IOS 同步异步请求JSON数据
2016-07-08 02:21
477 查看
IOS SDK为HTTP请求提供了同步和异步两种请求这种不同的API,而且可以使用Get或POST等请求方法。
1.同步Get请求
在贴代码之前先对项目有个整体的说明:如图所示
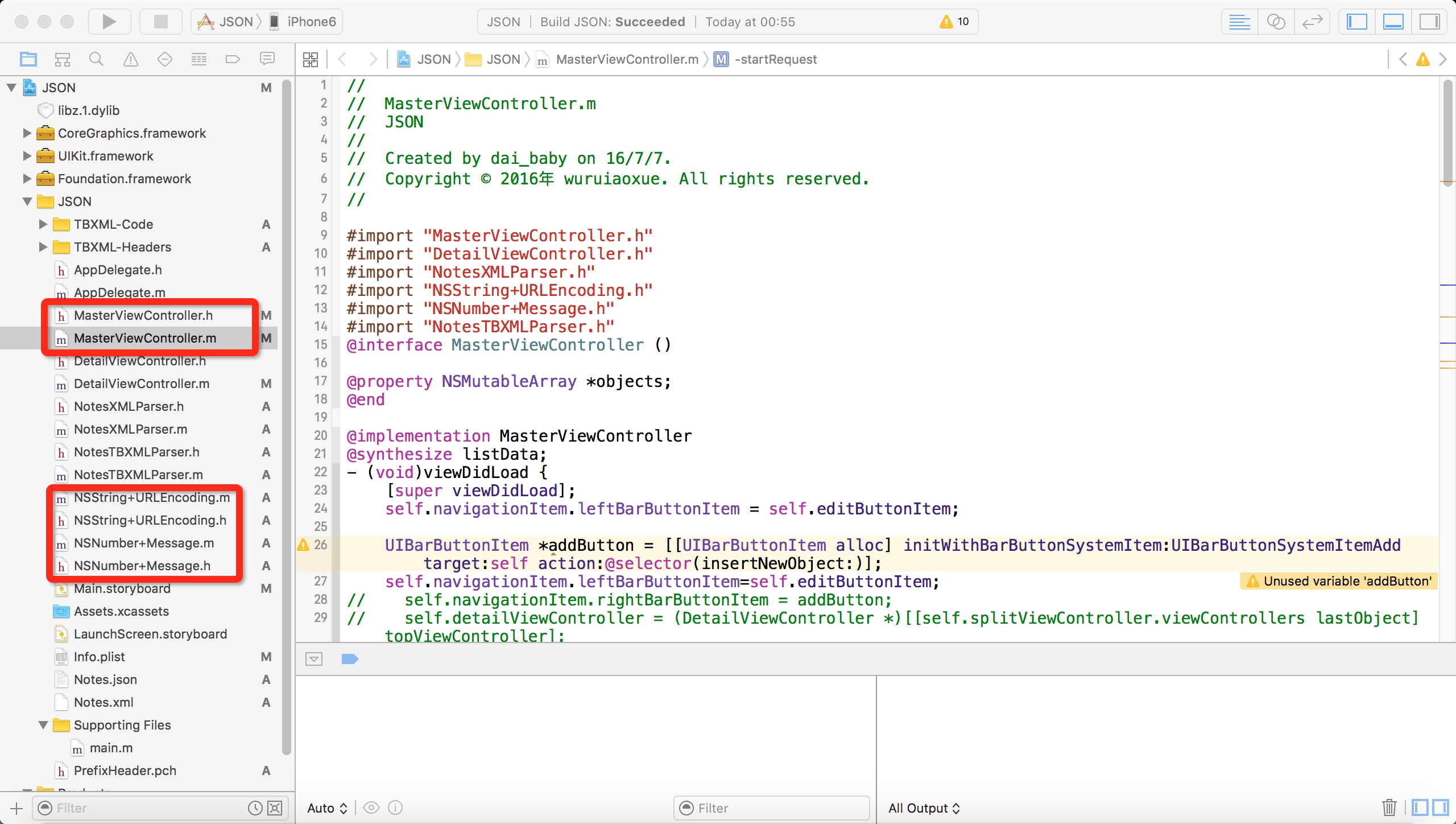
首先新建Master-Detail Application类型项目,我们可以看到会自动帮我们新建一些类,然后通过手动添加NSString_URLEncoding.h和NSNumber+Message.h类库主要用于对URL编码和对消息进行处理。
在MasterViewController类里添加如下变量以及方法
类接口
类实现
其中startRequest是请求Webservice服务器连接服务的方法
通过NSJSONSerialization类解析返回的数据,并将数据给tableView.
