java线程基础概念
2016-07-31 13:41
337 查看
1、线程的概念:

2、多线程的概念:
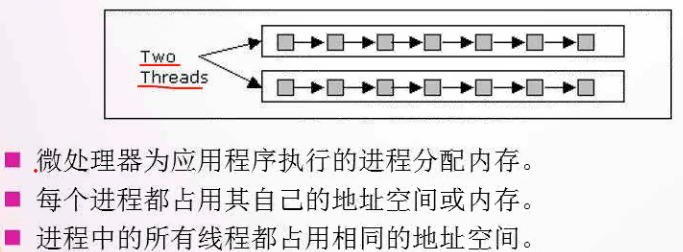
3、多线程的优点:
1)使用的系统资源最少
2)提升了性能
3)简化了程序结构
4、多线程的缺点:
1)竞争情况
2)死锁情况
3)锁饥饿
5、Thread类

用法参考代码:
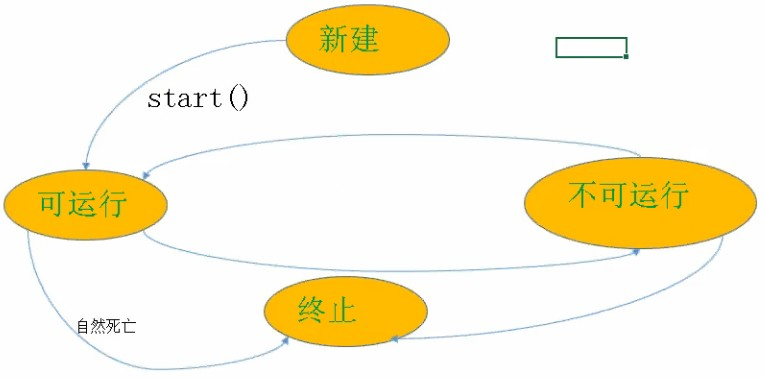
6、线程的生命周期,包含以下几个状态:
1)新建状态:创建线程Thread类实例后,进入新建状态
2)可运行状态:当start()方法被调用时,进入可运行状态
start()用于启动线程,为线程分配系统资源,然后传到run()方法
run()方法是线程的主方法
3)不可运行状态,以下几种情况会触发:
休眠 sleep()
等待 wait()
被其他线程终止
4)终止或死亡(不能重启已终止的线程),以下几种情况会触发:
run()方法里面代码执行完毕,正常死亡
stop()方法终止线程
生命周期间的流转:
7、创建单线程,有以下几种方式:
1)继承Thread类(实现了Runnable接口),步骤:
a)定义类继承:public class MyThread extends Thread
b)重写run方法:public void run()
c)创建线程类:MyThread t=new MyThread();
d) 启动线程:t.start()
代码如下:
a)定义类实现Runnable接口:public class MyRunnable implements Runnable
b)重写run方法:public void run()
c)创建实现了Runnable接口类的实例:MyRunnable t=new MyRunnable();
d)创建线程类的实例,传入r:Thread t=new Thread(r);
e) 启动线程:t.start()
代码如下:
1)isAlive 判断线程的状态
运行结果:
用法参考代码:
使用线程实现红绿灯的例子:

2、多线程的概念:

3、多线程的优点:
1)使用的系统资源最少
2)提升了性能
3)简化了程序结构
4、多线程的缺点:
1)竞争情况
2)死锁情况
3)锁饥饿
5、Thread类

用法参考代码:
public class FirstThread {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//获取当前java程序所在的线程
Thread th=Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("当前线程:"+th);//输出:当前线程:Thread[main,5,main]
System.out.println("线程的名称:"+th.getName());
th.setName("主线程");//设置线程名称
System.out.println("修改之后的线程名称:"+th.getName());
System.out.println("线程优先级:"+th.getPriority());
<span style="color:#FF0000;">th.setPriority(10);//设置线程优先级1-10
th.setPriority(th.MAX_PRIORITY);//最大优先级10
th.setPriority(th.MIN_PRIORITY);//最小优先级1
th.setPriority(th.NORM_PRIORITY);//默认优先级5
//非1-10的优先级则会抛出异常: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException</span>
th.setPriority(11);
System.out.println("修改之后的线程优先级:"+th.getPriority());
System.out.println("当前线程:"+th);//输出当前线程:Thread[主线程,10,main]
th.sleep(1000);
}
}6、线程的生命周期,包含以下几个状态:
1)新建状态:创建线程Thread类实例后,进入新建状态
2)可运行状态:当start()方法被调用时,进入可运行状态
start()用于启动线程,为线程分配系统资源,然后传到run()方法
run()方法是线程的主方法
3)不可运行状态,以下几种情况会触发:
休眠 sleep()
等待 wait()
被其他线程终止
4)终止或死亡(不能重启已终止的线程),以下几种情况会触发:
run()方法里面代码执行完毕,正常死亡
stop()方法终止线程
生命周期间的流转:

