页面的高级搜索查询
2016-07-22 00:00
369 查看
摘要: 搜索,查询,高级搜索,搜索查询,高级搜索查询
在页面显示信息的时候,有时候需要点击查询条件进行精确查询,而在点击不同的查询条件时,底层向数据库发送的SQL语句是不同的,而且在改变查询条件的时候是不能修改底层的源代码的,我们可以通过责任链模式在不修改源代码的情况下,动态改变查询条件。
在 Servlet 实现中,一般是通过 request.getParameter("name") 来获取页面表单的 name 的值的,这时候该方法是不能满足上诉要求的,所以需要通过以下方法来实现:Enumeration<String> enumeration = request.getParameterNames();。
好了,以下开始进入正题:
首先定义一个抽象类,该类定义了当前责任所要做的事情:
然后定义一个类实现上述的抽象类:
再定义一个类,作为这个链的开始。
接下来就是编写处理请求的 Servlet 了:
下面编写测试页面(只提供一部分代码):
在 web.xml 配置文件中位置该请求路径:
把项目发布到 Tomcat 中,启动服务器,运行 login.jsp:
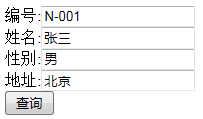
点击 “查询”,则后台打印的 SQL 语句如下:
select * from XXX where 1=1 and id = N-001 and sex = 男 and username = 张三 and adderss = 北京
此时在页面中添加新的一项,在不修改源代码的情况也会正常打印出正确的 SQL。
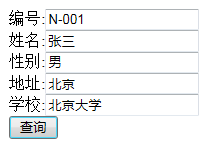
点击 “查询”,后台打印的 SQL 语句如下:
select * from XXX where 1=1 and id = N-001 and sex = 男 and username = 张三 and
school = 北京大学 and adderss = 北京
注意:
如果是这样写的话,必须得保证数据库中列的名字和页面组件中 name 的属性一致。
在页面显示信息的时候,有时候需要点击查询条件进行精确查询,而在点击不同的查询条件时,底层向数据库发送的SQL语句是不同的,而且在改变查询条件的时候是不能修改底层的源代码的,我们可以通过责任链模式在不修改源代码的情况下,动态改变查询条件。
在 Servlet 实现中,一般是通过 request.getParameter("name") 来获取页面表单的 name 的值的,这时候该方法是不能满足上诉要求的,所以需要通过以下方法来实现:Enumeration<String> enumeration = request.getParameterNames();。
好了,以下开始进入正题:
首先定义一个抽象类,该类定义了当前责任所要做的事情:
public abstract class QueryDuty {
/**
* 当前责任自己所要做到事情
* @param map: 组件的 name 和 value 的对应关系
* @param invocation: 责任链的入口,只需调用责任链的头的部分,后面会自动进行
* @return :返回当前组件执行后所形成的 sql.
*/
abstract public String doQuery(Map<String, String> map,MyActionInvocation invocation);
}然后定义一个类实现上述的抽象类:
public class InputValue extends QueryDuty{
private String key;//接收组件的 name 。
public InputValue(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
@Override
public String doQuery(Map<String, String> map,MyActionInvocation invocation) {
String value = map.get(this.key);//根据 name 获取到 value
String sql = "";
if (!value.equals("")) {
sql = " and "+this.key+" = "+map.get(this.key);
}
String nextSql = invocation.invoke(map);
return sql + nextSql;
}
}再定义一个类,作为这个链的开始。
/**
* 模拟 struts2 中拦截器的写法
*/
public class MyActionInvocation {
private Iterator<InputValue> iterator = null;
public MyActionInvocation(List<InputValue> list) {
this.iterator = list.iterator();
}
public String invoke(Map<String, String> map){
String sql = "";
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
InputValue inputValue = iterator.next();
sql = inputValue.doQuery(map,MyActionInvocation.this);
}
return sql ;
}
}接下来就是编写处理请求的 Servlet 了:
public class Dologin extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//获取所有的请求参数
Enumeration<String> enumeration = request.getParameterNames();
//用于存储参数的 name 和 value
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//用于存储创建的所有对象
ArrayList<InputValue> list = new ArrayList<InputValue>();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = (String) enumeration.nextElement();//获取 name
String value = request.getParameter(name);//根据 name 获取 value
map.put(name, value);
//创建组件对象
InputValue inputValue = new InputValue(name);//把 name 作为 key
list.add(inputValue);
}
//基础sql语句
StringBuffer baseSql = new StringBuffer("select * from XXX where 1=1");
//加 where 1=1 是在下面拼接sql语句的时候值添加 and 条件而不用添加 where 条件
MyActionInvocation invocation = new MyActionInvocation(list);
//调用责任链的链头
String sql = invocation.invoke(map);
StringBuffer allSql = baseSql.append(sql);
System.out.println(allSql);
}
}下面编写测试页面(只提供一部分代码):
<body> <%--用注册页面来进行模拟,即要进行高级检索的项 --%> <form action="doLogin1" method="post"> 编号:<input type="text" name="id"><br> 姓名:<input type="text" name="username"><br> 性别:<input type="text" name="sex"><br> 地址:<input type="text" name="adderss"><br> <input type="submit" value="查询"> </form> </body>
在 web.xml 配置文件中位置该请求路径:
<servlet> <servlet-name>doLogin1</servlet-name> <servlet-class>Dologin</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>doLogin1</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/doLogin1</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
把项目发布到 Tomcat 中,启动服务器,运行 login.jsp:

点击 “查询”,则后台打印的 SQL 语句如下:
select * from XXX where 1=1 and id = N-001 and sex = 男 and username = 张三 and adderss = 北京
此时在页面中添加新的一项,在不修改源代码的情况也会正常打印出正确的 SQL。

点击 “查询”,后台打印的 SQL 语句如下:
select * from XXX where 1=1 and id = N-001 and sex = 男 and username = 张三 and
school = 北京大学 and adderss = 北京
注意:
如果是这样写的话,必须得保证数据库中列的名字和页面组件中 name 的属性一致。
相关文章推荐
- 搜狗百度360市值齐跌:搜索引擎们陷入集体焦虑?
- 本人即将筹备败家日志,敬请期待!
- IE:使用搜索助手
- PowerShell实现查询打开某个文件的默认应用程序
- asp下查询xml的实现代码
- SQL语句实现查询SQL Server服务器名称和IP地址
- SQL多表连接查询实例分析(详细图文)
- 有关数据库SQL递归查询在不同数据库中的实现方法
- 日常收集常用SQL查询语句大全
- sql 多表连接查询
- SQL查询出表、存储过程、触发器的创建时间和最后修改时间示例
- C# linq查询之动态OrderBy用法实例
- C#使用linq语句查询数组中以特定字符开头元素的方法
- SQL语句实现查询并自动创建Missing Index
- SQL语句实现查询SQL Server内存使用状况
- 使用准则进行条件查询
- MySQL中查询日志与慢查询日志的基本学习教程
- MySQL实现树状所有子节点查询的方法
- MySQL中的基本查询语句学习笔记
- SQL SERVER 查询正在实行的SQL语句