结果如图所示:
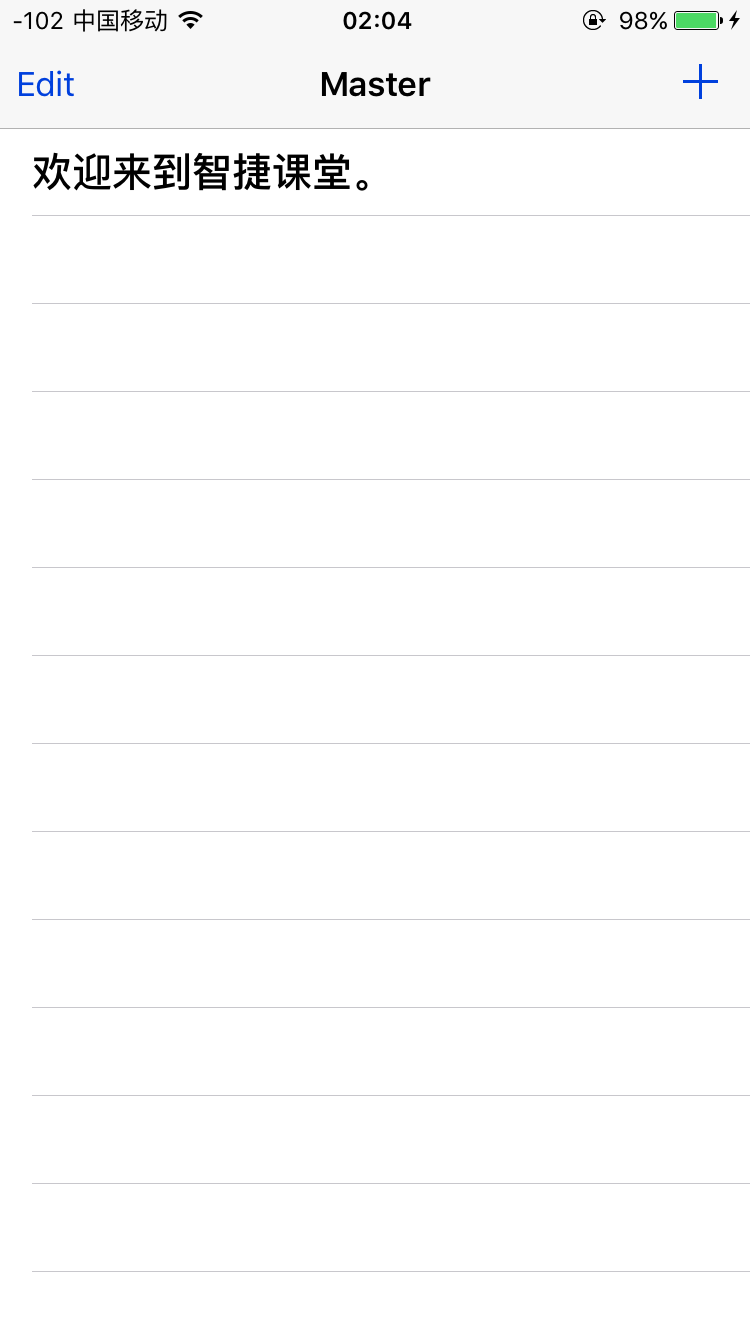
通过浏览器返回的JSON对象是这样的:
2.异步Get请求
还有一点需要说明的是:
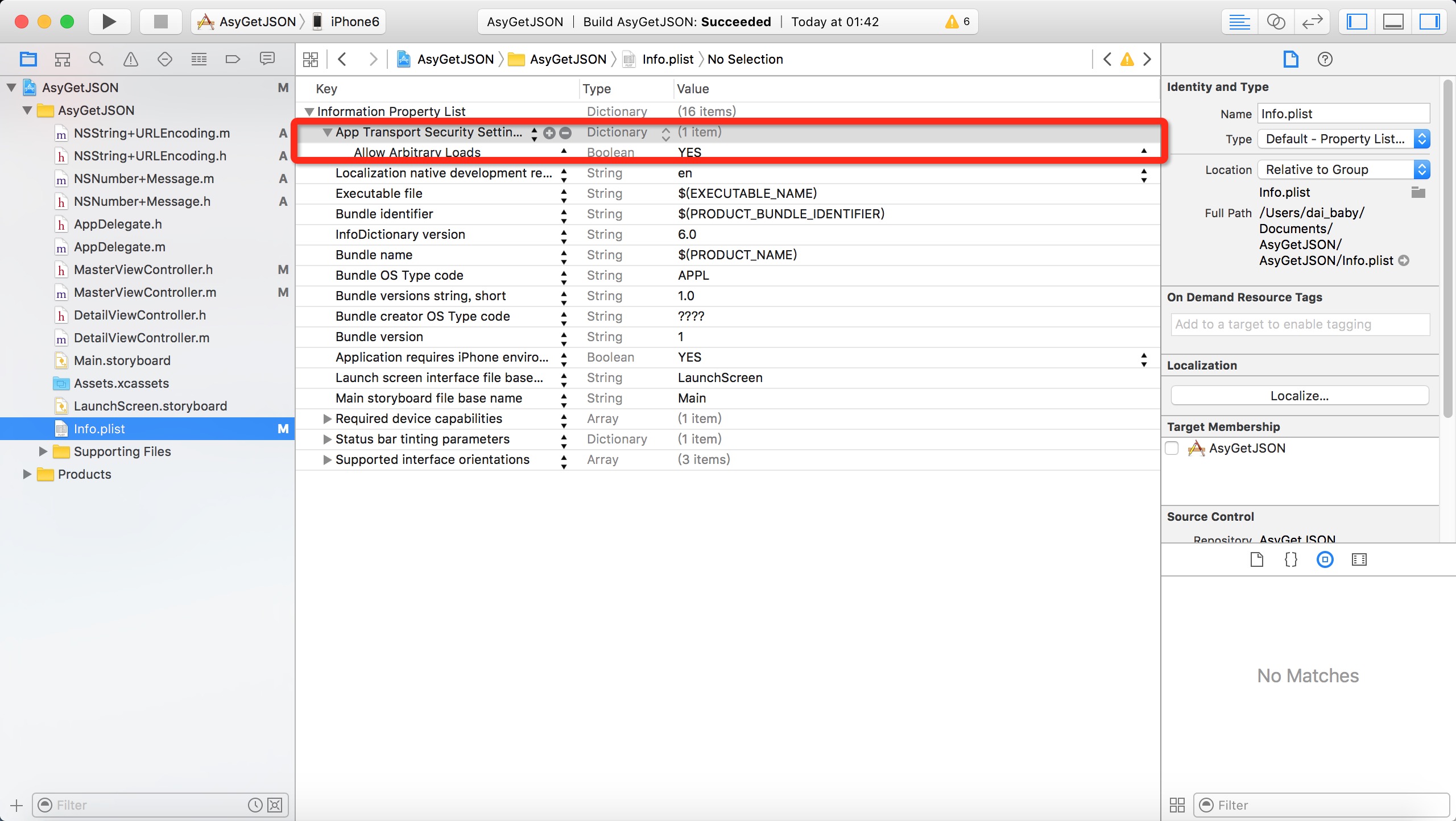
需要在Info.plist里添加如下选项,如图所示:
同步请求的用户体验不是很好,因此很多情况我们会采用异步调用。iOS SDK也提供了异步请求的方法,而异步请求会使用NSURLConnection委托协议NSURLConnectionDataDelegate.在请求的不同阶段会回调委托对象的不同方法。NSURLConnectionDataDelegate协议如下:
需要实现的主要方法有如下几个:
connection:didReceiveData
connection:didFailWithError:
connectionDidFinishLoading:
具体使用代码中会介绍。
MasterViewController接口:
MasterViewController实现:
调用结果和之前一样。至此所有的功能描述都已经结束,希望能给大家帮助!
1.同步Get请求
在贴代码之前先对项目有个整体的说明:如图所示

首先新建Master-Detail Application类型项目,我们可以看到会自动帮我们新建一些类,然后通过手动添加NSString_URLEncoding.h和NSNumber+Message.h类库主要用于对URL编码和对消息进行处理。
在MasterViewController类里添加如下变量以及方法
类接口
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @class DetailViewController; @interface MasterViewController : UITableViewController @property (strong, nonatomic) DetailViewController *detailViewController; @property(strong,nonatomic)NSMutableArray *listData; -(void)reloadView:(NSDictionary *)res; -(void)startRequest; @end
类实现
#import "MasterViewController.h"
#import "DetailViewController.h"
#import "NotesXMLParser.h"
#import "NSString+URLEncoding.h"
#import "NSNumber+Message.h"
#import "NotesTBXMLParser.h"
@interface MasterViewController ()
@property NSMutableArray *objects;
@end
@implementation MasterViewController
@synthesize listData;
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.navigationItem.leftBarButtonItem = self.editButtonItem;
UIBarButtonItem *addButton = [[UIBarButtonItem alloc] initWithBarButtonSystemItem:UIBarButtonSystemItemAdd target:self action:@selector(insertNewObject:)];
self.navigationItem.leftBarButtonItem=self.editButtonItem;
// self.navigationItem.rightBarButtonItem = addButton;
// self.detailViewController = (DetailViewController *)[[self.splitViewController.viewControllers lastObject] topViewController];
self.detailViewController=(DetailViewController *)[[self.splitViewController.viewControllers lastObject]topViewController];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter]addObserver:self selector:@selector(reloadView:) name:@"reloadViewNotification" object:nil];
// NotesXMLParser *parser=[NotesXMLParser new];
// [parser start];
// NSString *path=[[NSBundle mainBundle]pathForResource:@"Notes" ofType:@"json"];
// NSData *jsonData=[[NSData alloc]initWithContentsOfFile:path];
//
// NSError *error;
// id jsonObj=[NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:jsonData options:NSJSONReadingMutableLeaves error:&error];
//
// if(!jsonObj||error)
// {
// NSLog(@"JSON解码失败");
// }
// self.listData=[jsonObj objectForKey:@"Record"];
[self startRequest];
// NotesTBXMLParser *parser=[NotesTBXMLParser new];
// [parser start];
}
-(void)reloadView:(NSDictionary *)res
{
NSNumber *resultCodeObj=[res objectForKey:@"ResultCode"];
if([resultCodeObj integerValue]>=0)
{