7、创建单线程,有以下几种方式:
1)继承Thread类(实现了Runnable接口),步骤:
a)定义类继承:public class MyThread extends Thread
b)重写run方法:public void run()
c)创建线程类:MyThread t=new MyThread();
d) 启动线程:t.start()
代码如下:
public class MyThread extends Thread{
JFrame jf;
JTextField tf;
JLabel l;
JPanel jp;
//重写Thread的run方法
public void run(){//写线程执行的任务
jf=new JFrame("倒计时程序");
jp=new JPanel();
l=new JLabel("");
tf=new JTextField();
tf.setEnabled(false);//设置文本框不可以输入
Font f=new Font("宋体",10,18);//创建字体
tf.setBounds(50,10,20,100);
tf.setFont(f);
tf.setBackground(Color.BLACK);
jp.setBackground(Color.blue);
jf.add(jp);
jp.add(tf);
jp.add(l);
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setSize(300,100);
jf.setResizable(false);//设置不可改变大小
for(int i=60;i>0;i--){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
tf.setText("倒计时"+i+"秒");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jf, "时间到,游戏结束");
tf.setText("");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread t=new MyThread();
t.start();//只有调用start()方法才会执行run方法里面的内容
}
}2)实现Runnable接口(只有一个抽象方法run()),步骤:a)定义类实现Runnable接口:public class MyRunnable implements Runnable
b)重写run方法:public void run()
c)创建实现了Runnable接口类的实例:MyRunnable t=new MyRunnable();
d)创建线程类的实例,传入r:Thread t=new Thread(r);
e) 启动线程:t.start()
代码如下:
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
JFrame jf;
JTextField tf;
JLabel l;
JPanel jp;
@Override
public void run() {
jf=new JFrame("倒计时程序");
jp=new JPanel();
l=new JLabel("");
tf=new JTextField();
tf.setEnabled(false);//设置文本框不可以输入
Font f=new Font("宋体",10,18);//创建字体
tf.setBounds(50,10,20,100);
tf.setFont(f);
tf.setBackground(Color.BLACK);
jp.setBackground(Color.blue);
jf.add(jp);
jp.add(tf);
jp.add(l);
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setSize(300,100);
jf.setResizable(false);//设置不可改变大小
for(int i=60;i>0;i--){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
tf.setText("倒计时"+i+"秒");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jf, "时间到,游戏结束");
tf.setText("");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建实现了Runnable接口类的实例
MyRunnable r=new MyRunnable();
//2.创建线程类的实例,传入r
Thread t=new Thread(r);
t.start();
}
}8、创建多线程public class Race extends Thread{
String ThreadName;//线程名称
JFrame jf;
JLabel l;
JPanel jp1,jp2,jp3;//三个矩形
public Race(){//绘制界面
jf=new JFrame("多线程 矩形赛跑");
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setSize(400,200);
jf.setLayout(null);
l=new JLabel("");
l.setBounds(10, 10, 400, 200);
jf.add(l);
jp1=new JPanel();
jp1.setSize(20,20);
jp1.setBackground(Color.blue);
jp1.setBounds(10, 40, 20, 20);
jf.add(jp1);
jp2=new JPanel();
jp3=new JPanel();
jp2.setSize(20,20);
jp2.setBackground(Color.green);
jp2.setBounds(10, 80, 20, 20);
jf.add(jp2);
jp3.setSize(20,20);
jp3.setBackground(Color.yellow);
jp3.setBounds(10, 120, 20, 20);
jf.add(jp3);
}
public void run(){
try {//添加判断:如果是第2个线程,执行runb,第2个线程,执行rung,第3个线程,执行runy
if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("tb")){
runb();
}else if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("tg")){
rung();
}else if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("ty")){
runy();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//分别控制3个矩形X坐标的速度不同
public void runb() throws InterruptedException{
Random r=new Random();
int s=r.nextInt(180);//随机y坐标,显示高度
for(int i=0;i<=400;i+=10){
jp1.setBounds(i,s,20,20);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
public void rung() throws InterruptedException{
for(int i=0;i<=400;i+=5){
jp2.setBounds(i,80,20,20);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
public void runy() throws InterruptedException{
for(int i=0;i<=400;i+=16){
jp3.setBounds(i,120,20,20);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Race r=new Race();
Thread tb=new Thread(r);
tb.setName("tb");
Thread tg=new Thread(r);
tg.setName("tg");
Thread ty=new Thread(r);
ty.setName("ty");
tb.start(); tg.start(); ty.start();
}
}9、线程的特殊方法1)isAlive 判断线程的状态
public class IsAliveDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();// 调用苟照,同时创建线程
System.out.println(myThread.t + "是否还活着" + myThread.t.isAlive());
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程LOOP:" + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("主线程已被中断");
