687B: Remainders Game
2016-07-02 09:03
423 查看
Codeforces Round #360 Editorial [+ Challenges!]
B. Remainders Game
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Today Pari and Arya are playing a game called Remainders.
Pari chooses two positive integer x and
k, and tells Arya k but not
x. Arya have to find the value
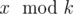
. There
are n ancient numbers
c1, c2, ..., cn and Pari has to tell Arya
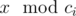
if Arya wants. Given
k and the ancient values, tell us if Arya has a winning strategy independent of value of
x or not. Formally, is it true that Arya can understand the value
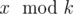
for any positive integer
x?
Note, that
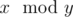
means the remainder of
x after dividing it by
y.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and
k (1 ≤ n,
k ≤ 1 000 000) — the number of ancient integers and value
k that is chosen by Pari.
The second line contains n integers
c1, c2, ..., cn (1 ≤ ci ≤ 1 000 000).
Output
Print "Yes" (without quotes) if Arya has a winning strategy independent of value of
x, or "No" (without quotes) otherwise.
Examples
Input
Output
Input
Output
Note
In the first sample, Arya can understand
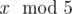
because
5 is one of the ancient numbers.
In the second sample, Arya can't be sure what
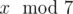
is. For example
1 and 7 have the same remainders after dividing by
2 and 3, but they differ in remainders after dividing by
7.
Hint
Assume the answer of a test is No. There must exist a pair of integers
x1 and
x2 such that both of them have the same remainders after dividing by any
ci, but they differ in remainders after dividing by
k. Find more facts about
x1 and x2!
Solution
Consider the x1 and
x2 from the hint part. We have
x1 - x2 ≡ 0 (
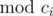
)
for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n.
So:
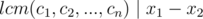
We also have
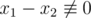
(
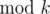
).
As a result:
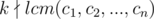
We've found a necessary condition. And I have to tell you it's also sufficient!
Assume
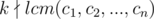
, we are going to prove there exists
x1, x2 such that
x1 - x2 ≡ 0 (
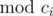
)
(for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n), and
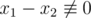
(
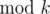
).
A possible solution is x1 = lcm(c1, c2, ..., cn)
and x2 = 2 × lcm(c1, c2, ..., cn), so the sufficiency
is also proved.
So you have to check if lcm(c1, c2, ..., cn) is divisible by
k, which could be done using prime factorization of
k and ci values.
For each integer x smaller than
MAXC, find it's greatest prime divisor gpdx using
sieve of Eratosthenes in
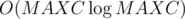
.
Then using gpd array, you can write the value of each coin as
p1q1p2q2...pmqm
where pi is a prime integer and
1 ≤ qi holds. This could be done in
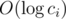
by moving from
ci to
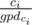
and adding
gpdci to the answer. And you can factorize
k by the same way. Now for every prime
p that
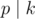
, see if there exists any coin
i that the power of
p in the factorization of ci is not smaller than the power of
p in the factorization of
k.
Complexity is
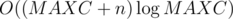
.
C++ code
原文链接:Codeforces Round #360 Editorial [+ Challenges!] - Codeforces
B. Remainders Game
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Today Pari and Arya are playing a game called Remainders.
Pari chooses two positive integer x and
k, and tells Arya k but not
x. Arya have to find the value
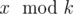
. There
are n ancient numbers
c1, c2, ..., cn and Pari has to tell Arya
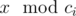
if Arya wants. Given
k and the ancient values, tell us if Arya has a winning strategy independent of value of
x or not. Formally, is it true that Arya can understand the value
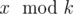
for any positive integer
x?
Note, that
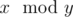
means the remainder of
x after dividing it by
y.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and
k (1 ≤ n,
k ≤ 1 000 000) — the number of ancient integers and value
k that is chosen by Pari.
The second line contains n integers
c1, c2, ..., cn (1 ≤ ci ≤ 1 000 000).
Output
Print "Yes" (without quotes) if Arya has a winning strategy independent of value of
x, or "No" (without quotes) otherwise.
