python argparse模块的简单使用
2016-06-20 11:33
901 查看
argparse的一个使用例子:
#! /usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf8
import socket
import argparse
def setArgparse():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="socket test")#添加模块描述
parser.add_argument('--host', action="store", dest="host", required=True)
parser.add_argument('--port', action='store', dest='port', type=int, required=True)
give_args = parser.parse_args()
host = give_args.host
port = give_args.port
try:
s= socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
except socket.error as e:
print 'Error create socket %s'.format(e)
if __name__ == "__main__":
setArgparse()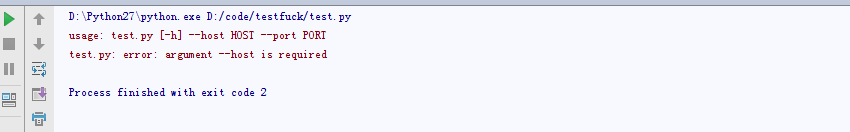
扩展例子:
import argparse
parse = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parse.add_argument("a", help="params means")
parse.add_argument("-C", "--gc", default="count")
parse.add_argument("--ga", help="params means ga",dest='simple_value',choices=['A', 'B', 'C', 0])
parse.add_argument("--gb", help="params means gb",action="store_const",const='value-to-store')
args = parse.parse_args()
print args.simple_value,args.gb,args.gc
### add_argument 说明
不带'--'的参数
调用脚本时必须输入值
参数输入的顺序与程序中定义的顺序一致
'-'的参数
可不输入 add_argument("-a")
类似有'--'的shortname,但程序中的变量名为定义的参数名
'--'参数
参数别名: 只能是1个字符,区分大小写
add_argument("-shortname","--name", help="params means"),但代码中不能使用shortname
dest: 参数在程序中对应的变量名称 add_argument("a",dest='code_name')
default: 参数默认值
help: 参数作用解释 add_argument("a", help="params means")
type : 默认string add_argument("c", type=int)
action:
store:默认action模式,存储值到指定变量。
store_const:存储值在参数的const部分指定,多用于实现非布尔的命令行flag。
store_true / store_false:布尔开关。 store_true.默认为False,输入则为true。 store_flase 相反
append:存储值到列表,该参数可以重复使用。
append_const:存储值到列表,存储值在参数的const部分指定。
count: 统计参数简写输入的个数 add_argument("-c", "--gc", action="count")
version 输出版本信息然后退出。
const:配合action="store_const|append_const"使用,默认值
choices:输入值的范围 add_argument("--gb", choices=['A', 'B', 'C', 0])
required : 默认False, 若为 True, 表示必须输入该参数
==================================================================================
Keyword Arguments:
- option_strings -- A list of command-line option strings which should be associated with this action.
- dest -- The name of the attribute to hold the created object(s)
- nargs -- The number of command-line arguments that should be consumed. By default, one argument will be consumed and a single value will be produced.
Other values include:
- N (an integer) consumes N arguments (and produces a list)
- '?' consumes zero or one arguments
- '*' consumes zero or more arguments (and produces a list)
- '+' consumes one or more arguments (and produces a list)
Note that the difference between the default and nargs=1 is that with the default, a single value will be produced, while with nargs=1, a list containing a single value will be produced.
- const -- The value to be produced if the option is specified and the option uses an action that takes no values.
- default -- The value to be produced if the option is not specified.
- type -- A callable that accepts a single string argument, and returns the converted value.
The standard Python types str, int, float, and complex are useful examples of such callables. If None, str is used.
- choices -- A container of values that should be allowed.
If not None, after a command-line argument has been converted to the appropriate type, an exception will be raised if it is not a member of this collection.
- required -- True if the action must always be specified at the command line. This is only meaningful for optional command-line arguments.
- help -- The help string describing the argument.
- metavar -- The name to be used for the option's argument with the help string. If None, the 'dest' value will be used as the name.import argparse
# sub-command functions
def subcmd_list(args):
print "list"
def subcmd_create(args):
print "create"
def subcmd_delete(args):
print "delete"
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
subparsers = parser.add_subparsers(help='commands')
# A list command
list_parser = subparsers.add_parser('list', help='Listcontents')
list_parser.add_argument('dirname', action='store', help='Directory tolist')
list_parse.set_defaults(func=subcmd_list)
# A create command
create_parser = subparsers.add_parser('create', help='Create a directory')
create_parser.add_argument('dirname',action='store',help='New directoryto create')
create_parser.add_argument('--read-only',default=False, action='store_true',help='Setpermissions to prevent writing to the directory')
create_parser .set_defaults(func=subcmd_create)
# A delete command
delete_parser = subparsers.add_parser('delete',help='Remove a directory')
delete_parser.add_argument( 'dirname', action='store',help='The directory to remove')
delete_parser.add_argument('--recursive', '-r',default=False, action='store_true',help='Remove thecontents of the directory, too')
delete_parser .set_defaults(func=subcmd_delete)
args = parser.parse_args()
# call subcmd
args.fun(args)
相关文章推荐
- Python动态类型的学习---引用的理解
- Python3写爬虫(四)多线程实现数据爬取
- 垃圾邮件过滤器 python简单实现
- 下载并遍历 names.txt 文件,输出长度最长的回文人名。
- install and upgrade scrapy
- Scrapy的架构介绍
- Centos6 编译安装Python
- 使用Python生成Excel格式的图片
- 让Python文件也可以当bat文件运行
- [Python]推算数独
- Python中zip()函数用法举例
- Python中map()函数浅析
- Python将excel导入到mysql中
- Python在CAM软件Genesis2000中的应用
- 使用Shiboken为C++和Qt库创建Python绑定
- FREEBASIC 编译可被python调用的dll函数示例
- Python 七步捉虫法
