poj 2631 1985 hdoj 2196 <树的直径>
2016-07-26 14:02
423 查看
Roads in the North
Description
Building and maintaining roads among communities in the far North is an expensive business. With this in mind, the roads are build such that there is only one route from a village to a village that does not pass through some other village twice.
Given is an area in the far North comprising a number of villages and roads among them such that any village can be reached by road from any other village. Your job is to find the road distance between the two most remote villages in the area.
The area has up to 10,000 villages connected by road segments. The villages are numbered from 1.
Input
Input to the problem is a sequence of lines, each containing three positive integers: the number of a village, the number of a different village, and the length of the road segment connecting the villages in kilometers. All road segments are two-way.
Output
You are to output a single integer: the road distance between the two most remote villages in the area.
Sample Input
Sample Output
Source
The UofA Local 1999.10.16
树的直径 即树中任意两点距离的最大值。
求树的直径:
步骤1:从任意一点p求最远点Q。
此最远点Q必是树的直径的一个顶点--
当p点在树的直径上时,Q一定是树的直径的一个顶点。
当p点不在树的直径上,则p到Q必然于树的直径相交于一点O,那么O到Q必然就是树的直径的后半段了,Q依然是树的直径的一个顶点。
步骤2:从Q点求最远距离。
不定数组用queue和vector相比较--vector在存储和查询时更高效
queue代码超时:
vector代码:
Cow Marathon
Description
After hearing about the epidemic of obesity in the USA, Farmer John wants his cows to get more exercise, so he has committed to create a bovine marathon for his cows to run. The marathon route will include a pair of farms and a path comprised of a sequence
of roads between them. Since FJ wants the cows to get as much exercise as possible he wants to find the two farms on his map that are the farthest apart from each other (distance being measured in terms of total length of road on the path between the two farms).
Help him determine the distances between this farthest pair of farms.
Input
* Lines 1.....: Same input format as "Navigation Nightmare".
Output
* Line 1: An integer giving the distance between the farthest pair of farms.
Sample Input
Sample Output
Hint
The longest marathon runs from farm 2 via roads 4, 1, 6 and 3 to farm 5 and is of length 20+3+13+9+7=52.
Source
USACO 2004 February
所以把上面代码的10100改成40100----------main中加入输n和m,方向只输入不需要记录就行了
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 5643 Accepted Submission(s): 2821
Problem Description
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the
net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.
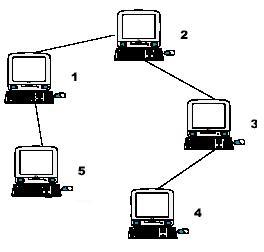
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also
get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
Input
Input file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N (N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers - number of computer, to which i-th computer is connected
and length of cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9. Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
Output
For each case output N lines. i-th line must contain number Si for i-th computer (1<=i<=N).
Sample Input
5
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
Sample Output
3
2
3
4
4
Author
scnu
题意:求每个电脑到其他电脑的最远距离:
数的直径的应用:树上各点到距离其最远的点一定是树的直径的一个顶点--
所以我们可以先求出树的直径的两个顶点--然后从两个顶点求到每个点的距离--
每个电脑的最远距离就是到两个顶点距离的最大值
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int fer[10200];
struct node{
int to,w;
int next;
}bian[22000];
int head[10200];
struct node1 {
int dian;
int chang;
bool friend operator <(node1 xx,node1 yy)
{
return xx.chang>yy.chang;
}
}now,qian;
int length[10200][2];
int bfs(int xx,int lei)
{
int lp=0;
priority_queue<node1> que;
bool fafe[10200];
memset(fafe,true,sizeof(fafe));
now.dian=xx;now.chang=0;
que.push(now);
fafe[xx]=false;
int i,j,x,y;
while (!que.empty())
{
now=que.top();
que.pop();
x=now.dian;
if (lei==1)
length[x][0]=now.chang;
else if (lei==2)
length[x][1]=now.chang;
// printf("0000 %d %d\n",x,head[x]);
lp=x;
for (i=head[x];i!=-1;i=bian[i].next)
{
// printf("%d 66\n",i);
if (fafe[bian[i].to])
{
qian.dian=bian[i].to;
qian.chang=now.chang+bian[i].w;
fafe[bian[i].to]=false;
que.push(qian);
}
}
}
return lp;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while (~scanf("%d",&n))
{
int a,b;
memset(bian,0,sizeof(bian));
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
head[i]=-1;
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
bian[2*i-4].to=a;
bian[i*2-4].w=b;
bian[2*i-4].next=head[i];
head[i]=2*i-4;
bian[2*i-3].to=i;
bian[i*2-3].w=b;
bian[2*i-3].next=head[a];
head[a]=2*i-3;
}
memset(length,0,sizeof(length));
int kai=bfs(1,0);
int jie=bfs(kai,1);
bfs(jie,2);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d\n",max(length[i][0],length[i][1]));
}
return 0;
}
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 2502 | Accepted: 1226 |
Building and maintaining roads among communities in the far North is an expensive business. With this in mind, the roads are build such that there is only one route from a village to a village that does not pass through some other village twice.
