多线程下载 与 断点续传
2016-06-01 13:54
204 查看
今天学习了多线程的的下载。向大家分享一下。
首先呢,什么是多线程下载。现在有三个人去同一个服务器里下载 同一个资源。 而服务器的带宽是均分给每一个线程的。那么机智的你当然想下载的更快,所以你开了多个线程来下载。假设服务器的带宽是9M,有三个人下载 每个人开的单线程在执行下载任务的话。当然你和其他两个均分9M带宽,为3M。但这是你开启了3个线程下载,就是当前有5个线程均分服务器的总带宽 而你拥有的速度 就是 你开启的线程数* (服务器总带宽/ 当前下载的总线程数) 这里为3*(9/5) 速度为其他两个的3倍。
基本概念有了,那我们知道什么听起来 高大上的 多线程下载 也就是多开启几个线程下载而已。那开启多个线程 又会 给我们带来哪些问题
总结一下
一:我们得把需要下载的总文件的长度,分配好给对应的线程来负责下载,也就是计算好每个线程对应的下载区间
二:我们每个线程得到的数据流 应该是 对应下载任务区间的流
三:我们每个线程的写入开始位置应该是 对应下载区间的首位置
四:下载文件前 在硬盘上开辟一个等容量的空间,来用储存下载的文件
接下来看一看代码,看一看 这些问题分别在代码的哪些地方得到解决:
上面代码大概可以概括为
1第一遍拿到流 为了得到要下载文件的大小 lenght
2 拿到大小为的是 为所要下载的文件 开辟 同样大小的空间,并且在 for 循环中为每个线程 分配好下载区间(前几个线程分配的大小为lenght/ThreadCound,最后一个线程例外 可能多出来也可能少出来一点,但是endIndex 必然是 lenght-1)
3. 开启了若干个线程来执行下载任务(这里我们定义了三个)
然后 看一下DownThreads 里面的代码
这就每个线程里的逻辑代码:
里面添加了断点续传 功能 说白了 就是将你上次下载到哪里 那个Index 存在对应线程的临时文件中 ,这样再次下载的时候就不用再从一开始下载。最后结束线程的个数 为开启线程的总数 就把这些临时文件删除(说明文件已经下完)。
运行图:
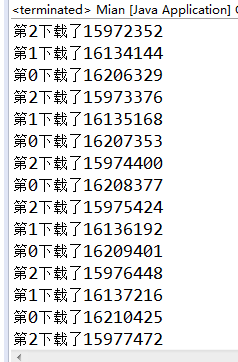
下载到的 API文档
这里是下载过程是中断过一次的,说明断点续传是可以的
首先呢,什么是多线程下载。现在有三个人去同一个服务器里下载 同一个资源。 而服务器的带宽是均分给每一个线程的。那么机智的你当然想下载的更快,所以你开了多个线程来下载。假设服务器的带宽是9M,有三个人下载 每个人开的单线程在执行下载任务的话。当然你和其他两个均分9M带宽,为3M。但这是你开启了3个线程下载,就是当前有5个线程均分服务器的总带宽 而你拥有的速度 就是 你开启的线程数* (服务器总带宽/ 当前下载的总线程数) 这里为3*(9/5) 速度为其他两个的3倍。
基本概念有了,那我们知道什么听起来 高大上的 多线程下载 也就是多开启几个线程下载而已。那开启多个线程 又会 给我们带来哪些问题
总结一下
一:我们得把需要下载的总文件的长度,分配好给对应的线程来负责下载,也就是计算好每个线程对应的下载区间
二:我们每个线程得到的数据流 应该是 对应下载任务区间的流
三:我们每个线程的写入开始位置应该是 对应下载区间的首位置
四:下载文件前 在硬盘上开辟一个等容量的空间,来用储存下载的文件
接下来看一看代码,看一看 这些问题分别在代码的哪些地方得到解决:
public class Mian {
// 线程数量
private static int ThreadCount = 3;
// 路径,该路径是网上一个 android api文档下载路径
public static final String PATH ="http://dl.download.csdn.net/down10/20150115/202d14961bdf45de7dbb9c17efb39496.chm?response-content-disposition=attachment%3Bfilename%3D%22Android%E5%AE%98%E6%96%B9API%E6%96%87%E6%A1%A3%E5%AE%8C%E6%95%B4%E7%89%88.chm%22&OSSAccessKeyId=9q6nvzoJGowBj4q1&Expires=1464750083&Signature=efVjCq9nB8mlj2z0R%2FGrchRZYu8%3D";
//记录下载完成 的线程数量,其目的是为了在所有线程都下载完 将临时文件删除
public static int FinishedThread = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
URL url = new URL(PATH);
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url
.openConnection();
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
connection.setConnectTimeout(8000);
connection.setReadTimeout(8000);
System.out.println(connection.getResponseCode()+"!!!!!!!");
if (connection.getResponseCode() == 200) {
int lenght = connection.getContentLength();
System.out.println(lenght/1024+".....");
int size = (int) (lenght / ThreadCount);
// 拿到了文件的长度,在下载前要建造一个大小相等的空文件
File file = new File("view.chm");
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rwd");
raf.setLength(lenght);
for (int id = 0; id < ThreadCount; id++) {
// 1.确定每个线程的下载区间
// 2.开启线程 下载
int startIndex = (id * size);
int endIndex = (id + 1) * size - 1;
if (id == ThreadCount - 1) {
endIndex = (int) (lenght - 1);
}
System.out.println("第"+id+"个进程的下载区间为"+startIndex+"----"+endIndex);
DownThreads downThreads = new DownThreads(startIndex, endIndex, PATH, id,ThreadCount);
downThreads.start();
}
}
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}上面代码大概可以概括为
1第一遍拿到流 为了得到要下载文件的大小 lenght
2 拿到大小为的是 为所要下载的文件 开辟 同样大小的空间,并且在 for 循环中为每个线程 分配好下载区间(前几个线程分配的大小为lenght/ThreadCound,最后一个线程例外 可能多出来也可能少出来一点,但是endIndex 必然是 lenght-1)
3. 开启了若干个线程来执行下载任务(这里我们定义了三个)
然后 看一下DownThreads 里面的代码
public class DownThreads extends Thread {
private int startIndex;
private int endIndex;
private String path;
