图的遍历 - 数据结构
2016-07-05 03:41
621 查看
图的遍历 - 数据结构
概述
图的遍历是指从图中的任一顶点出发,对图中的所有顶点访问一次且只访问一次。图的遍历操作和树的遍历操作功能相似。图的遍历是图的一种基本操作,图的其它算法如求解图的连通性问题,拓扑排序,求关键路径等都是建立在遍历算法的基础之上。由于图结构本身的复杂性,所以图的遍历操作也较复杂,主要表现在以下四个方面:
① 在图结构中,没有一个“自然”的首结点,图中任意一个顶点都可作为第一个被访问的结点。
② 在非连通图中,从一个顶点出发,只能够访问它所在的连通分量上的所有顶点,因此,还需考虑如何选取下一个出发点以访问图中其余的连通分量。
③ 在图结构中,如果有回路存在,那么一个顶点被访问之后,有可能沿回路又回到该顶点。
④ 在图结构中,一个顶点可以和其它多个顶点相连,当这样的顶点访问过后,存在如何选取下一个要访问的顶点的问题。
图的遍历通常有深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索两种方式,他们对无向图和有向图都适用。
1.深度优先搜索
深度优先搜索(Depth_Fisrst Search)遍历类似于树的先根遍历,是树的先根遍历的推广。假设初始状态是图中所有顶点未曾被访问,则深度优先搜索可从图中某个顶点发v 出发,访问此顶点,然后依次从v 的未被访问的邻接点出发深度优先遍历图,直至图中所有和v 有路径相通的顶点都被访问到;若此时图中尚有顶点未被访问,则另选图中一个未曾被访问的顶点作起始点,重复上述过程,直至图中所有顶点都被访问到为止。
以如下图的无向图G5为例,进行图的深度优先搜索:
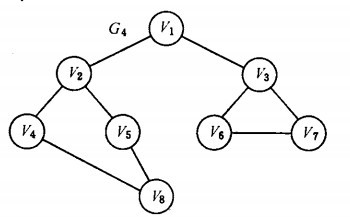
G5
搜索过程:
假设从顶点v1 出发进行搜索,在访问了顶点v1 之后,选择邻接点v2。因为v2 未曾访问,则从v2 出发进行搜索。依次类推,接着从v4 、v8 、v5 出发进行搜索。在访问了v5 之后,由于v5 的邻接点都已被访问,则搜索回到v8。由于同样的理由,搜索继续回到v4,v2 直至v1,此时由于v1 的另一个邻接点未被访问,则搜索又从v1 到v3,再继续进行下去由此,得到的顶点访问序列为:

显然,这是一个递归的过程。为了在遍历过程中便于区分顶点是否已被访问,需附设访问标志数组visited[0:n-1], ,其初值为FALSE ,一旦某个顶点被访问,则其相应的分量置为TRUE。
1)邻接矩阵的存储方式实现:
[cpp] view plain copy
print?
// stdafx.h : include file for standard system include files,
// or project specific include files that are used frequently, but
// are changed infrequently
//
#pragma once
#include "targetver.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//宏定义
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define NULL 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
#define INFINITY INT_MAX
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 30
typedef int Status ;
typedef int ElemType ;
typedef int VrType ;
typedef char VertexType ;
/************************************************************************/
/* 数组表示:邻接矩阵数据结构
*/
/************************************************************************/
typedef struct ArcCell{
VrType adj; //顶点关系类型,对无权图,0/1表示是否相邻,有权图表示权值
ArcCell *info; //弧相关信息的指针
}ArcCell, AdjMatrix[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
typedef struct{
VertexType vexs[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //顶点向量
AdjMatrix arcs; //邻接矩阵
int vexnum,arcnum; //图的当前顶点数和弧数
}MGraph;
[cpp] view plain copy
print?
