psutil等
3、自己开发的模块
import的模块查找路径:
1、当前目录
2、pythonpath全局路径
注:自己创建的文件名不要与模块名相同,不然导入时,导入的将是创建的文件而不是模块
三、Flask
Flask是一个使用Python编写的轻量级Web应用框架。其WSGI工具箱采用Werkzeug,模板引擎则使用Jinja2。
1、安装flask框架
[root@test1 python]# yum install -y python-pip [root@test1 python]# pip install flask
2、写一个hello world
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf-8
from flask import Flask # 引入flask的启动模块
app = Flask(__name__) # 创建一个app
@app.route('/') # 监听路由,即url
def index(): # 路由对应的处理函数
return 'hello world!'
if __name__=='__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0',port='8888') # 启动app,监听在8888端口运行结果

3、使用request
request里面包含一次网络请求所有的内容,所有get的url参数都在request.args这个变量里,request.args是一个类似字典的数据,flask通过request.args.get获取前端url给的参数
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf-8
from flask import Flask,request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return 'hello world!'
@app.route('/hello')
def hello():
name = request.args.get('name','world') # 获取请求的参数
return 'hello %s'%name
if __name__=='__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0',port='8888')在url中通过name=Alice传入参数

4、使用模板
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf-8
from flask import Flask,request,render_template
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return 'hello world!'
@app.route('/hello')
def hello():
name = request.args.get('name','world') # 获取参数
return render_template('hello.html',name=name) # 将参数传入模板
# return 'hello %s'%name
if __name__=='__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0',port='8888')模板文件hello.html
Hello,my name is `name`
运行结果

当使用模板时,render_template会自动到当前目录下的templates目录下去查找请求的html文件,并将参数替换
flask使用的是jinja2模板语言:
``.``.``.``包裹的表示变量
{%...%}包裹的是python的语句
循环语法:
{% for x in arr%}
...
{%endfor%}
循环结束,if同理
5、redirect跳转
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf-8
from flask import Flask,request,render_template,redirect
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
name = request.args.get('name')
pwd = request.args.get('password')
if name=='admin' and pwd=='admin': # 用户名密码为admin,就跳转
return redirect('/admin')
else:
return 'hello %s'%name
@app.route('/admin')
def hello():
with open('user.txt',) as fo:
names = [names.split(':') for names in fo.read().split('\n')] # 显示已有的账户密码
return render_template('user.html',names=names)
if __name__=='__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0',port='8888')user.html文件
<table border='1'>
<thead>
<tr>
<td> Name </td>
<td> Password </td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for name in names %}
{% if name[0] and name[1] %}
<tr>
<td>{{name[0]}}</td>
<td>{{name[1]}}</td>
</tr>
{%endif%}
{%endfor%}
</tbody>
</table>显示结果:
非admin用户

admin用户和密码

跳转后

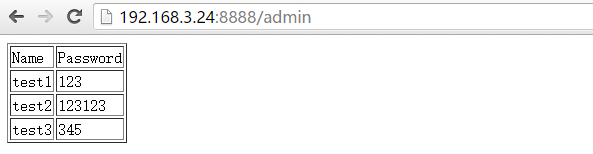
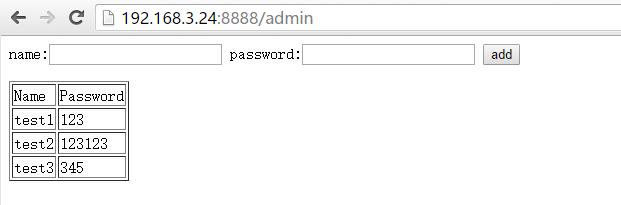
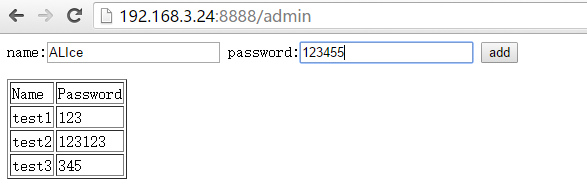
6、在5的基础上将添加用户功能进行美化
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf-8
from flask import Flask,request,render_template,redirect
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return 'hello world'
@app.route('/useradd')
def useradd():
name = request.args.get('name')
pwd = request.args.get('password')
if name and pwd:
with open('user.txt','a+') as fo:
fo.write('%s:%s\n'%(name,pwd))
return redirect('/admin')
else:
return 'need user and password'
@app.route('/admin')
def hello():
with open('user.txt',) as fo:
names = [names.split(':') for names in fo.read().split('\n')]
return render_template('user.html',names=names)
if __name__=='__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0',port='8888')user.html代码为:
<form action='/useradd'>
name:<input type='text' name='name'>
password:<input type='text' name='password'>
<input type='submit' value='add'>
</form>
<table border='1'> <thead> <tr> <td> Name </td> <td> Password </td> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for name in names %} {% if name[0] and name[1] %} <tr> <td>{{name[0]}}</td> <td>{{name[1]}}</td> </tr> {%endif%} {%endfor%} </tbody> </table>
运行结果:



7、html常见标签
table:后端向前端展示数据
form:前段向后端提交数据
action:提交的地址(url)
input:输入框
type:输入类型
text:文本
submit:提交按钮
value:按钮上的文字
password:密码已点或星显示
checkbox:多选框
radio:单选框
name:字段名
8、其他常见标签:
p:一段话
br:换行
hr:一个横线
a herf="":锚点(超链接)
img:图片标签
widh:宽度
height:高度
相关文章推荐
- python学习第五天 - 分支循环(for...in,break,continue)
- 人生苦短,我用Python 学习笔记——第五天
- Python学习日记 第五天
- Codecademy网学习Python第五天
- python学习---第五天
- python学习笔记:第五天( 字典)
- python学习日记_第五天(ex12~13)
- Python快速学习第五天
- python学习第五天 List和tuple类型介绍及其List切片
- python学习之路-第五天-python的数据结构
- Python学习第五天----tar命令及vim编辑器使用及硬盘分区方法
- 学习Python第五天
- 学习大数据第五天:最小二乘法的Python实现(二)
- 学习python的第五天
- Python学习第五天——第一周总结
- python学习笔记:第五天( 列表、元组)
- Python 学习第五天
- 据廖雪峰python3教程----python学习第五天
- 第五天学习python
- Python学习第五天