Given is an area in the far North comprising a number of villages and roads among them such that any village can be reached by road from any other village. Your job is to find the road distance between the two most remote villages in the area.
The area has up to 10,000 villages connected by road segments. The villages are numbered from 1.
Input
Input to the problem is a sequence of lines, each containing three positive integers: the number of a village, the number of a different village, and the length of the road segment connecting the villages in kilometers. All road segments are two-way.
Output
You are to output a single integer: the road distance between the two most remote villages in the area.
Sample Input
5 1 6 1 4 5 6 3 9 2 6 8 6 1 7
Sample Output
22
Source
The UofA Local 1999.10.16
树的直径 即树中任意两点距离的最大值。
求树的直径:
步骤1:从任意一点p求最远点Q。
此最远点Q必是树的直径的一个顶点--
当p点在树的直径上时,Q一定是树的直径的一个顶点。
当p点不在树的直径上,则p到Q必然于树的直径相交于一点O,那么O到Q必然就是树的直径的后半段了,Q依然是树的直径的一个顶点。
步骤2:从Q点求最远距离。
不定数组用queue和vector相比较--vector在存储和查询时更高效
queue代码超时:
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct no{
int dian;
int chang;
bool friend operator <(no xx,no yy)
{
return xx.chang>yy.chang;
}
} now,qian;
struct node {
int ge;
queue <no> s1,s2;
}dian[10100];
int n,ll,chang;
void bfs(int ii)
{
ll=0;chang=0;
bool fafe[10100];
memset(fafe,true,sizeof(fafe));
priority_queue<no> que;fafe[ii]=false;
for (int i=0;i<dian[ii].ge;i++)
{
now=dian[ii].s1.front();
dian[ii].s1.pop();
dian[ii].s2.push(now);
que.push(now);
fafe[now.dian]=false;
}
while (!que.empty())
{
now=que.top();
que.pop();
ll=now.dian;chang=now.chang;
for (int i=0;i<dian[now.dian].ge;i++)
{
qian=dian[now.dian].s1.front();
dian[now.dian].s1.pop();
dian[now.dian].s2.push(qian);
if (fafe[qian.dian])
{
qian.chang+=now.chang;
que.push(qian);
fafe[qian.dian]=false;
}
}
}
}
void dfs(int ii)
{
ll=0;chang=0;
bool fafe[10100];
memset(fafe,true,sizeof(fafe));
priority_queue<no> que;fafe[ii]=false;
for (int i=0;i<dian[ii].ge;i++)
{
now=dian[ii].s2.front();
dian[ii].s2.pop();
que.push(now);
fafe[now.dian]=false;
}
while (!que.empty())
{
now=que.top();
que.pop();
ll=now.dian;chang=now.chang;
for (int i=0;i<dian[now.dian].ge;i++)
{
qian=dian[now.dian].s2.front();
dian[now.dian].s2.pop();
if (fafe[qian.dian])
{
qian.chang+=now.chang;
que.push(qian);
fafe[qian.dian]=false;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
n=0;
for (int i=0;i<10100;i++)
dian[i].ge=0;
while (scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)==3)
{
now.dian=b;now.chang=c;
dian[a].s1.push(now);
dian[a].ge++;
now.dian=a;
dian.s1.push(now);
dian[b].ge++;
n=max(n,max(a,b));
}
bfs(1);
// printf("%d\n",ll);
dfs(ll);
printf("%d\n",chang);
//printf("chu\n");
return 0;
}vector代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct no{
int dian;
int chang;
bool friend operator <(no xx,no yy)
{
return xx.chang>yy.chang;
}
} now,qian;
struct node {
int ge;
vector <int > chang ;
vector <int > dian ;
}dian[10100];
int n,ll,chang,dd,cl;
void bfs(int ii)
{
ll=0;chang=0;
bool fafe[10100];
memset(fafe,true,sizeof(fafe));
priority_queue<no> que;fafe[ii]=false;
for (int i=0;i<dian[ii].ge;i++)
{
dd=dian[ii].dian[i];
cl=dian[ii].chang[i];
now.chang=cl;
now.dian=dd;
que.push(now);
fafe[dd]=false;
}
while (!que.empty())
{
qian=que.top();
que.pop();
ll=qian.dian;chang=qian.chang;ii=qian.dian;
for (int i=0;i<dian[ii].ge;i++)
{
dd=dian[ii].dian[i];
cl=dian[ii].chang[i];
now.chang=cl+qian.chang;
now.dian=dd;
if (fafe[dd])
{
que.push(now);
fafe[dd]=false;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
n=0;
for (int i=0;i<10100;i++)
dian[i].ge=0;
while (~scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c))
{
dian[a].dian.push_back(b);
dian[a].chang.push_back(c);
dian[a].ge++;
dian[b].dian.push_back(a);
dian[b].chang.push_back(c);
dian[b].ge++;
n=max(n,max(a,b));
}
bfs(1);
// printf("%d\n",ll);
bfs(ll);
printf("%d\n",chang);
return 0;
}Cow Marathon
| [b]Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 30000K | |
| Total Submissions: 4771 | Accepted: 2348 | |
| Case Time Limit: 1000MS |
After hearing about the epidemic of obesity in the USA, Farmer John wants his cows to get more exercise, so he has committed to create a bovine marathon for his cows to run. The marathon route will include a pair of farms and a path comprised of a sequence
of roads between them. Since FJ wants the cows to get as much exercise as possible he wants to find the two farms on his map that are the farthest apart from each other (distance being measured in terms of total length of road on the path between the two farms).