// Test.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
bool visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //访问标识
Status (*VisitFunc) (int v); //函数变量
/************************************************************************/
/*
确定顶点v在图G的位置
*/
/************************************************************************/
int LocateVex(MGraph G,VertexType v)
{
for(int i = 0; i<G.vexnum; ++i) {
if(G.vexs[i] == v) return i;//找到
}
return -1;//不存在
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
*/
/************************************************************************/
int FirstAdjVex(MGraph G,int v)
{
int i ;
for(i = 0; i<G.vexnum; i++)
if( G.arcs[v][i].adj ) return i;
if(i == (G.vexnum -1)) return -1;
return -1;
}
int NextAdjVex(MGraph G,int v,int w)
{
int i;
for( i = w+1; i<G.vexnum; i++)//+1
if(G.arcs[v][i].adj) return i;
if(i == (G.vexnum -1)) return -1;
return -1;
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
邻接矩阵的无向图的创建:
注释的代码可以动态生成图。
*/
/************************************************************************/
void CreatUDG(MGraph &G){
cout<<"创建邻接矩阵的无向图:"<<endl;
int i,j,k,w;
//G5的存储:
G.arcnum = 8;
G.vexnum = 9;
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;++i)
for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;++j) {
G.arcs[i][j].adj=0;
G.arcs[i][j].info=NULL;
}
G.vexs[0] = '1';
G.vexs[1] = '2';
G.vexs[2] = '3';
G.vexs[3] = '4';
G.vexs[4] = '5';
G.vexs[5] = '6';
G.vexs[6] = '7';
G.vexs[7] = '8';
G.arcs[0][1].adj = 1;
G.arcs[0][1].info = NULL;
G.arcs[1][0].adj = 1;
G.arcs[1][0].info = NULL;
G.arcs[1][3].adj = 1;
G.arcs[1][3].info = NULL;
G.arcs[3][1].adj = 1;
G.arcs[3][1].info = NULL;
G.arcs[3][7].adj = 1;
G.arcs[3][7].info = NULL;
G.arcs[7][3].adj = 1;
G.arcs[7][3].info = NULL;
G.arcs[7][4].adj = 1;
G.arcs[7][4].info = NULL;
G.arcs[4][7].adj = 1;
G.arcs[4][7].info = NULL;
G.arcs[4][1].adj = 1;
G.arcs[4][1].info = NULL;
G.arcs[1][4].adj = 1;
G.arcs[1][4].info = NULL;
G.arcs[0][2].adj = 1;
G.arcs[0][2].info = NULL;
G.arcs[2][0].adj = 1;
G.arcs[2][0].info = NULL;
G.arcs[2][5].adj = 1;
G.arcs[2][5].info = NULL;
G.arcs[5][2].adj = 1;
G.arcs[5][2].info = NULL;
G.arcs[5][6].adj = 1;
G.arcs[5][6].info = NULL;
G.arcs[6][5].adj = 1;
G.arcs[6][5].info = NULL;
G.arcs[6][2].adj = 1;
G.arcs[6][2].info = NULL;
G.arcs[2][6].adj = 1;
G.arcs[2][6].info = NULL;
return ;
/*
char v1,v2;
cout<<"请输入无向图顶点个数和边数:"<<endl;
cin>>G.vexnum>>G.arcnum;
cout<<"请输入"<<G.vexnum<<"个顶点的值:"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;++i) cin>>G.vexs[i];
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;++i)
for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;++j) {
G.arcs[i][j].adj=0;
G.arcs[i][j].info=NULL;
}
for( k=1;k<=G.arcnum;++k){
cout<<"请输入第"<<k<<"条边的两个顶点值和它们的权重:"<<endl;
cin>>v1>>v2>>w;
i = LocateVex(G,v1); j=LocateVex(G,v2);
G.arcs[i][j].adj=w;
G.arcs[j][i]=G.arcs[i][j];