self.listData=[res objectForKey:@"Record"];
[self.tableView reloadData];
}else
{
NSString *errorStr=[resultCodeObj errorMessage];
UIAlertView *alterView=[[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:@"错误信息" message:errorStr delegate:nil cancelButtonTitle:@"OK" otherButtonTitles: nil];
[alterView show];
}
}
-(void)startRequest
{
NSString *strURL=[[NSString alloc]initWithFormat:@"http://www.51work6.com/service/mynotes/WebService.php?email=%@&type=%@&action=%@",@"784087156@qq.com",@"JSON",@"query"];
// NSURL *url=[strURL stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSURL *url=[NSURL URLWithString:[strURL URLEncodedString]];
NSURLRequest *request=[[NSURLRequest alloc]initWithURL:url];
NSDate *data=[NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request returningResponse:nil error:nil];
NSLog(@"请求完成…");
NSDictionary *resDict=[NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:NSJSONReadingMutableLeaves error:nil];
[self reloadView:resDict];
}
//-(void)reloadView:(NSNotification *)notification
//{
// NSMutableArray *resList=[notification object];
// self.listData=resList;
// [self.tableView reloadData];
//}
- (void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated {
self.clearsSelectionOnViewWillAppear = self.splitViewController.isCollapsed;
[super viewWillAppear:animated];
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
- (void)insertNewObject:(id)sender {
if (!self.objects) {
self.objects = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
}
[self.objects insertObject:[NSDate date] atIndex:0];
NSIndexPath *indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:0 inSection:0];
[self.tableView insertRowsAtIndexPaths:@[indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationAutomatic];
}
#pragma mark - Segues
- (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender {
if ([[segue identifier] isEqualToString:@"showDetail"]) {
NSIndexPath *indexPath = [self.tableView indexPathForSelectedRow];
NSDate *object = self.objects[indexPath.row];
DetailViewController *controller = (DetailViewController *)[[segue destinationViewController] topViewController];
[controller setDetailItem:object];
controller.navigationItem.leftBarButtonItem = self.splitViewController.displayModeButtonItem;
controller.navigationItem.leftItemsSupplementBackButton = YES;
}
}
#pragma mark - Table View
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView {
return 1;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return self.listData.count;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:@"Cell" forIndexPath:indexPath];
NSMutableDictionary *dict=self.listData[indexPath.row];
//NSDate *object = self.objects[indexPath.row];
cell.textLabel.text = [dict objectForKey:@"Content"];
cell.detailTextLabel.text=[dict objectForKey:@"CDate"];
return cell;
}
