Spring源码解读1——Resource定位
2016-06-18 00:00
453 查看
IoC容器的初始化过程包括bean资源的定位、载入和注册三个过程。本节讨论bean(resource)的定位。
以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的初始化为例:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext f = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
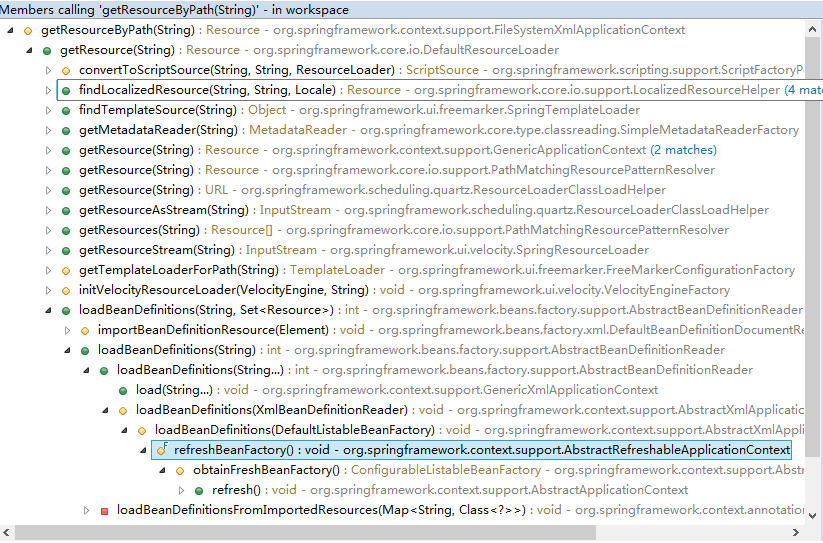
程序的入口是这个refresh()。
继承关系:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext--AbstractXmlApplicationContext--AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext(继续完善新的细节) --*AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext(实现了refresh()的细节,同时抛出新的模板方法) --*AbstractApplicationContext(定义了模板方法refresh())
祖先类定义了方法,后续的继承类实现了细节,最后的实现类就可以直接调用到完整的refresh()了。这也是模板设计模式的思想。
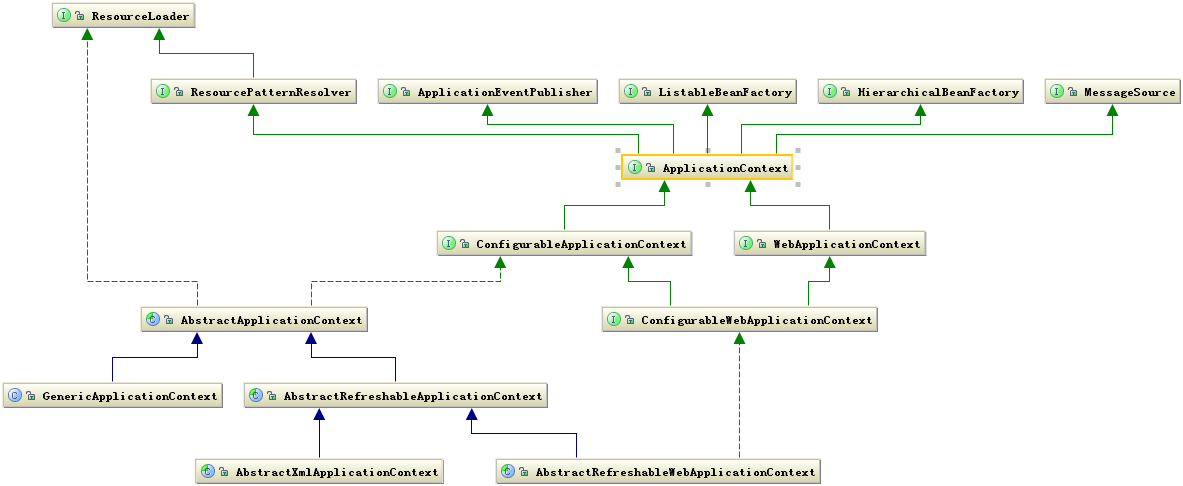
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext容器提供了getResourceByPath方法的实现,就是为了处理既不是classpath标识,又不是URL标识的Resource定位这种情况。
现在,Bean定义的Resource得到了,下面我们继续跟随程序执行方向,分析XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法。
编程式调用IOC容器,可以使我们更清楚的看到其工作过程:

