Dalvik学习笔记--启动过程
2016-07-26 23:41
417 查看
学习老罗的博客,顺便记点笔记,强化记忆
代码用的4.3,与老罗不一样的地方会标注出来
从AndroidRuntime.start开始
GetStaticMethodID函数用于获取方法id,一个参数为目标类,第二个为方法名,第三个是参数描述(是不是很像smali代码)
CallStaticVoidMethod函数第一个参数为目标类,第二个为方法id,第三个是可变参数
这里有个小小的变化就是toSlashClassName将原来的几行代码封装了一下。
实例创建startVm函数
该函数很长,但是大致可以分为三部分
比如在propBuf中存放dalvik.vm.checkjni的信息,如果propBuf字符串为“true”,就将checkJni设置为true
当然最后调用JNI_CreateJavaVM函数。
上述提到的DvmGlobals结构体定义文件dalvik/vm/Globals.h中,JNIInvokeInterface结构体定义在文件dalvik/libnativehelper/include/nativehelper/jni.h中,JavaVMExt和JNIEnvExt结构体定义在文件dalvik/vm/JniInternal.h中。
接下来是dvmCreateJNIEnv函数
再看dvmStartup函数
到这里实例的创建和初始化工作就算完成了,dvmStartup函数也算结束了,要注意的是dvmStartup函数反回的是一个字符串。
JNI_CreateJavaVM函数中是这样调用的
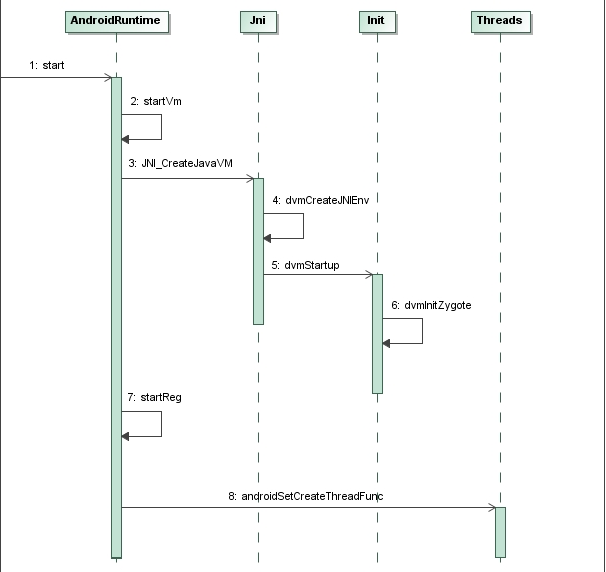
最后附上老罗的图
代码用的4.3,与老罗不一样的地方会标注出来
从AndroidRuntime.start开始
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const char* options)
{
......
/* start the virtual machine */
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//此函数为空函数,原文注释:If AndroidRuntime had anything to do here, we'd have done it in 'start'.
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
jstring optionsStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");<span style="white-space:pre">
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(2, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//构造2个元素的String数组
optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options);<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//第一个元素为类名
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 1, optionsStr);<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//第二个为设置
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//将字符串中的 . 替换为 /
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//获取main方法的id
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//调用main方法
......