}
*/
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 有向图邻接矩阵的创建
*/
/************************************************************************/
void CreatDG(MGraph &G){
int i,j,k,w;
char v1,v2;
G.arcnum = 8;
G.vexnum = 9;
cout<<"请输入有向图顶点个数和边数:";
cin>> G.vexnum>> G.arcnum;
cout<<"请输入"<<G.vexnum<<"个顶点的值:"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;++i) cin>>G.vexs[i];
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;++i)
for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;++j) {
G.arcs[i][j].adj = 0;
G.arcs[i][j].info = NULL;
}
for( k=1;k<=G.arcnum;++k){
cout<<"请输入第"<<k<<"条边的两个顶点值和它们的权重:"<<endl;
cin>>v1>>v2>>w;
i= LocateVex(G,v1); j = LocateVex(G,v2);
G.arcs[i][j].adj = w;
}
}
void visitVex(MGraph G, int v){
cout<<G.vexs[v]<<" ";
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 以V为出发点对图G 进行递归地DFS 搜索
*/
/************************************************************************/
void DFS(MGraph G,int v){
visited[v] = true;
visitVex( G, v); //访问第v 个顶点
for(int w = FirstAdjVex(G,v); w>=0; w = NextAdjVex(G,v,w)){
if(!visited[w]) DFS(G,w); //w未访问过,递归DFS搜索
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
无向图的深度遍历
*/
/************************************************************************/
void DFSTraverse(MGraph G){//
int v;
for( v = 0; v < G.vexnum; ++v) visited[v] = false;
for( v = 0; v < G.vexnum; )
if(!visited[v]) DFS( G, v); //v未访问过,从vi开始DFS搜索
++v;//不要像书上写的那样,++v放到for语句,这样会导致多出一次访问
}
void printMGraph(MGraph G){
cout<<"邻接矩阵已经创建,邻接矩阵为:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++)
cout<<G.arcs[i][j].adj<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
}
void main(){
MGraph G;
CreatUDG(G);
printMGraph(G);
cout<<"无向图邻接矩阵的深度遍历结果:"<<endl;
DFSTraverse(G);
}
2) 邻接表的表示实现方式
[cpp] view plain copy
print?
// stdafx.h : include file for standard system include files,
// or project specific include files that are used frequently, but
// are changed infrequently
//
#pragma once
#include "targetver.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//宏定义
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define NULL 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
#define INFINITY INT_MAX
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 30
typedef int Status ;
typedef int ElemType ;
typedef int VrType ;
typedef char VertexType ;
/************************************************************************/
/* 邻接表示的图数据结构
*/
/************************************************************************/
//定义边结点,即表节点
typedef struct ArcNode
{
int adjvex; //弧所指的顶点位置
ArcNode *nextarc; //指向下一条弧的指针
}ArcNode;
//定义顶点节点,即头节点
typedef struct VNode
{
VertexType data; //顶点信息
ArcNode *firstarc; //指向第一条依附该顶点的弧的指针
}VNode,AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
//定义无向图
typedef struct
{
AdjList vertices;
int vexnum,arcnum; //图的当前顶点数和弧数
}ALGraph;
[cpp] view plain copy
print?