- (BOOL)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView canEditRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
// Return NO if you do not want the specified item to be editable.
return YES;
}
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView commitEditingStyle:(UITableViewCellEditingStyle)editingStyle forRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
if (editingStyle == UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete) {
[self.objects removeObjectAtIndex:indexPath.row];
[tableView deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:@[indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
} else if (editingStyle == UITableViewCellEditingStyleInsert) {
// Create a new instance of the appropriate class, insert it into the array, and add a new row to the table view.
}
}
@end其中startRequest是请求Webservice服务器连接服务的方法
-(void)startRequest
{
NSString *strURL=[[NSString alloc]initWithFormat:@"http://www.51work6.com/service/mynotes/WebService.php?email=%@&type=%@&action=%@",@"784087156@qq.com",@"JSON",@"query"];
// NSURL *url=[strURL stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSURL *url=[NSURL URLWithString:[strURL URLEncodedString]];
NSURLRequest *request=[[NSURLRequest alloc]initWithURL:url];
NSDate *data=[NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request returningResponse:nil error:nil];
NSLog(@"请求完成…");
NSDictionary *resDict=[NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:NSJSONReadingMutableLeaves error:nil];
[self reloadView:resDict];
}通过NSJSONSerialization类解析返回的数据,并将数据给tableView.
结果如图所示:

通过浏览器返回的JSON对象是这样的:
{"ResultCode":0,"Record":[{"ID":4290,"CDate":"2016-05-18","Content":"欢迎来到智捷课堂。"}]}2.异步Get请求
还有一点需要说明的是:
Google后查证,iOS9引入了新特性App Transport Security (ATS)。详情:App Transport Security (ATS) 新特性要求App内访问的网络必须使用HTTPS协议。 但是现在公司的项目使用的是HTTP协议,使用私有加密方式保证数据安全。现在也不能马上改成HTTPS协议传输。
需要在Info.plist里添加如下选项,如图所示:

同步请求的用户体验不是很好,因此很多情况我们会采用异步调用。iOS SDK也提供了异步请求的方法,而异步请求会使用NSURLConnection委托协议NSURLConnectionDataDelegate.在请求的不同阶段会回调委托对象的不同方法。NSURLConnectionDataDelegate协议如下:
/*
NSURLConnection.h
Copyright (c) 2003-2015, Apple Inc. All rights reserved.
Public header file.
*/
#import <Foundation/NSObject.h>
@class NSArray;
@class NSURL;
@class NSCachedURLResponse;
@class NSData;
@class NSError;
@class NSURLAuthenticationChallenge;
@class NSURLConnectionInternal;
@class NSURLRequest;
@class NSURLResponse;
@class NSRunLoop;
@class NSInputStream;
@class NSURLProtectionSpace;
@class NSOperationQueue;
@protocol NSURLConnectionDelegate;
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
/*** DEPRECATED: The NSURLConnection class should no longer be used. NSURLSession is the replacement for NSURLConnection ***/
/*!
@class NSURLConnection
@abstract
An NSURLConnection object provides support to perform
asynchronous loads of a URL request, providing data to a
client supplied delegate.