}GetStaticMethodID函数用于获取方法id,一个参数为目标类,第二个为方法名,第三个是参数描述(是不是很像smali代码)
CallStaticVoidMethod函数第一个参数为目标类,第二个为方法id,第三个是可变参数
这里有个小小的变化就是toSlashClassName将原来的几行代码封装了一下。
实例创建startVm函数
该函数很长,但是大致可以分为三部分
int AndroidRuntime::startVm(JavaVM** pJavaVM, JNIEnv** pEnv)
{
int result = -1;
JavaVMInitArgs initArgs;
JavaVMOption opt;
char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char stackTraceFileBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char dexoptFlagsBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char enableAssertBuf[sizeof("-ea:")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char jniOptsBuf[sizeof("-Xjniopts:")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char heapstartsizeOptsBuf[sizeof("-Xms")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char heapsizeOptsBuf[sizeof("-Xmx")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char heapgrowthlimitOptsBuf[sizeof("-XX:HeapGrowthLimit=")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char heapminfreeOptsBuf[sizeof("-XX:HeapMinFree=")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char heapmaxfreeOptsBuf[sizeof("-XX:HeapMaxFree=")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char heaptargetutilizationOptsBuf[sizeof("-XX:HeapTargetUtilization=")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char extraOptsBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char* stackTraceFile = NULL;
bool checkJni = false;
bool checkDexSum = false;
bool logStdio = false;
enum {
kEMDefault,
kEMIntPortable,
kEMIntFast,
kEMJitCompiler,
} executionMode = kEMDefault;先声明字符串用于存放配置信息,声明标志变量property_get("dalvik.vm.checkjni", propBuf, "");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "true") == 0) {
checkJni = true;
} else if (strcmp(propBuf, "false") != 0) {
/* property is neither true nor false; fall back on kernel parameter */
property_get("ro.kernel.android.checkjni", propBuf, "");
if (propBuf[0] == '1') {
checkJni = true;
}
}
......
/* Force interpreter-only mode for selected methods */
char jitMethodBuf[sizeof("-Xjitmethod:") + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("dalvik.vm.jit.method", propBuf, "");
if (strlen(propBuf) > 0) {
strcpy(jitMethodBuf, "-Xjitmethod:");
strcat(jitMethodBuf, propBuf);
opt.optionString = jitMethodBuf;
mOptions.add(opt);
}第二部分大多都是上述这种形式,先用property_get函数,在之前声明的字符串中存放配置信息,比较后设置对应的标志变量比如在propBuf中存放dalvik.vm.checkjni的信息,如果propBuf字符串为“true”,就将checkJni设置为true
if (executionMode == kEMIntPortable) {
opt.optionString = "-Xint:portable";
mOptions.add(opt);
} else if (executionMode == kEMIntFast) {
opt.optionString = "-Xint:fast";
mOptions.add(opt);
} else if (executionMode == kEMJitCompiler) {
opt.optionString = "-Xint:jit";
mOptions.add(opt);
}
if (checkDexSum) {
/* perform additional DEX checksum tests */
opt.optionString = "-Xcheckdexsum";
mOptions.add(opt);
}
......再根据这些标志变量进行设置。/*
* Initialize the VM.
*
* The JavaVM* is essentially per-process, and the JNIEnv* is per-thread.
* If this call succeeds, the VM is ready, and we can start issuing
* JNI calls.
*/
if (JNI_CreateJavaVM(pJavaVM, pEnv, &initArgs) < 0) {
ALOGE("JNI_CreateJavaVM failed\n");
goto bail;
}当然最后调用JNI_CreateJavaVM函数。
/*
* Create a new VM instance.
*
* The current thread becomes the main VM thread. We return immediately,
* which effectively means the caller is executing in a native method.
*/
jint JNI_CreateJavaVM(JavaVM** p_vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* vm_args) {
const JavaVMInitArgs* args = (JavaVMInitArgs*) vm_args;
if (args->version < JNI_VERSION_1_2) {
return JNI_EVERSION;
}
// TODO: don't allow creation of multiple VMs -- one per customer for now
/* zero globals; not strictly necessary the first time a VM is started */
memset(&gDvm, 0, sizeof(gDvm));
/*
* Set up structures for JNIEnv and VM.
*/
JavaVMExt* pVM = (JavaVMExt*) calloc(1, sizeof(JavaVMExt));
pVM->funcTable = &gInvokeInterface;
pVM->envList = NULL;
dvmInitMutex(&pVM->envListLock);
UniquePtr<const char*[]> argv(new const char*[args->nOptions]);
memset(argv.get(), 0, sizeof(char*) * (args->nOptions));
/*
* Convert JNI args to argv.
*
* We have to pull out vfprintf/exit/abort, because they use the
* "extraInfo" field to pass function pointer "hooks" in. We also
* look for the -Xcheck:jni stuff here.
