codeforces 676B B. Pyramid of Glasses(模拟)
2016-05-29 13:18
381 查看
题目链接:[b]B. Pyramid of Glasses[/b]time limit per test
1 secondmemory limit per test
256 megabytesinput
standard inputoutput
standard outputMary has just graduated from one well-known University and is now attending celebration party. Students like to dream of a beautiful life, so they used champagne glasses to construct a small pyramid. The height of the pyramid is n. The top level consists of only 1 glass, that stands on 2 glasses on the second level (counting from the top), then 3 glasses on the third level and so on.The bottom level consists of n glasses.Vlad has seen in the movies many times how the champagne beautifully flows from top levels to bottom ones, filling all the glasses simultaneously. So he took a bottle and started to pour it in the glass located at the top of the pyramid.Each second, Vlad pours to the top glass the amount of champagne equal to the size of exactly one glass. If the glass is already full, but there is some champagne flowing in it, then it pours over the edge of the glass and is equally distributed over two glasses standing under. If the overflowed glass is at the bottom level, then the champagne pours on the table. For the purpose of this problem we consider that champagne is distributed among pyramid glasses immediately. Vlad is interested in the number of completely full glasses if he stops pouring champagne in t seconds.Pictures below illustrate the pyramid consisting of three levels.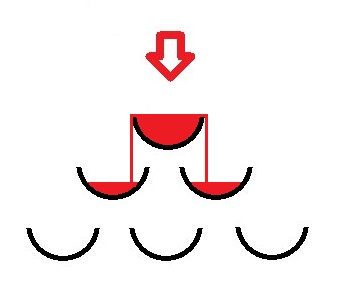
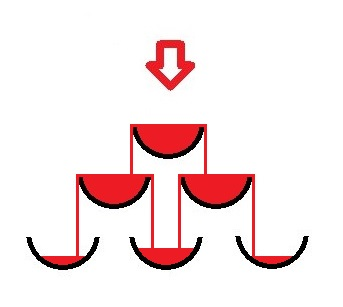 InputThe only line of the input contains two integers n and t (1 ≤ n ≤ 10, 0 ≤ t ≤ 10 000) — the height of the pyramid and the number of seconds Vlad will be pouring champagne from the bottle.OutputPrint the single integer — the number of completely full glasses after t seconds.Examplesinput
InputThe only line of the input contains two integers n and t (1 ≤ n ≤ 10, 0 ≤ t ≤ 10 000) — the height of the pyramid and the number of seconds Vlad will be pouring champagne from the bottle.OutputPrint the single integer — the number of completely full glasses after t seconds.Examplesinput
1 secondmemory limit per test
256 megabytesinput
standard inputoutput
standard outputMary has just graduated from one well-known University and is now attending celebration party. Students like to dream of a beautiful life, so they used champagne glasses to construct a small pyramid. The height of the pyramid is n. The top level consists of only 1 glass, that stands on 2 glasses on the second level (counting from the top), then 3 glasses on the third level and so on.The bottom level consists of n glasses.Vlad has seen in the movies many times how the champagne beautifully flows from top levels to bottom ones, filling all the glasses simultaneously. So he took a bottle and started to pour it in the glass located at the top of the pyramid.Each second, Vlad pours to the top glass the amount of champagne equal to the size of exactly one glass. If the glass is already full, but there is some champagne flowing in it, then it pours over the edge of the glass and is equally distributed over two glasses standing under. If the overflowed glass is at the bottom level, then the champagne pours on the table. For the purpose of this problem we consider that champagne is distributed among pyramid glasses immediately. Vlad is interested in the number of completely full glasses if he stops pouring champagne in t seconds.Pictures below illustrate the pyramid consisting of three levels.

 InputThe only line of the input contains two integers n and t (1 ≤ n ≤ 10, 0 ≤ t ≤ 10 000) — the height of the pyramid and the number of seconds Vlad will be pouring champagne from the bottle.OutputPrint the single integer — the number of completely full glasses after t seconds.Examplesinput
InputThe only line of the input contains two integers n and t (1 ≤ n ≤ 10, 0 ≤ t ≤ 10 000) — the height of the pyramid and the number of seconds Vlad will be pouring champagne from the bottle.OutputPrint the single integer — the number of completely full glasses after t seconds.Examplesinput3 5output
4input
4 8output
6 题意: 像图中那样摆放杯子,共n层,问t分之后有多少杯子被倒满了; 思路: 模拟倒酒的过程,然后再统计就好了; AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/*
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
*/
using namespace std;
#define Riep(n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
#define Riop(n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
#define Rjep(n) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
#define Rjop(n) for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
#define mst(ss,b) memset(ss,b,sizeof(ss));
typedef long long LL;
const LL mod=1e9+7;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const LL inf=1e18;
const int N=1e6+4;
int n,t;
double a[20][20];
void fun()
{
a[1][1]+=1;
Riep(n)
{
Rjep(i)
{
if(a[i][j]>1)
{
a[i+1][j]+=(a[i][j]-1)/2;
a[i+1][j+1]+=(a[i][j]-1)/2;
a[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&t);
for(int i=1;i<=t;i++)fun();
int ans=0;
Riep(n)
{
Rjep(i)if(a[i][j]>=1)ans++;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 谈谈数据库中MyISAM与InnoDB区别
- TCP/IP之大明王朝邮差
- js中random的应用
- AsyncTask 坑 (三)AsyncTask对象多次执行
- 安卓初识基础控件_CheckBox
- Calendar类中add/set/roll方法的区别
- NumPy 数组矩阵运算
- shell命令-dpkg
- Unix & Linux 笔记(12)
- Java发邮件
- tearing
- HDFS原理与操作及API编程
- nodejs抓取网页的源码,并保存到本地文件
- 多线程操作数据库--WAL模式--一写多读并行
- 负数在计算机中如何表示
- IOS中的单例模式
- HDUOJ 1018 Big Number (斯特林公式)
- 实现Walker之闪屏界面的实现分析
- zznu 1257 HDU1052 田忌赛马
- STL学习笔记--4、序列式容器之list