Help him determine the distances between this farthest pair of farms.
Input
* Lines 1.....: Same input format as "Navigation Nightmare".
Output
* Line 1: An integer giving the distance between the farthest pair of farms.
Sample Input
7 6 1 6 13 E 6 3 9 E 3 5 7 S 4 1 3 N 2 4 20 W 4 7 2 S
Sample Output
52
Hint
The longest marathon runs from farm 2 via roads 4, 1, 6 and 3 to farm 5 and is of length 20+3+13+9+7=52.
Source
USACO 2004 February
1.题目虽然既给了点数也给了边数,但实际上边数永远是点数-1,也就是这始终是一棵树。 2.这是一颗无根树,边也都是无向边 3.那个什么nightmare的数据格式完全是坑人的,最后那个表示方向的字符无视掉就好
所以把上面代码的10100改成40100----------main中加入输n和m,方向只输入不需要记录就行了
Computer
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 5643 Accepted Submission(s): 2821
Problem Description
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the
net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.

Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also
get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
Input
Input file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N (N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers - number of computer, to which i-th computer is connected
and length of cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9. Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
Output
For each case output N lines. i-th line must contain number Si for i-th computer (1<=i<=N).
Sample Input
5
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
Sample Output
3
2
3
4
4
Author
scnu
题意:求每个电脑到其他电脑的最远距离:
数的直径的应用:树上各点到距离其最远的点一定是树的直径的一个顶点--
所以我们可以先求出树的直径的两个顶点--然后从两个顶点求到每个点的距离--
每个电脑的最远距离就是到两个顶点距离的最大值
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int fer[10200];
struct node{
int to,w;
int next;
}bian[22000];
int head[10200];
struct node1 {
int dian;
int chang;
bool friend operator <(node1 xx,node1 yy)
{
return xx.chang>yy.chang;
}
}now,qian;
int length[10200][2];
int bfs(int xx,int lei)
{
int lp=0;
priority_queue<node1> que;
bool fafe[10200];
memset(fafe,true,sizeof(fafe));
now.dian=xx;now.chang=0;
que.push(now);
fafe[xx]=false;
int i,j,x,y;
while (!que.empty())
{
now=que.top();
que.pop();
x=now.dian;
if (lei==1)
length[x][0]=now.chang;
else if (lei==2)
length[x][1]=now.chang;
// printf("0000 %d %d\n",x,head[x]);
lp=x;
for (i=head[x];i!=-1;i=bian[i].next)
{
// printf("%d 66\n",i);
if (fafe[bian[i].to])
{
qian.dian=bian[i].to;
qian.chang=now.chang+bian[i].w;
fafe[bian[i].to]=false;
que.push(qian);
}
}
}
return lp;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while (~scanf("%d",&n))
{
int a,b;
memset(bian,0,sizeof(bian));
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
head[i]=-1;
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
bian[2*i-4].to=a;
bian[i*2-4].w=b;
bian[2*i-4].next=head[i];
head[i]=2*i-4;
bian[2*i-3].to=i;
bian[i*2-3].w=b;
bian[2*i-3].next=head[a];
head[a]=2*i-3;
}
memset(length,0,sizeof(length));
int kai=bfs(1,0);
int jie=bfs(kai,1);
bfs(jie,2);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d\n",max(length[i][0],length[i][1]));
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 8.Hibernate Open Session In View模式
- VBA CurrentRegion属性示例
- 链表基本操作(删除,插入,查找)
- 黑马程序员杭州校区,喜迎PHP 学科入驻
- 高性能Web服务器nginx
- Leach协议在ns2下函数调用视图
- C#中Thread.sleep() 【转载】
- (十六)企业部分之lvs
- JVM性能调优监控工具jps、jstack、jmap、jhat、jstat、hprof使用详解
- mapreduce生命周期的解释及其优化
- iOS 开发者文档翻译 URL Session的生命周期
- linux中的SEM_UNDO
- 设计模式_观察者模式
- mysql 主从原理
- 关于舆情项目的技术点整理(数据库版)
- 如何查看google chrome 插件源码
- C#--职业路线图
- C#中如何获取数据库中表的信息和列的信息
- java 四种reference的对比
- 更改linux系统的SHELL