*/
int argc = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < args->nOptions; i++) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//收集虚拟机相关信息
const char* optStr = args->options[i].optionString;
if (optStr == NULL) {
dvmFprintf(stderr, "ERROR: CreateJavaVM failed: argument %d was NULL\n", i);
return JNI_ERR;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "vfprintf") == 0) {
gDvm.vfprintfHook = (int (*)(FILE *, const char*, va_list))args->options[i].extraInfo;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "exit") == 0) {
gDvm.exitHook = (void (*)(int)) args->options[i].extraInfo;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "abort") == 0) {
gDvm.abortHook = (void (*)(void))args->options[i].extraInfo;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "sensitiveThread") == 0) {
gDvm.isSensitiveThreadHook = (bool (*)(void))args->options[i].extraInfo;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "-Xcheck:jni") == 0) {
gDvmJni.useCheckJni = true;
} else if (strncmp(optStr, "-Xjniopts:", 10) == 0) {
char* jniOpts = strdup(optStr + 10);
size_t jniOptCount = 1;
for (char* p = jniOpts; *p != 0; ++p) {
if (*p == ',') {
++jniOptCount;
*p = 0;
}
}
char* jniOpt = jniOpts;
for (size_t i = 0; i < jniOptCount; ++i) {
if (strcmp(jniOpt, "warnonly") == 0) {
gDvmJni.warnOnly = true;
} else if (strcmp(jniOpt, "forcecopy") == 0) {
gDvmJni.forceCopy = true;
} else if (strcmp(jniOpt, "logThirdPartyJni") == 0) {
gDvmJni.logThirdPartyJni = true;
} else {
dvmFprintf(stderr, "ERROR: CreateJavaVM failed: unknown -Xjniopts option '%s'\n",
jniOpt);
return JNI_ERR;
}
jniOpt += strlen(jniOpt) + 1;
}
free(jniOpts);
} else {
/* regular option */
argv[argc++] = optStr;
}
}
if (gDvmJni.useCheckJni) {
dvmUseCheckedJniVm(pVM);
}
if (gDvmJni.jniVm != NULL) {
dvmFprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Dalvik only supports one VM per process\n");
return JNI_ERR;
}
gDvmJni.jniVm = (JavaVM*) pVM;
/*
* Create a JNIEnv for the main thread. We need to have something set up
* here because some of the class initialization we do when starting
* up the VM will call into native code.
*/
JNIEnvExt* pEnv = (JNIEnvExt*) dvmCreateJNIEnv(NULL);
/* Initialize VM. */
gDvm.initializing = true;
std::string status =
dvmStartup(argc, argv.get(), args->ignoreUnrecognized, (JNIEnv*)pEnv);<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//初始化虚拟机,关键函数,其他代码都是为他的参数做准备
gDvm.initializing = false;
if (!status.empty()) {
free(pEnv);
free(pVM);
ALOGW("CreateJavaVM failed: %s", status.c_str());
return JNI_ERR;
}
/*
* Success! Return stuff to caller.