// Test.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
bool visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //访问标识
Status (*VisitFunc) (int v); //函数变量
/************************************************************************/
/* 在无向图中添加以m,n为顶点的边
*/
/************************************************************************/
void ArcAdd(ALGraph &G,int m,int n){
ArcNode *p,*h,*q;
p = new ArcNode;
p->adjvex = m;
p->nextarc = NULL;
h = q = G.vertices
.firstarc;
if(q == NULL)
G.vertices
.firstarc = p;
else {
if((p->adjvex)>(q->adjvex)){
p->nextarc = q;
G.vertices
.firstarc = p;
}
else {
while( G.vertices
.firstarc != NULL && q->nextarc != NULL && (p->adjvex)<(q->adjvex)){ //使邻接表中边的数据按大到小排列。
h = q;
q = q->nextarc;
}
if(q->nextarc == NULL&&(p->adjvex)<(q->adjvex)){
q->nextarc = p;
}
else {
p->nextarc = q;
h->nextarc = p;
}
}
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
创建无向图
*/
/************************************************************************/
void CreateDG(ALGraph &G){
cout<<"请输入顶点个数和边数:"<<endl;
cin>> G.vexnum>> G.arcnum;
cout<<"请输入顶点值:"<<endl;
for(int i= 1; i<= G.vexnum; i++) {
char t;
cin>>t;
G.vertices[i].data = t;
G.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
int m, n;
for(int k = 1; k<=G.arcnum; k++){
cout<<"请输入第"<<k<<"条边的两个顶点:"<<endl;
cin>>m>>n;
if(m<= G.vexnum && n <= G.vexnum && m>0 && n>0){
ArcAdd(G, m, n);
ArcAdd(G, n, m);
}
else cout<<"ERROR."<<endl;
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 打印邻接表的无向图
*/
/************************************************************************/
void PrintGraph(ALGraph G)
{
cout<<"无向图的创建完成,该图的邻接表表示为:"<<endl;
ArcNode *p;
for(int i=1; i<=G.vexnum; i++)
{
if(G.vertices[i].firstarc == NULL)
cout<<i<<G.vertices[i].data<<"-->NULL"<<endl;
else
{
p = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
cout<<i<<G.vertices[i].data<<"-->";
while(p->nextarc!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->adjvex<<"-->";
p = p->nextarc;
}
cout<<p->adjvex<<"-->NULL"<<endl;
}
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 返回v的第一个邻接顶点。若顶点在G中没有邻接表顶点,则返回“空”。
*/
/************************************************************************/
int FirstAdjVex(ALGraph G,int v)
{
if(G.vertices[v].firstarc)
return G.vertices[v].firstarc->adjvex;
else
return NULL;
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
返回v的(相对于w的)下一个邻接顶点。若w是v的最后一个邻接点,则返回“回”。
*/
/************************************************************************/
int NextAdjVex(ALGraph G,int v,int w)
{
ArcNode *p;
if(G.vertices[v].firstarc==NULL)
return NULL;
else {
p = G.vertices[v].firstarc;
while(p->adjvex!=w) p = p->nextarc;
if(p->nextarc == NULL) return NULL;
else return p->nextarc->adjvex;
}
}
void visitVex(ALGraph G, int v){
cout<<G.vertices[v].data<<" ";
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
无向图的深度遍历
*/
/************************************************************************/
//从第v个顶点出发递归地深度优先遍历图G
void DFS(ALGraph G,int v)
{
visited[v] = true;
visitVex(G, v);
for(int w = FirstAdjVex(G,v);w >= 1; w = NextAdjVex(G,v,w))
if(!visited[w]) DFS(G,w);
}
//对图G作深度优先遍历
void DFSTraverse(ALGraph G)
{
for(int v = 1; v <= G.vexnum; v++) visited[v]=false;
for(int m = 1; m <= G.vexnum; m++)
if(!visited[m]) DFS(G,m);
}
void main(){