@discussion
The interface for NSURLConnection is very sparse, providing
only the controls to start and cancel asynchronous loads of a
URL request.<p>
An NSURLConnection may be used for loading of resource data
directly to memory, in which case an
NSURLConnectionDataDelegate should be supplied, or for
downloading of resource data directly to a file, in which case
an NSURLConnectionDownloadDelegate is used. The delegate is
retained by the NSURLConnection until a terminal condition is
encountered. These two delegates are logically subclasses of
the base protocol, NSURLConnectionDelegate.<p>
A terminal condition produced by the loader will result in a
connection:didFailWithError: in the case of an error, or
connectiondidFinishLoading: or connectionDidFinishDownloading:
delegate message.<p>
The -cancel message hints to the loader that a resource load
should be abandoned but does not guarantee that more delegate
messages will not be delivered. If -cancel does cause the
load to be abandoned, the delegate will be released without
further messages. In general, a caller should be prepared for
-cancel to have no effect, and internally ignore any delegate
callbacks until the delegate is released.
Scheduling of an NSURLConnection specifies the context in
which delegate callbacks will be made, but the actual IO may
occur on a separate thread and should be considered an
implementation detail.<p>
When created, an NSURLConnection performs a deep-copy of the
NSURLRequest. This copy is available through the
-originalRequest method. As the connection performs the load,
this request may change as a result of protocol
canonicalization or due to following redirects.
-currentRequest can be used to retrieve this value.<p>
An NSURLConnections created with the
+connectionWithRequest:delegate: or -initWithRequest:delegate:
methods are scheduled on the current runloop immediately, and
it is not necessary to send the -start message to begin the
resource load.<p>
NSURLConnections created with
-initWithRequest:delegate:startImmediately: are not
automatically scheduled. Use -scheduleWithRunLoop:forMode: or
-setDelegateQueue: to specify the context for delegate
callbacks, and -start to begin the load. If you do not
explicitly schedule the connection before -start, it will be
scheduled on the current runloop and mode automatically.<p>
The NSURLConnectionSynchronousLoading category adds
+sendSynchronousRequest:returningResponse:error, which blocks
the current thread until the resource data is available or an
error occurs. It should be noted that using this method on an
applications main run loop may result in an unacceptably long
delay in a user interface and its use is strongly
discourage.<p>
The NSURLConnectionQueuedLoading category implements
+sendAsynchronousRequest:queue:completionHandler, providing
similar simplicity but provides a mechanism where the current
runloop is not blocked.<p>
Both of the immediate loading categories do not provide for
customization of resource load, and do not allow the caller to
respond to, e.g., authentication challenges.<p>
*/
@interface NSURLConnection : NSObject
{
@private
NSURLConnectionInternal *_internal;
}
/* Designated initializer */
- (nullable instancetype)initWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request delegate:(nullable id)delegate startImmediately:(BOOL)startImmediately NS_DEPRECATED(10_5, 10_11, 2_0, 9_0, "Use NSURLSession (see NSURLSession.h)") __WATCHOS_PROHIBITED;
- (nullable instancetype)initWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request delegate:(nullable id)delegate NS_DEPRECATED(10_3, 10_11, 2_0, 9_0, "Use NSURLSession (see NSURLSession.h)") __WATCHOS_PROHIBITED;
+ (nullable NSURLConnection*)connectionWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request delegate:(nullable id)delegate NS_DEPRECATED(10_3, 10_11, 2_0, 9_0, "Use NSURLSession (see NSURLSession.h)") __WATCHOS_PROHIBITED;
@property (readonly, copy) NSURLRequest *originalRequest NS_AVAILABLE(10_8, 5_0);
@property (readonly, copy) NSURLRequest *currentRequest NS_AVAILABLE(10_8, 5_0);
- (void)start NS_AVAILABLE(10_5, 2_0);
- (void)cancel;
- (void)scheduleInRunLoop:(NSRunLoop *)aRunLoop forMode:(NSString *)mode NS_AVAILABLE(10_5, 2_0);
- (void)unscheduleFromRunLoop:(NSRunLoop *)aRunLoop forMode:(NSString *)mode NS_AVAILABLE(10_5, 2_0);
- (void)setDelegateQueue:(nullable NSOperationQueue*) queue NS_AVAILABLE(10_7, 5_0);
/*!
@method canHandleRequest:
@abstract
Performs a "preflight" operation that performs
some speculative checks to see if a connection can
be initialized, and the associated I/O that is
started in the initializer methods can begin.
@discussion
The result of this method is valid only as long as
no protocols are registered or unregistered, and
as long as the request is not mutated (if the
request is mutable). Hence, clients should be
prepared to handle failures even if they have
performed request preflighting by calling this
method.
@param
request The request to preflight.
@result
YES if it is likely that the given request can be used to
initialize a connection and the associated I/O can be
started
NO
*/
+ (BOOL)canHandleRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request;
@end
/*!
@protocol NSURLConnectionDelegate
@abstract
Delegate methods that are common to all forms of
NSURLConnection. These are all optional. This
protocol should be considered a base class for the
NSURLConnectionDataDelegate and
NSURLConnectionDownloadDelegate protocols.