*/
dvmChangeStatus(NULL, THREAD_NATIVE);
*p_env = (JNIEnv*) pEnv;
*p_vm = (JavaVM*) pVM;
ALOGV("CreateJavaVM succeeded");
return JNI_OK;
}代码注释很全,简单说一下。先给一个虚拟机实例分配空间,初始化需要切换当前线程状态,需要保存设置和创建一个运行环境,gDvm就是用来收集虚拟机信息的全局变量(给实例分配的空间也保存在当中),用于在不同线程状态间传递虚拟机实例,argv保存从vm_args传递过来的参数,通过这个几个变量就可以切换线程状态创建虚拟机实例。创建完成后再通过dvmChangeStatus切换回去(Return stuff to caller)。然后将实例(pVM)和环境(pEnv)传递给调用者。上述提到的DvmGlobals结构体定义文件dalvik/vm/Globals.h中,JNIInvokeInterface结构体定义在文件dalvik/libnativehelper/include/nativehelper/jni.h中,JavaVMExt和JNIEnvExt结构体定义在文件dalvik/vm/JniInternal.h中。
接下来是dvmCreateJNIEnv函数
JNIEnv* dvmCreateJNIEnv(Thread* self) {
JavaVMExt* vm = (JavaVMExt*) gDvmJni.jniVm;
//if (self != NULL)
// ALOGI("Ent CreateJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self);
assert(vm != NULL);
JNIEnvExt* newEnv = (JNIEnvExt*) calloc(1, sizeof(JNIEnvExt));<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//创建一个JNIEnvExt对象
newEnv->funcTable = &gNativeInterface;<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//设置本地借口表
if (self != NULL) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//self表示所要关联的线程
dvmSetJniEnvThreadId((JNIEnv*) newEnv, self);<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//设置关联的函数
assert(newEnv->envThreadId != 0);
} else {
/* make it obvious if we fail to initialize these later */
newEnv->envThreadId = 0x77777775;<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//表示还未与线程关联
newEnv->self = (Thread*) 0x77777779;
}
if (gDvmJni.useCheckJni) {
dvmUseCheckedJniEnv(newEnv);
}
ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&vm->envListLock);
/* insert at head of list */
newEnv->next = vm->envList;<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//newEnv的宿主虚拟机是vm,也就是之前创建的实例
assert(newEnv->prev == NULL);
if (vm->envList == NULL) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//将newEnv插入到vm->envList链表中
// rare, but possible
vm->envList = newEnv;
} else {
vm->envList->prev = newEnv;
}
vm->envList = newEnv;
//if (self != NULL)
// ALOGI("Xit CreateJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self);
return (JNIEnv*) newEnv;
} 在一个Dalvik虚拟机里面,可以运行多个线程。所有关联有JNI环境的线程都有一个对应的JNIEnvExt对象,这些JNIEnvExt对象相互连接在一起保存在用来描述其宿主Dalvik虚拟机的一个JavaVMExt对象的成员变量envList中。因此,前面创建的JNIEnvExt对象需要连接到其宿主Dalvik虚拟机的JavaVMExt链表中去。再看dvmStartup函数
std::string dvmStartup(int argc, const char* const argv[],
bool ignoreUnrecognized, JNIEnv* pEnv)
{
ScopedShutdown scopedShutdown;
assert(gDvm.initializing);
ALOGV("VM init args (%d):", argc);
for (int i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
ALOGV(" %d: '%s'", i, argv[i]);
}
setCommandLineDefaults();<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//设置默认项
/*
* Process the option flags (if any).
*/
int cc = processOptions(argc, argv, ignoreUnrecognized);<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//处理启动选项
if (cc != 0) {
if (cc < 0) {
dvmFprintf(stderr, "\n");
usage("dalvikvm");
}
return "syntax error";
}与老罗代码相比没有了dvmPropertiesStartup来分配空间/*
* Initialize components.
*/
dvmQuasiAtomicsStartup();
if (!dvmAllocTrackerStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//对象分配记录子模块
return "dvmAllocTrackerStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmGcStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//GC子模块
return "dvmGcStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmThreadStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//线程列表
return "dvmThreadStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmInlineNativeStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//内建Native函数表
return "dvmInlineNativeStartup";
}
if (!dvmRegisterMapStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//寄存器映射集
return "dvmRegisterMapStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmInstanceofStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//实例操作符子模块
return "dvmInstanceofStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmClassStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//启动类加载器
return "dvmClassStartup failed";
}
/*
* At this point, the system is guaranteed to be sufficiently
* initialized that we can look up classes and class members. This
* call populates the gDvm instance with all the class and member
* references that the VM wants to use directly.
