深入理解JAVA I/O系列四:RandomAccessFile
2016-07-24 10:32
836 查看
一、简述

这个是JDK上的截图,我们可以看到它的父类是Object,没有继承字节流、字符流家族中任何一个类。并且它实现了DataInput、DataOutput这两个接口,也就意味着这个类既可以读也可以写。
二、存在的意义
1、是JAVA I/O流体系中功能最丰富的文件内容访问类,它提供了众多方法来访问文件内容。2、由于可以自由访问文件的任意位置,所以如果需要访问文件的部分内容,RandomAccessFile将是更好的选择。
3、可以用来访问保存数据记录的文件,文件的记录的大小不必相同,但是其大小和位置必须是可知的。
这个类在很多资料上翻译成中文都是:随机访问文件,在中文里,随机是具有不确定的含义,指一会访问这里,一会访问那里的意思。如果以这种语义来解释的话,就会感到很困惑。其实,Random在英文中不仅仅有随机,还有任意的意思。如果中文名为任意访问文件是不是就会更好的理解。任意表示我们可以指定文件中任何一个位置去操作一个文件。
三、DEMO演示
(1)、写入文件
public class RandomAccessFileTest
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("d:/data.txt","rw");
Person p = new Person(1001,"xiaoming",1.80d);
p.write(raf);
}
}
class Person
{
int id;
String name;
double height;
public Person()
{
}
public Person(int id, String name, double height)
{
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.height = height;
}
public void write(RandomAccessFile raf) throws IOException
{
raf.write(id);
raf.writeUTF(name);
raf.writeDouble(height);
}
}执行结果:
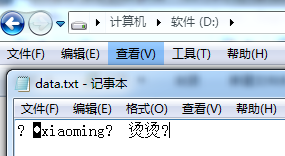
1、执行结果乱码是由于写入的是二进制文件,这个待会我们再使用程序读取。(这个跟前面介绍的DataInputStream、DataOutputStream类似)
2、第五行中,RandomAccessFile的构造函数除了指定了要写入了文件,还有另外一个参数:mod,主要用来指定打开文件的访问模式。

3、读取的方式就是读取基本数据类型,其中第28行使用的方法是:
writeUTF(String str)
使用 modified UTF-8 编码以与机器无关的方式将一个字符串写入该文件,这个方法就是将字符串写入文件,而且不用担心会出现乱码,因为使用的编码方式是UTF-8
(2)、文件读取
由于刚才写入的是二进制文件,现在使用程序去读取文件:public class RandomAccessFileTest
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("d:/data.txt", "rw");
Person p = new Person(1001, "xiaoming", 1.80d);
p.write(raf);// 写入文件后,任意访问文件的指针在文件的结尾
raf.seek(0);// 读取时,将指针重置到文件的开始位置。
Person p2 = new Person();
p2.read(raf);
System.out.println("id=" + p2.getId() + ";name=" + p2.getName()
+ ";height=" + p2.getHeight());
}
}
class Person
{
int id;
String name;
double height;
public Person()
{
}
public Person(int id, String name, double height)
{
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.height = height;
}
public void write(RandomAccessFile raf) throws IOException
{
raf.writeInt(id);
raf.writeUTF(name);
raf.writeDouble(height);
}
public void read(RandomAccessFile raf) throws IOException
{
this.id = raf.readInt();
this.name = raf.readUTF();
this.height = raf.readDouble();
}
public int getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(int id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public double getHeight()
{
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height)
{
this.height = height;
}
}执行结果:
id=1001;name=xiaoming;height=1.8
1、在39-43行代码中,由于是按基本数据类型写入和读取,所以在读取的时候一定严格按照写入的顺序。
2、第9行的位置上,由于在写入的时候,导致访问的指针的位置在文件的结尾处,现在读取的时候,需要将访问指针的位置重置到文件开头处。
(3)、追加内容
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("D:/out.txt","rw");
raf.seek(raf.length());
raf.write("\r\n中国移动阅读基地".getBytes());
}执行结果:
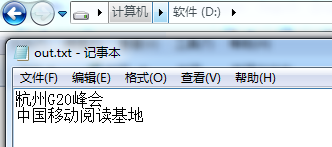
1、这段程序演示了在文件原有内容的基础上去追加内容。其中seek方法就是将访问指针移动到文件内容的末尾。
2、RandomAccessFile依然只能追加,不能像文件的指定位置插入内容。如果强制将文件记录指针移动到中间位置后开始输出内容,则新的内容会覆盖文件中原有的内容。
3、如果需要向文件指定的位置插入内容,程序需要先把插入点后面的内容读入缓冲区,等插入完成后,再讲缓冲区的内容追加到文件的后面。
(4)、指定位置插入
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
insert("d:/out.txt",5,"插入的内容");
}
catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void insert(String fileName,long pos,String content) throws IOException
{
//创建临时空文件
File tempFile = File.createTempFile("temp",null);
//在虚拟机终止时,请求删除此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录
tempFile.deleteOnExit();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(tempFile);
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(fileName,"rw");
raf.seek(pos);
byte[] buffer = new byte[4];
int num = 0;
while(-1 != (num = raf.read(buffer)))
{
fos.write(buffer,0,num);
}
raf.seek(pos);
raf.write(content.getBytes());
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(tempFile);
while(-1 != (num = fis.read(buffer)))
{
raf.write(buffer,0,num);
}
}执行结果:

1、这里插入内容的原理就是:先把插入点后面的内容读入缓冲区,等插入完成后,再讲缓冲区的内容追加到文件的后面。
相关文章推荐
- Java千百问_09基础类库(004)_java.lang.management包有什么功能
- java实现文字版P图
- spring,springmvc,mybatis整合开发时报的异常:Servlet.init() for servlet springMvc threw exc
- 解决jdk环境变量设置完后,在cmd中运行javac出现’javac‘不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序或批处理文件的错误提示
- java多线程之定时器Timer
- Java 返回一个整数的各个数字之和的一种方法
- java疯狂总结2
- Java堆、栈、方法区的简单分析
- thingking in java test2.11练习(6)
- 【Java】面向对象(二)继承
- Java集合框架(三)day_17
- Java遍历文件目录
- Java千百问_09基础类库(003)_java.math包有什么功能
- 5、时间日期和数字
- javac不是内部或外部命令 解决方法
- JAVA 打印指定月份日历
- github not authorized eclipse
- 4、字符串
- 理解RxJava:(二)Operator,Operator
- 如何在Java中使用注释