@discussion
connection:didFailWithError: will be called at
most once, if an error occurs during a resource
load. No other callbacks will be made after.<p>
connectionShouldUseCredentialStorage: will be
called at most once, before a resource load begins
(which means it may be called during construction
of the connection.) The delegate should return
TRUE if the connection should consult the shared
NSURLCredentialStorage in response to
authentication challenges. Regardless of the
result, the authentication challenge methods may
still be called.
connection:willSendRequestForAuthenticationChallenge:
is the preferred (Mac OS X 10.7 and iOS 5.0 or
later) mechanism for responding to authentication
challenges. See
<Foundation/NSURLAuthenticationChallenge.h> for
more information on dealing with the various types
of authentication challenges.
connection:canAuthenticateAgainstProtectionSpace:
connection:didReciveAuthenticationChallenge:
connection:didCancelAuthenticationChallenge: are
deprected and new code should adopt
connection:willSendRequestForAuthenticationChallenge.
The older delegates will still be called for
compatability, but incur more latency in dealing
with the authentication challenge.
*/
@protocol NSURLConnectionDelegate <NSObject>
@optional
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didFailWithError:(NSError *)error;
- (BOOL)connectionShouldUseCredentialStorage:(NSURLConnection *)connection;
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection willSendRequestForAuthenticationChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge;
- (BOOL)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection canAuthenticateAgainstProtectionSpace:(NSURLProtectionSpace *)protectionSpace NS_DEPRECATED(10_6, 10_10, 3_0, 8_0, "Use -connection:willSendRequestForAuthenticationChallenge: instead.");
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveAuthenticationChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge NS_DEPRECATED(10_2, 10_10, 2_0, 8_0, "Use -connection:willSendRequestForAuthenticationChallenge: instead.");
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didCancelAuthenticationChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge NS_DEPRECATED(10_2, 10_10, 2_0, 8_0, "Use -connection:willSendRequestForAuthenticationChallenge: instead.");
@end
/*!
@protocol NSURLConnectionDataDelegate
@abstract
Delegate methods used for loading data to memory.
These delegate methods are all optional.
@discussion
connection:willSendRequest:redirectResponse: is
called whenever an connection determines that it
must change URLs in order to continue loading a
request. This gives the delegate an opportunity
inspect and if necessary modify a request. A
delegate can cause the request to abort by either
calling the connections -cancel method, or by
returning nil from this callback.<p>
There is one subtle difference which results from
this choice. If -cancel is called in the delegate
method, all processing for the connection stops,
and no further delegate callbacks will be sent. If
the delegate returns nil, the connection will
continue to process, and this has special
relevance in the case where the redirectResponse
argument is non-nil. In this case, any data that
is loaded for the connection will be sent to the
delegate, and the delegate will receive a finished
or failure delegate callback as appropriate.<p>
connection:didReceiveResponse: is called when
enough data has been read to construct an
NSURLResponse object. In the event of a protocol
which may return multiple responses (such as HTTP
multipart/x-mixed-replace) the delegate should be
prepared to inspect the new response and make
itself ready for data callbacks as appropriate.<p>
connection:didReceiveData: is called with a single
immutable NSData object to the delegate,
representing the next portion of the data loaded
from the connection. This is the only guaranteed
for the delegate to receive the data from the
resource load.<p>
connection:needNewBodyStream: is called when the
loader must retransmit a requests payload, due to
connection errors or authentication challenges.
Delegates should construct a new unopened and
autoreleased NSInputStream. If not implemented,
the loader will be required to spool the bytes to
be uploaded to disk, a potentially expensive
operation. Returning nil will cancel the
connection.
connection:didSendBodyData:totalBytesWritten:totalBytesExpectedToWrite:
is called during an upload operation to provide
progress feedback. Note that the values may
change in unexpected ways if the request needs to
be retransmitted.<p>
connection:willCacheResponse: gives the delegate
an opportunity to inspect and modify the
NSCachedURLResponse which will be cached by the
loader if caching is enabled for the original
NSURLRequest. Returning nil from this delegate
will prevent the resource from being cached. Note
that the -data method of the cached response may
return an autoreleased in-memory copy of the true
data, and should not be used as an alternative to
receiving and accumulating the data through
connection:didReceiveData:<p>
connectionDidFinishLoading: is called when all
connection processing has completed successfully,
before the delegate is released by the
connection.<p>
*/
@protocol NSURLConnectionDataDelegate <NSURLConnectionDelegate>
@optional
- (nullable NSURLRequest *)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection willSendRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request redirectResponse:(nullable NSURLResponse *)response;
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response;
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveData:(NSData *)data;
- (nullable NSInputStream *)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection needNewBodyStream:(NSURLRequest *)request;
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didSendBodyData:(NSInteger)bytesWritten
totalBytesWritten:(NSInteger)totalBytesWritten
totalBytesExpectedToWrite:(NSInteger)totalBytesExpectedToWrite;
- (nullable NSCachedURLResponse *)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection willCacheResponse:(NSCachedURLResponse *)cachedResponse;
- (void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection *)connection;
@end
/*!
@protocol NSURLConnectionDownloadDelegate
@abstract
Delegate methods used to perform resource
downloads directly to a disk file. All the
methods are optional with the exception of
connectionDidFinishDownloading:destinationURL:
which must be implemented in order to inform the
delegate of the location of the finished download.