*/
if (!dvmFindRequiredClassesAndMembers()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//重要类和函数
return "dvmFindRequiredClassesAndMembers failed";
}
if (!dvmStringInternStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//字符串池
return "dvmStringInternStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmNativeStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//so库加载表
return "dvmNativeStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmInternalNativeStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//内部Native函数表
return "dvmInternalNativeStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmJniStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//全局引用表
return "dvmJniStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmProfilingStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//性能分析子模块
return "dvmProfilingStartup failed";
}
/*
* Create a table of methods for which we will substitute an "inline"
* version for performance.
*/
if (!dvmCreateInlineSubsTable()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//内联函数表
return "dvmCreateInlineSubsTable failed";
}
/*
* Miscellaneous class library validation.
*/
if (!dvmValidateBoxClasses()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//验证虚拟机中相应的装箱类
return "dvmValidateBoxClasses failed";
}
/*
* Do the last bits of Thread struct initialization we need to allow
* JNI calls to work.
*/
if (!dvmPrepMainForJni(pEnv)) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//准备主线程JNI环境
return "dvmPrepMainForJni failed";
}
/*
* Explicitly initialize java.lang.Class. This doesn't happen
* automatically because it's allocated specially (it's an instance
* of itself). Must happen before registration of system natives,
* which make some calls that throw assertions if the classes they
* operate on aren't initialized.
*/
if (!dvmInitClass(gDvm.classJavaLangClass)) {//确保目标类初始化
return "couldn't initialized java.lang.Class";
}
/*
* Register the system native methods, which are registered through JNI.
*/
if (!registerSystemNatives(pEnv)) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//为JAVA核心类注册JNI方法
return "couldn't register system natives";
}
/*
* Do some "late" initialization for the memory allocator. This may
* allocate storage and initialize classes.
*/
if (!dvmCreateStockExceptions()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//预创建与内存相关的异样对象
return "dvmCreateStockExceptions failed";
}
/*
* At this point, the VM is in a pretty good state. Finish prep on
* the main thread (specifically, create a java.lang.Thread object to go
* along with our Thread struct). Note we will probably be executing
* some interpreted class initializer code in here.
*/
if (!dvmPrepMainThread()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//为主线程创建ThreadGroup对象
return "dvmPrepMainThread failed";
}
/*
* Make sure we haven't accumulated any tracked references. The main
* thread should be starting with a clean slate.
*/
if (dvmReferenceTableEntries(&dvmThreadSelf()->internalLocalRefTable) != 0)<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//确保主线程当前不应用JAVA对象,保证一个干净的入口
{
ALOGW("Warning: tracked references remain post-initialization");
dvmDumpReferenceTable(&dvmThreadSelf()->internalLocalRefTable, "MAIN");
}
/* general debugging setup */
if (!dvmDebuggerStartup()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//初始化调试环境
return "dvmDebuggerStartup failed";
}
if (!dvmGcStartupClasses()) {<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>// GC class
return "dvmGcStartupClasses failed";
}初始化各项子模块/*
* Init for either zygote mode or non-zygote mode. The key difference
* is that we don't start any additional threads in Zygote mode.
*/
if (gDvm.zygote) {
if (!initZygote()) {
return "initZygote failed";
}
} else {
if (!dvmInitAfterZygote()) {
return "dvmInitAfterZygote failed";
}
}判断是否在zygote中启动虚拟机,注意是initZygote不是dvmInitZygote/*
* Do zygote-mode-only initialization.
*/
static bool initZygote()
{
/* zygote goes into its own process group */
setpgid(0,0);
// See storage config details at http://source.android.com/tech/storage/ // Create private mount namespace shared by all children
if (unshare(CLONE_NEWNS) == -1) {
SLOGE("Failed to unshare(): %s", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
// Mark rootfs as being a slave so that changes from default
// namespace only flow into our children.
if (mount("rootfs", "/", NULL, (MS_SLAVE | MS_REC), NULL) == -1) {
SLOGE("Failed to mount() rootfs as MS_SLAVE: %s", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
// Create a staging tmpfs that is shared by our children; they will
// bind mount storage into their respective private namespaces, which
// are isolated from each other.