System.out.println(myThread.t + "是否还活着" + myThread.t.isAlive());
System.out.println("主线程终止");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable {
Thread t;
public MyThread() {
t = new Thread(this, "子线程");
System.out.println("当前线程是:" + t);
t.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(t + "LOOP:" + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(t + "已被中断");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}运行结果:
当前线程是:Thread[子线程,5,main] Thread[子线程,5,main]是否还活着true 主线程LOOP:1 Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:1 主线程LOOP:2 主线程LOOP:3 Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:2 主线程LOOP:4 主线程LOOP:5 Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:3 Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:4 Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:52)join方法: 允许线程等待,直到调用该方法的线程终止为止
用法参考代码:
public class jojnDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();// 调用苟照,同时创建线程
System.out.println(myThread.t + "是否还活着" + myThread.t.isAlive());
try {
myThread.t.join();//主线程等待子程序执行结束
System.out.println("主线程开始执行");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(myThread.t + "是否还活着" + myThread.t.isAlive());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable {
Thread t;
public MyThread() {
t = new Thread(this, "子线程");
System.out.println("当前线程是:" + t);
t.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(t + "LOOP:" + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(t + "已被中断");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}运行结果:当前线程是:Thread[子线程,5,main] Thread[子线程,5,main]是否还活着true Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:1 Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:2 Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:3 Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:4 Thread[子线程,5,main]LOOP:5 主线程开始执行
使用线程实现红绿灯的例子:
import java.awt.Color;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class SignalDemo extends JFrame implements Runnable {
JPanel red, yellow, green;
JLabel time, show;
public SignalDemo() {
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.black);
setSize(100, 250);
setVisible(true);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setLayout(null);
red = new JPanel();
red.setBackground(Color.red);
red.setBounds(40, 20, 40, 40);
yellow = new JPanel();
yellow.setBackground(Color.yellow);
yellow.setBounds(40, 70, 40, 40);
green = new JPanel();
green.setBackground(Color.green);
green.setBounds(40, 120, 40, 40);
add(red);
add(yellow);
add(green);
time = new JLabel("剩余时间:");
time.setForeground(Color.white);
time.setBounds(40, 170, 100, 40);
add(time);
show = new JLabel("");
show.setForeground(Color.white);
show.setBounds(95, 170, 100, 40);
add(show);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SignalDemo s = new SignalDemo();
Thread t = new Thread(s);
t.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
// 红灯亮
red.setBackground(Color.red);
yellow.setBackground(Color.gray);
green.setBackground(Color.gray);
for (int i = 3; i > 0; i--) {
show.setText(String.valueOf(i));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
// 绿灯亮
red.setBackground(Color.gray);
yellow.setBackground(Color.gray);
green.setBackground(Color.green);
for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) {
show.setText(String.valueOf(i));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
// 黄灯亮
red.setBackground(Color.gray);
yellow.setBackground(Color.yellow);
green.setBackground(Color.gray);
for (int i = 2; i > 0; i--) {
show.setText(String.valueOf(i));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
相关文章推荐
- Java基础的线程概念
- java多线程与高并发库应用(一)线程基础概念
- java线程(1)--概念基础
- java线程总结1--线程的一些概念基础以及线程状态
- Java基础之线程概念
- JAVA线程之一----基础概念
- 线程的相关概念--Java基础065
- 再学java基础(10) 线程概念&操作
- java线程(1)--概念基础
- Java基础——线程范围内的共享数据概念和作用
- Java线程安全基础概念解析
- java基础进阶(文件列表,线程,线程组)编程实例(4篇)
- 学习Java的30个基本概念-Java基础-Java-编程开发
- 范例解说Java里的线程概念与线程同步技术
- Java线程:概念与原理
- Java 101之线程基础
- Java 线程/内存模型的缺陷和增强-Java基础-Java-编程开发
- java基础知识(线程方面)
- JAVA程序员必读:基础篇(1.b)面向对象编程概念
- JAVA程序员必读:基础篇(1.a)面向对象编程概念