ALGraph G;
CreateDG(G);
PrintGraph(G);
DFSTraverse(G);
}
分析上述算法,在遍历时,对图中每个顶点至多调用一次DFS 函数,因为一旦某个顶点被标志成已被访问,就不再从它出发进行搜索。因此,遍历图的过程实质上是对每个顶点查找其邻接点的过程。其耗费的时间则取决于所采用的存储结构。当用二维数组表示邻接矩阵图的存储结构时,查找每个顶点的邻接点所需时间为O(n2) ,其中n 为图中顶点数。而当以邻接表作图的存储结构时,找邻接点所需时间为O(e),其中e 为无向图中边的数或有向图中弧的数。由此,当以邻接表作存储结构时,深度优先搜索遍历图的时间复杂度为O(n+e) 。
2.广度优先搜索
广度优先搜索(Breadth_First Search) 遍历类似于树的按层次遍历的过程。假设从图中某顶点v 出发,在访问了v 之后依次访问v 的各个未曾访问过和邻接点,然后分别从这些邻接点出发依次访问它们的邻接点,并使“先被访问的顶点的邻接点”先于“后被访问的顶点的邻接点”被访问,直至图中所有已被访问的顶点的邻接点都被访问到。若此时图中尚有顶点未被访问,则另选图中一个未曾被访问的顶点作起始点,重复上述过程,直至图中所有顶点都被访问到为止。换句话说,广度优先搜索遍历图的过程中以v 为起始点,由近至远,依次访问和v 有路径相通且路径长度为1,2,…的顶点。
对图如下图所示无向图G5 进行广度优先搜索遍历:

广度搜索过程:

首先访问v1 和v1 的邻接点v2 和v3,然后依次访问v2 的邻接点v4 和v5 及v3 的邻接点v6 和v7,最后访问v4 的邻接点v8。由于这些顶点的邻接点均已被访问,并且图中所有顶点都被访问,由些完成了图的遍历。得到的顶点访问序列为:
v1→v2 →v3 →v4→ v5→ v6→ v7 →v8
和深度优先搜索类似,在遍历的过程中也需要一个访问标志数组。并且,为了顺次访问路径长度为2、3、…的顶点,需附设队列以存储已被访问的路径长度为1、2、… 的顶点。
实现:
[cpp] view plain copy
print?
// stdafx.h : include file for standard system include files,
// or project specific include files that are used frequently, but
// are changed infrequently
//
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
[cpp] view plain copy
print?
// func.h :
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//宏定义
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define NULL 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
#define INFINITY INT_MAX
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 30
typedef int Status ;
typedef int ElemType ;
typedef int VrType ;
typedef char VertexType ;
/************************************************************************/
/* 邻接表示的图数据结构
*/
/************************************************************************/
//定义边结点
typedef struct ArcNode
{
int adjvex; //弧所指的顶点位置
ArcNode *nextarc; //指向下一条弧的指针
}ArcNode;
//定义顶点结点
typedef struct VNode
{
VertexType data; //顶点信息
ArcNode *firstarc; //指向第一条依附该顶点的弧的指针
}VNode,AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
//定义无向图
typedef struct
{
AdjList vertices;
int vexnum,arcnum; //图的当前顶点数和弧数
}ALGraph;
/************************************************************************/
/* 需要 */
/************************************************************************/
typedef struct node //定义结点
{
char data;
node *next;
}*Link;
typedef struct //定义链表
{
Link head,tail;
int len;
}Queue;
/************************************************************************/
/* 构造一个带头结点和尾结点的空的线性链表队列Q
*/
/************************************************************************/
Status InitQueue(Queue &Q)
{
Q.head = new node;
Q.head->next = Q.tail = new node;
Q.tail->next = NULL;
Q.len = 0;
return 0;
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
//在线性链表的队列L的结尾添加一个结点
*/
/************************************************************************/
void EnQueue(Queue &Q,int e)
{
Link q = new node;
Q.tail->next = q;
Q.tail->data = e;
Q.tail = q;
Q.tail->next = NULL;
Q.len++;
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 出列,并将出列的元素值用e返回
*/
/************************************************************************/
void DeleteQueue(Queue &Q,int &e)
{
if(Q.head->next == Q.tail) {
cout<<"队列为空"<<endl;
e = NULL;
} else {
Link p,q;
p = Q.head->next;
q = p->next;
Q.head->next = q;
e = p->data;
delete p;
Q.len--;
}
}
[cpp] view plain copy
print?
