大话设计模式25----中介者模式
2016-07-26 16:35
567 查看
大话设计模式
1 中介者模式(Mediator)结构图
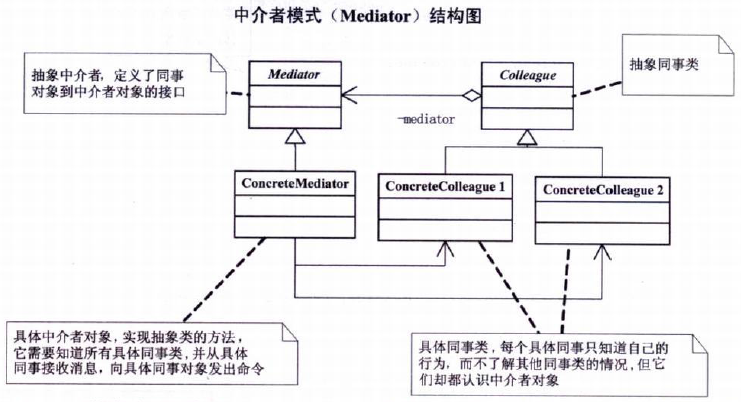
2 对中介者模式的一些解释
概念:用一个中介对象来封装一些列的对象交互。中介者使各对象不需要显示地相互吸引,从而使其偶尔松散,而且可以独立地改变他们之间的交互。【DP】中介者模式的优点
Mediator的出现减少了各个Colleague的耦合,使得可以独立地改变和复用各个Colleague,比如任何国家的改变不会影响到其他国家,而只是与安理会发生变化。
由于把对象如何协作进行了抽象,将中介作为一个独立的概念并将其封装起在一个对象中,这样关注的对象就从对象各自本身的行为转移到他们之间的交互上来,也就是站在一个更宏观的角度去看待系统。
中介者模式的缺点
由于ConcreteMediator控制了集中化,于是就把交互复杂性变为了中介者的复杂性,这就使得中介者会变得比任何一个ConcreteColleague都复杂。
中介者模式的用途
中介者模式一般应用于一组对象以定义良好但是复杂的方式进行通信的场合,以及想定制一个分布在多个类中的行为,而又不想生成太多的子类的场合。
3 C++源代码实现
3.1 代码结构图
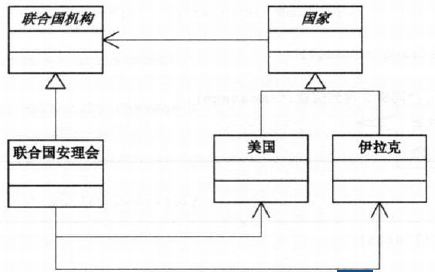
3.2 源代码
UnitedNations.h类#ifndef _UNITEDNATIONS_H_
#define _UNITEDNATIONS_H_
#include<string>
using std::string;
class Country;
//Mediator
class UnitedNations
{
public:
virtual void Declare(const string &message, Country *colleague) = 0;
virtual void setUSA(Country *contry) = 0;
virtual void setIraq(Country *country) = 0;
};
//ConcreteMediator
class UnitedNationsSecurityCouncil :public UnitedNations
{
private:
Country *colleague1;
Country *clooeague2;
public:
void setUSA(Country *country) override;
void setIraq(Country *country) override;
void Declare(const string &message, Country *colleague) override;
};
#endifUnitedNations.cpp
#include"UnitedNations.h"
#include"Country.h"
void UnitedNationsSecurityCouncil::setUSA(Country *country)
{
this->colleague1 = country;
}
void UnitedNationsSecurityCouncil::setIraq(Country *country)
{
this->clooeague2 = country;
}
void UnitedNationsSecurityCouncil::Declare(const string &message, Country *colleague)
{
if (typeid(*colleague) == typeid(*colleague1))
{
colleague1->GetMessage(message);
}
else
{
clooeague2->GetMessage(message);
}
}Country.h
#ifndef _COUNTRY_H_
#define _COUNTRY_H_
#include<string>
using std::string;
class UnitedNations;
class Country
{
protected:
UnitedNations * mediator;
public:
virtual void Declare(const string &message) = 0;
virtual void GetMessage(const string &message) = 0;
};
class USA :public Country
{
public:
USA(UnitedNations *un);
void Declare(const string &message) override;
void GetMessage(const string &message) override;
};
class Iraq :public Country
{
public:
Iraq(UnitedNations *un);
void Declare(const string &message) override;
void GetMessage(const string &message) override;
};
#endifCountry.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include"Country.h"
#include"UnitedNations.h"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
USA::USA(UnitedNations *un)
{
this->mediator = un;
}
void USA::Declare(const string &message)
{
mediator->Declare(message, this);
}
void USA::GetMessage(const string &message)
{
cout << "美国获得对象信息:" << message << endl;
}
Iraq::Iraq(UnitedNations *un)
{
this->mediator = un;
}
void Iraq::Declare(const string &message)
{
mediator->Declare(message, this);
}
void Iraq::GetMessage(const string &message)
{
cout << "伊拉克获得对象信息:" << message << endl;
}客户端Client
#include"Country.h"
#include"UnitedNations.h"
int main()
{
UnitedNationsSecurityCouncil *unsc = new UnitedNationsSecurityCouncil();
USA *usa = new USA(unsc);
Iraq *iraq = new Iraq(unsc);
unsc->setUSA(usa);
unsc->setIraq(iraq);
usa->Declare("不准研究核武器,否则我们将发动战争");
iraq->Declare("我们没有核武器,但是我们不怕战争");
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果:
美国获得对象信息:不准研究核武器,否则我们将发动战争 伊拉克获得对象信息:我们没有核武器,但是我们不怕战争 请按任意键继续. . .
相关文章推荐
- 使用C++实现JNI接口需要注意的事项
- 关于指针的一些事情
- c++ primer 第五版 笔记前言
- share_ptr的几个注意点
- Lua中调用C++函数示例
- Lua教程(一):在C++中嵌入Lua脚本
- Lua教程(二):C++和Lua相互传递数据示例
- C++联合体转换成C#结构的实现方法
- C++高级程序员成长之路
- C++编写简单的打靶游戏
- C++ 自定义控件的移植问题
- C++变位词问题分析
- C/C++数据对齐详细解析
- C++基于栈实现铁轨问题
- C++中引用的使用总结
- 使用Lua来扩展C++程序的方法
- C++中调用Lua函数实例
- Lua和C++的通信流程代码实例
- C++的template模板中class与typename关键字的区别分析
- C与C++之间相互调用实例方法讲解