Examples
Input
4 5 2 3 5 12
Output
Yes
Input
2 7 2 3
Output
No
Note
In the first sample, Arya can understand
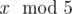
because
5 is one of the ancient numbers.
In the second sample, Arya can't be sure what
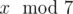
is. For example
1 and 7 have the same remainders after dividing by
2 and 3, but they differ in remainders after dividing by
7.
Hint
Assume the answer of a test is No. There must exist a pair of integers
x1 and
x2 such that both of them have the same remainders after dividing by any
ci, but they differ in remainders after dividing by
k. Find more facts about
x1 and x2!
Solution
Consider the x1 and
x2 from the hint part. We have
x1 - x2 ≡ 0 (
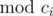
)
for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n.
So:
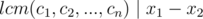
We also have
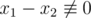
(
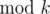
).
As a result:
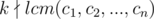
We've found a necessary condition. And I have to tell you it's also sufficient!
Assume
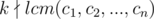
, we are going to prove there exists
x1, x2 such that
x1 - x2 ≡ 0 (
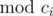
)
(for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n), and
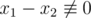
(
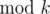
).
A possible solution is x1 = lcm(c1, c2, ..., cn)
and x2 = 2 × lcm(c1, c2, ..., cn), so the sufficiency
is also proved.
So you have to check if lcm(c1, c2, ..., cn) is divisible by
k, which could be done using prime factorization of
k and ci values.
For each integer x smaller than
MAXC, find it's greatest prime divisor gpdx using
sieve of Eratosthenes in
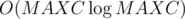
.
Then using gpd array, you can write the value of each coin as
p1q1p2q2...pmqm
where pi is a prime integer and
1 ≤ qi holds. This could be done in
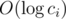
by moving from
ci to
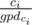
and adding
gpdci to the answer. And you can factorize
k by the same way. Now for every prime
p that
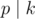
, see if there exists any coin
i that the power of
p in the factorization of ci is not smaller than the power of
p in the factorization of
k.
Complexity is
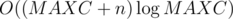
.
C++ code
// . .. ... .... ..... be name khoda ..... .... ... .. . \\
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline int in() { int x; scanf("%d", &x); return x; }
const long long N = 1200021;
int cntP
, isP
;
int main()
{
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++)
if(!isP[i])
for(int j = i; j < N; j += i)
isP[j] = i;
int n = in(), k = in();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x = in();
while(x > 1)
{
int p = isP[x];
int cnt = 0;
while(x % p == 0)
{
cnt++;
x /= p;
}
cntP[p] = max(cntP[p], cnt);
}
}
bool ok = 1;
while(k > 1)
{
ok &= (cntP[isP[k]] > 0);
cntP[isP[k]]--;
k /= isP[k];
}
cout << (ok ? "Yes\n" : "No\n");
}原文链接:Codeforces Round #360 Editorial [+ Challenges!] - Codeforces
相关文章推荐
- [leetcode]11. Container With Most Water
- RAID 2.0
- strong区别于retain
- http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/7f41ecec1b7a2e593d095ce6.html
- 172. Factorial Trailing Zeroes
- Codeforces Round #360 (Div. 2) D. Remainders Game
- LeetCode - 11. Container With Most Water
- Mybaits深入了解(二)—-入门实例
- Error:Maven Resources Compiler: Failed to copy 'XXX' to 'YYY': YYY (拒绝访问。)
- Error:Maven Resources Compiler: Failed to copy 'XXX' to 'YYY': YYY (拒绝访问。)
- Repairing Company(poj 3216)
- Mybaits深入了解(一)----带你入门
- AIX 交换分区使用并定位
- Failed with exception Unable to rename: hdfs://ns1/tmp/hive-hadoop/hive...to...
- waits events statisc
- Xen环境下搭建NFS实现Domain0与DomainU之间共享文件
- 使用SDK Program FPGA failed 的解决办法
- Codeforces Round #360 (Div. 2) D. Remainders Game(数学)
- Unsupported major.minor version 52.0 (unable to load class com.servlet.MailSenderServlet)
- failback 和failover