// Test.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "func.h"
bool visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //访问标识
Status (*VisitFunc) (int v); //函数变量
/************************************************************************/
/* 在无向图中添加以m,n为顶点的边
*/
/************************************************************************/
void ArcAdd(ALGraph &G,int m,int n){
ArcNode *p,*h,*q;
p = new ArcNode;
p->adjvex = m;
p->nextarc = NULL;
h = q = G.vertices
.firstarc;
if(q == NULL)
G.vertices
.firstarc = p;
else {
if((p->adjvex)>(q->adjvex)){
p->nextarc = q;
G.vertices
.firstarc = p;
}
else {
while( G.vertices
.firstarc != NULL && q->nextarc != NULL && (p->adjvex)<(q->adjvex)){
//使邻接表中边的数据按大到小排列。
h = q;
q = q->nextarc;
}
if(q->nextarc == NULL&&(p->adjvex)<(q->adjvex)){
q->nextarc = p;
}
else {
p->nextarc = q;
h->nextarc = p;
}
}
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
创建无向图
*/
/************************************************************************/
void CreateDG(ALGraph &G){
cout<<"请输入顶点个数和边数:"<<endl;
cin>> G.vexnum>> G.arcnum;
cout<<"请输入顶点值:"<<endl;
for(int i= 1; i<= G.vexnum; i++) {
char t;
cin>>t;
G.vertices[i].data = t;
G.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
int m, n;
for(int k = 1; k<=G.arcnum; k++){
cout<<"请输入第"<<k<<"条边的两个顶点:"<<endl;
cin>>m>>n;
if(m<= G.vexnum && n <= G.vexnum && m>0 && n>0){
ArcAdd(G, m, n);
ArcAdd(G, n, m);
}
else cout<<"ERROR."<<endl;
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 打印邻接表的无向图
*/
/************************************************************************/
void PrintGraph(ALGraph G)
{
cout<<"无向图的创建完成,该图的邻接表表示为:"<<endl;
ArcNode *p;
for(int i=1; i<=G.vexnum; i++)
{
if(G.vertices[i].firstarc == NULL)
cout<<i<<G.vertices[i].data<<"-->NULL"<<endl;
else
{
p = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
cout<<i<<G.vertices[i].data<<"-->";
while(p->nextarc!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->adjvex<<"-->";
p = p->nextarc;
}
cout<<p->adjvex<<"-->NULL"<<endl;
}
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 返回v的第一个邻接顶点。若顶点在G中没有邻接表顶点,则返回“空”。
*/
/************************************************************************/
int FirstAdjVex(ALGraph G,int v)
{
if(G.vertices[v].firstarc)
return G.vertices[v].firstarc->adjvex;
else
return NULL;
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
返回v的(相对于w的)下一个邻接顶点。若w是v的最后一个邻接点,则返回“回”。
*/
/************************************************************************/
int NextAdjVex(ALGraph G,int v,int w)
{
ArcNode *p;
if(G.vertices[v].firstarc==NULL)
return NULL;
else {
p = G.vertices[v].firstarc;
while(p->adjvex!=w) p = p->nextarc;
if(p->nextarc == NULL) return NULL;
else return p->nextarc->adjvex;
}
}
void visitVex(ALGraph G, int v){
cout<<G.vertices[v].data<<" ";
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
广度优先遍历图G
*/
/************************************************************************/
void BFSTraverse(ALGraph G)
{
Queue Q;
int u;
for(int m=1; m<= G.vexnum; m++) visited[m] = false;
InitQueue(Q);//借助辅助队列。
for(int v=1;v<=G.vexnum;v++)
if(!visited[v]) {
visited[v]=true;
visitVex(G,v);
EnQueue(Q,v);
while(Q.len!=0)
{
DeleteQueue(Q,u);
for(int w=FirstAdjVex(G,u);w>=1;w=NextAdjVex(G,u,w))
if(!visited[w])
{
visited[w]=true;
visitVex(G,v);
EnQueue(Q,w);
}
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
void main(){
ALGraph G;
CreateDG(G);
PrintGraph(G);
cout<<"广度优先搜索的结果为:"<<endl;
BFSTraverse(G);
}
分析上述算法,每个顶点至多进一次队列。遍历图的过程实质是通过边或弧找邻接点的过程,因此广度优先搜索遍历图的时间复杂度和深度优先搜索遍历相同,两者不同之处仅仅在于对顶点访问的顺序不同。