This delegate and download implementation is
currently only available on iOS 5.0 or later.
@discussion
connection:didWriteData:totalBytesWritten:expectedTotalBytes:
provides progress information about the state of
the download, the number of bytes written since
the last delegate callback, the total number of
bytes written to disk and the total number of
bytes that are expected (or 0 if this is unknown.)
connectionDidResumeDownloading:totalBytesWritten:expectedTotalBytes:
is called when the connection is able to resume an
in progress download. This may happen due to a
connection or network failure.
connectionDidFinishDownloading:destinationURL: is
a terminal event which indicates the completion of
a download and provides the location of the file.
The file will be located in the applications cache
directory and is guaranteed to exist for the
duration of the delegate callback. The
implication is that the delegate should copy or
move the download to a more persistent location if
desired.
*/
@protocol NSURLConnectionDownloadDelegate <NSURLConnectionDelegate>
@optional
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didWriteData:(long long)bytesWritten totalBytesWritten:(long long)totalBytesWritten expectedTotalBytes:(long long) expectedTotalBytes;
- (void)connectionDidResumeDownloading:(NSURLConnection *)connection totalBytesWritten:(long long)totalBytesWritten expectedTotalBytes:(long long) expectedTotalBytes;
@required
- (void)connectionDidFinishDownloading:(NSURLConnection *)connection destinationURL:(NSURL *) destinationURL;
@end
/*!
@category NSURLConnection(NSURLConnectionSynchronousLoading)
@abstract
The NSURLConnectionSynchronousLoading category on
NSURLConnection provides the interface to perform
synchronous loading of URL requests.
*/
@interface NSURLConnection (NSURLConnectionSynchronousLoading)
/*!
@method sendSynchronousRequest:returningResponse:error:
@abstract
Performs a synchronous load of the given request,
returning an NSURLResponse in the given out
parameter.
@discussion
A synchronous load for the given request is built on
top of the asynchronous loading code made available
by the class. The calling thread is blocked while
the asynchronous loading system performs the URL load
on a thread spawned specifically for this load
request. No special threading or run loop
configuration is necessary in the calling thread in
order to perform a synchronous load. For instance,
the calling thread need not be running its run loop.
@param
request The request to load. Note that the request is
deep-copied as part of the initialization
process. Changes made to the request argument after
this method returns do not affect the request that is
used for the loading process.
@param
response An out parameter which is filled in with the
response generated by performing the load.
@param
error Out parameter (may be NULL) used if an error occurs
while processing the request. Will not be modified if the
load succeeds.
@result The content of the URL resulting from performing the load,
or nil if the load failed.
*/
+ (nullable NSData *)sendSynchronousRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request returningResponse:(NSURLResponse * __nullable * __nullable)response error:(NSError **)error NS_DEPRECATED(10_3, 10_11, 2_0, 9_0, "Use [NSURLSession dataTaskWithRequest:completionHandler:] (see NSURLSession.h") __WATCHOS_PROHIBITED;
@end
/*!
@category NSURLConnection(NSURLConnectionQueuedLoading)
The NSURLConnectionQueuedLoading category on NSURLConnection
provides the interface to perform asynchronous loading of URL
requests where the results of the request are delivered to a
block via an NSOperationQueue.
Note that there is no guarantee of load ordering implied by this
method.
*/
@interface NSURLConnection (NSURLConnectionQueuedLoading)
/*!
@method sendAsynchronousRequest:queue:completionHandler:
@abstract
Performs an asynchronous load of the given
request. When the request has completed or failed,
the block will be executed from the context of the
specified NSOperationQueue.
@discussion
This is a convenience routine that allows for
asynchronous loading of an url based resource. If
the resource load is successful, the data parameter
to the callback will contain the resource data and
the error parameter will be nil. If the resource
load fails, the data parameter will be nil and the
error will contain information about the failure.
@param
request The request to load. Note that the request is
deep-copied as part of the initialization
process. Changes made to the request argument after
this method returns do not affect the request that
is used for the loading process.
@param
queue An NSOperationQueue upon which the handler block will
be dispatched.
@param
handler A block which receives the results of the resource load.