const char* target_base = getenv("EMULATED_STORAGE_TARGET");
if (target_base != NULL) {
if (mount("tmpfs", target_base, "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID | MS_NODEV,
"uid=0,gid=1028,mode=0050") == -1) {
SLOGE("Failed to mount tmpfs to %s: %s", target_base, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
}
// Mark /system as NOSUID | NODEV
const char* android_root = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (android_root == NULL) {
SLOGE("environment variable ANDROID_ROOT does not exist?!?!");
return -1;
}
std::string mountDev(getMountsDevDir(android_root));
if (mountDev.empty()) {
SLOGE("Unable to find mount point for %s", android_root);
return -1;
}
if (mount(mountDev.c_str(), android_root, "none",
MS_REMOUNT | MS_NOSUID | MS_NODEV | MS_RDONLY | MS_BIND, NULL) == -1) {
SLOGE("Remount of %s failed: %s", android_root, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
#ifdef HAVE_ANDROID_OS
if (prctl(PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS, 1, 0, 0, 0) < 0) {
if (errno == EINVAL) {
SLOGW("PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS failed. "
"Is your kernel compiled correctly?: %s", strerror(errno));
// Don't return -1 here, since it's expected that not all
// kernels will support this option.
} else {
SLOGW("PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS failed: %s", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
}
#endif
return true;
}注释比较全,主要是父子进程共享资源的问题。到这里实例的创建和初始化工作就算完成了,dvmStartup函数也算结束了,要注意的是dvmStartup函数反回的是一个字符串。
JNI_CreateJavaVM函数中是这样调用的
std::string status = dvmStartup(argc, argv.get(), args->ignoreUnrecognized, (JNIEnv*)pEnv);
if (!status.empty()) {
free(pEnv);
free(pVM);
ALOGW("CreateJavaVM failed: %s", status.c_str());
return JNI_ERR;
}返回到AndroidRuntime::start,之后执行的函数是startReg,注册Android核心类的JNI方法int AndroidRuntime::startReg(JNIEnv* env)
{
/*
* This hook causes all future threads created in this process to be
* attached to the JavaVM. (This needs to go away in favor of JNI
* Attach calls.)
*/
androidSetCreateThreadFunc((android_create_thread_fn) javaCreateThreadEtc);
ALOGV("--- registering native functions ---\n");
/*
* Every "register" function calls one or more things that return
* a local reference (e.g. FindClass). Because we haven't really
* started the VM yet, they're all getting stored in the base frame
* and never released. Use Push/Pop to manage the storage.
*/
env->PushLocalFrame(200);
if (register_jni_procs(gRegJNI, NELEM(gRegJNI), env) < 0) {
env->PopLocalFrame(NULL);
return -1;
}
env->PopLocalFrame(NULL);
//createJavaThread("fubar", quickTest, (void*) "hello");
return 0;
}总结:创建实例,处理配置信息 ——> 收集配置信息,创建环境 ——> 切换线程状态,初始化虚拟机实例 ——> 注册核心方法 ——> 启动main方法最后附上老罗的图

相关文章推荐
- Android中实现根据资源名获取资源ID
- (转) 实时SLAM的未来及与深度学习的比较
- Java线程优先级
- 利用Java针对MySql封装的jdbc框架类 JdbcUtils 完整实现(包含增删改查、JavaBean反射原理,附源码)
- PHP.INI配置:文件上传功能配置
- JAVA 过滤标签将html内容转换为文本
- lucene源码分析---7
- 暑假集训第1天链表-数据结构上机测试2-1:单链表操作A
- 在express4上使用socket.io 1.4.6版本的心得(node.js实战读书笔记2)
- C - Can you find it? HDU 2141
- 销售数据聚类、关联分析
- 线程的生命周期及状态转换
- fatal error LNK1123: 转换到 COFF 期间失败: 文件无效或损坏
- (转) ICCV 2015:21篇最火爆研究论文
- linux基础-crontab
- Cpp Primer - constexpr
- TensorFlow 简易安装
- iOS-应用生命周期
- mybatis+MySQL--CRUD
- File类