以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的初始化为例:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext f = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");

程序的入口是这个refresh()。
[code=language-java]public class FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(){
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
//开始
refresh();
}
}
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
return new FileSystemResource(path);
}
}继承关系:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext--AbstractXmlApplicationContext--AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext(继续完善新的细节) --*AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext(实现了refresh()的细节,同时抛出新的模板方法) --*AbstractApplicationContext(定义了模板方法refresh())
祖先类定义了方法,后续的继承类实现了细节,最后的实现类就可以直接调用到完整的refresh()了。这也是模板设计模式的思想。

[code=language-java]public class AbstractApplicationContext{
public void refresh(){
prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//refreshBeanFactory(),getBeanFactory()都是模板模式,由其子类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext()实现
//非编程式调用时(new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(".xml")),会创建一个默认的BeanFactory
//AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext创建Factory,并且给Factory设置一些功能
refreshBeanFactory();
//此处得到上述创建的Factory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
}[code=language-java]public class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext{
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//模板模式,由子类AbstractXmlApplicationContext实现
//给Factory设置一些功能
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
}[code=language-java]
public abstract class AbstractXmlApplicationContext{
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory){
//创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader,即创建Bean读取器
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
//问题:factory的作用?
//reader把解析完成的资源放在BeanDefinition中,再把BeanDefinition放入factory
//(括号里的this)为Bean读取器设置Spring资源加载器,AbstractXmlApplicationContext的
//祖先父类AbstractApplicationContext继承DefaultResourceLoader,因此,容器本身也是一个资源加载器
//给reader设置loader
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader){
//getConfigLocations()可以取到之前在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext中
//的setConfigLocations()方法设置的文件路径
//setConfigLocations、getConfigLocations 都是AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext里的方法
//在Context中可以得到资源,而编程式调用时就必须手动设置了
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
//Xml Bean读取器调用其父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader读取定位Bean的定义资源
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
}[code=language-java]public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
//==========reader其实是用loader来加载配置文件的
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//registry就是new Reader时传入的factory
this.registry = registry;
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) {
return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null);
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int counter = 0;
for (String location : locations) {
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
return counter;
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) {
// 获取在IoC容器初始化过程中设置的资源加载器(AbstractXmlApplicationContext)
//即beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
try {
throw new Exception(
"Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 加载单个指定位置的Bean定义资源文件
//AbstractXmlApplicationContext中,beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
//resourceLoader(即xmlContext)的父类DefaultResourceLoader的getResource
//AbstractApplicationContext继承DefaultResourceLoader
//DefaultResourceLoader中的getResource():
//return new ClassPathResource;
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
// 委派调用其子类XmlBeanDefinitionReader的方法,实现加载功能
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
return loadCount;
}
protected abstract int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource);
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
}[code=language-java]public class DefaultResourceLoader{
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
}FileSystemXmlApplicationContext容器提供了getResourceByPath方法的实现,就是为了处理既不是classpath标识,又不是URL标识的Resource定位这种情况。
现在,Bean定义的Resource得到了,下面我们继续跟随程序执行方向,分析XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法。
编程式调用IOC容器,可以使我们更清楚的看到其工作过程:

相关文章推荐
- spring MVC和spring的注解
- SpringMvc与Struts2的对比
- Spring中Bean对象的创建
- Spring-AOP
- JVM(一):Java内存区域与内存溢出异常
- eclipse安装git,上传和下载详解
- JDK环境变量中dt.jar、tools.jar等变量值的作用
- java开发环境搭建
- eclipse配置maven下载源码
- Spring AOP 实现原理与 CGLIB 应用
- 谈谈对Spring IOC的理解
- Java爬虫
- java常用的框架介绍
- 初识Java
- springmvc+datagrid+json分页
- (JAVA+TESTNG 一)JDK,JRE,JVM区别与联系
- Java把内存划分成两种:一种是栈内存,一种是堆内存。
- Java常用基础代码
- Java--多线程编程
- Binary Tree Level Order Traversal的java实现