*/
+ (void)sendAsynchronousRequest:(NSURLRequest*) request
queue:(NSOperationQueue*) queue
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLResponse* __nullable response, NSData* __nullable data, NSError* __nullable connectionError)) handler NS_DEPRECATED(10_7, 10_11, 5_0, 9_0, "Use [NSURLSession dataTaskWithRequest:completionHandler:] (see NSURLSession.h") __WATCHOS_PROHIBITED;
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END需要实现的主要方法有如下几个:
connection:didReceiveData
connection:didFailWithError:
connectionDidFinishLoading:
具体使用代码中会介绍。
MasterViewController接口:
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @class DetailViewController; @interface MasterViewController : UITableViewController @property (strong, nonatomic) DetailViewController *detailViewController; @property(nonatomic,strong)NSMutableArray *objects; @property(nonatomic,strong)NSMutableData *datas; -(void)reloadView:(NSDictionary *)res; -(void)startRequest;; @end
MasterViewController实现:
#import "MasterViewController.h"
#import "DetailViewController.h"
#import "NSNumber+Message.h"
@interface MasterViewController ()<NSURLConnectionDataDelegate>
@end
@implementation MasterViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
self.navigationItem.leftBarButtonItem = self.editButtonItem;
UIBarButtonItem *addButton = [[UIBarButtonItem alloc] initWithBarButtonSystemItem:UIBarButtonSystemItemAdd target:self action:@selector(insertNewObject:)];
self.navigationItem.rightBarButtonItem = addButton;
self.detailViewController = (DetailViewController *)[[self.splitViewController.viewControllers lastObject] topViewController];
[self startRequest];
}
-(void)startRequest
{
NSString *strURL=[[NSString alloc]initWithFormat:@"http://www.51work6.com/service/mynotes/WebService.php?email=%@&type=%@&action=%@",@"784087156@qq.com",@"JSON",@"query"];
strURL=[strURL stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSURL *url=[NSURL URLWithString:strURL];
NSURLRequest *request=[[NSURLRequest alloc]initWithURL:url];
NSURLConnection *connection=[[NSURLConnection alloc]initWithRequest:request delegate:self];
if(connection)
{
self.datas=[NSMutableData new];
}
}
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveData:(NSData *)data
{
[self.datas appendData:data];
}
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didFailWithError:(NSError *)error
{
NSLog(@"%@",[error localizedDescription]);
}
- (void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection *)connection
{
NSDictionary *dict=[NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:self.datas options:NSJSONReadingMutableLeaves error:nil];
[self reloadView:dict];
}
-(void)reloadView:(NSDictionary *)res
{
NSNumber *resultCode=[res objectForKey:@"ResultCode"];
if([resultCode integerValue]>=0)
{
self.objects=[res objectForKey:@"Record"];
[self.tableView reloadData];
}else
{
NSString *errorStr=[resultCode errorMessage];
UIAlertView *alertView=[[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:@"错误信息" message:errorStr delegate:nil cancelButtonTitle:@"OK" otherButtonTitles: nil];
[alertView show];
}
}
- (void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated {
self.clearsSelectionOnViewWillAppear = self.splitViewController.isCollapsed;
[super viewWillAppear:animated];
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
- (void)insertNewObject:(id)sender {
if (!self.objects) {
self.objects = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
}
[self.objects insertObject:[NSDate date] atIndex:0];
NSIndexPath *indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:0 inSection:0];
[self.tableView insertRowsAtIndexPaths:@[indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationAutomatic];
}
#pragma mark - Segues
- (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender {
if ([[segue identifier] isEqualToString:@"showDetail"]) {
NSIndexPath *indexPath = [self.tableView indexPathForSelectedRow];
NSDate *object = self.objects[indexPath.row];
DetailViewController *controller = (DetailViewController *)[[segue destinationViewController] topViewController];
[controller setDetailItem:object];
controller.navigationItem.leftBarButtonItem = self.splitViewController.displayModeButtonItem;
controller.navigationItem.leftItemsSupplementBackButton = YES;
}
}
#pragma mark - Table View
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView {
return 1;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return self.objects.count;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:@"Cell" forIndexPath:indexPath];
NSMutableDictionary *dict=self.objects[indexPath.row];
cell.textLabel.text = [dict objectForKey:@"Content"];
cell.detailTextLabel.text=[dict objectForKey:@"CDate"];
return cell;
}
- (BOOL)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView canEditRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
// Return NO if you do not want the specified item to be editable.
return YES;
}
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView commitEditingStyle:(UITableViewCellEditingStyle)editingStyle forRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
if (editingStyle == UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete) {
[self.objects removeObjectAtIndex:indexPath.row];
[tableView deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:@[indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
} else if (editingStyle == UITableViewCellEditingStyleInsert) {
// Create a new instance of the appropriate class, insert it into the array, and add a new row to the table view.
}
}
@end调用结果和之前一样。至此所有的功能描述都已经结束,希望能给大家帮助!
相关文章推荐
- 峰回路转,Firefox 浏览器即将重返 iOS 平台
- 峰回路转,Firefox 浏览器即将重返 iOS 平台
- 不可修补的 iOS 漏洞可能导致 iPhone 4s 到 iPhone X 永久越狱
- iOS 12.4 系统遭黑客破解,漏洞危及数百万用户
- 每日安全资讯:NSO,一家专业入侵 iPhone 的神秘公司
- [转][源代码]Comex公布JailbreakMe 3.0源代码
- 讲解iOS开发中基本的定位功能实现
- iOS中定位当前位置坐标及转换为火星坐标的方法
- js判断客户端是iOS还是Android等移动终端的方法
- iOS应用开发中AFNetworking库的常用HTTP操作方法小结
- iOS应用中UISearchDisplayController搜索效果的用法
- iOS App开发中的UISegmentedControl分段组件用法总结
- IOS开发环境windows化攻略
- iOS应用中UITableView左滑自定义选项及批量删除的实现
- iOS中UIAlertView警告框组件的使用教程
- 浅析iOS应用开发中线程间的通信与线程安全问题
- iOS中的UIKeyboard键盘视图使用方法小结
- 检测iOS设备是否越狱的方法
- .net平台推送ios消息的实现方法