private int threadId;
private int TheardCount;
public DownThreads(int startIndex, int endIndex, String path, int threadId,
int ThreadCount) {
super();
this.startIndex = startIndex;
this.endIndex = endIndex;
this.path = path;
this.threadId = threadId;
this.TheardCount = ThreadCount;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.run();
URL url;
try {
//关于断点续传 有三个文件存下当前下载的 长度
File fileProgress = new File(threadId + ".txt");
//上次的进度 从三个临时文件读取
int lastProgress = 0;
//如果文件存在 说明 不是第一次下载 是没下载完的状态 那么这是就要将startIndex 改为文件里记录的地方
if (fileProgress.exists()) {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileProgress);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
fis));
lastProgress = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
//新的起始位置 为原始的起始 位置 + 文件里记录的位置
startIndex += lastProgress;
}
url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
connection.setConnectTimeout(8000);
connection.setReadTimeout(8000);
// 得到对应下载区间的流
connection.setRequestProperty("Range", "bytes=" + startIndex + "-"+ endIndex);
if (connection.getResponseCode() == 206) {
InputStream is = connection.getInputStream();
File file = new File("view.chm");
// 填充空白的文件 生成一个空白有大小的文件 主文件
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rwd");
// 从该位置开始写入
raf.seek(startIndex);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
//total 每单个线程下载的总量 初始值为文件记录的 位置值 如为第一次下载文件不存在 那么 为lastProgress的初始值 0
int total = lastProgress;
while ((len = is.read(b)) != -1) {
raf.write(b, 0, len);
total = total + len;
RandomAccessFile rafProgress = new RandomAccessFile(
fileProgress, "rwd");
rafProgress.write((total + "").getBytes());
rafProgress.close();
System.out.println("第" + threadId + "下载了" + total);
}
System.out.println("第" + threadId + "个线程" + "下载结束!!!!");
Mian.FinishedThread++;
//将Mian.FinishedThread写入文件EndThreadCountFile
File CountFile = new File("EndThreadCount.txt");
RandomAccessFile rafCount = new RandomAccessFile(CountFile, "rwd");
rafCount.write((Mian.FinishedThread+"").getBytes());;
System.out.println(Mian.FinishedThread + "!!!!!!!!!");
//当文件都全部下完 即每个线程任务都结束了 那么删除这三个文件
/*有以文件用于记录已经完成的线程数 因为单单用一个int 来记录存在逻辑上的bug
当其中两个线程结束了,另一个未结束。这时你暂停下载。那么等下次在断点续传的时候 这个int 值只能加到一(假设有三个线程),永远都删除不掉临时文件
因为数据并没有持久化,用文件来保存就不一样了,但是记得最后将它也删除*/
if (CountFile.exists() && readMyFile(CountFile) == TheardCount ) {
System.out.println("if()" + Mian.FinishedThread
+ "!!!!!!!!!");
for (int i = 0; i < TheardCount; i++) {
File f = new File(i + ".txt");
f.delete();
}
CountFile.delete();
}
raf.close();
is.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private int readMyFile(File file) throws Exception{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
int Count = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
return Count;
}
}这就每个线程里的逻辑代码:
里面添加了断点续传 功能 说白了 就是将你上次下载到哪里 那个Index 存在对应线程的临时文件中 ,这样再次下载的时候就不用再从一开始下载。最后结束线程的个数 为开启线程的总数 就把这些临时文件删除(说明文件已经下完)。
运行图:


下载到的 API文档

这里是下载过程是中断过一次的,说明断点续传是可以的
相关文章推荐
- Python3写爬虫(四)多线程实现数据爬取
- C#实现多线程的同步方法实例分析
- 浅谈chuck-lua中的多线程
- C#简单多线程同步和优先权用法实例
- C#多线程学习之(四)使用线程池进行多线程的自动管理
- C#多线程编程中的锁系统(三)
- 解析C#多线程编程中异步多线程的实现及线程池的使用
- C#多线程学习之(六)互斥对象用法实例
- 基于一个应用程序多线程误用的分析详解
- C#多线程学习之(三)生产者和消费者用法分析
- C#多线程学习之(一)多线程的相关概念分析
- C#多线程之Thread中Thread.IsAlive属性用法分析
- 分享我在工作中遇到的多线程下导致RCW无法释放的问题
- C#多线程编程之使用ReaderWriterLock类实现多用户读与单用户写同步的方法
- C#控制台下测试多线程的方法
- 21天学习android开发教程之SurfaceView与多线程的混搭
- Ruby 多线程的潜力和弱点分析
- C#中WPF使用多线程调用窗体组件的方法
- C#如何对多线程、多任务管理(demo)
- C#实现多线程的Web代理服务器实例
