caffe中LRN的实现
2016-05-26 16:38
183 查看
原文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/kkk584520/article/details/42032013
LRN全称为Local Response Normalization,即局部响应归一化层,具体实现在CAFFE_ROOT/src/caffe/layers/lrn_layer.cpp和同一目录下lrn_layer.cu中。
该层需要参数有:
norm_region: 选择对相邻通道间归一化还是通道内空间区域归一化,默认为ACROSS_CHANNELS,即通道间归一化;
local_size:两种表示(1)通道间归一化时表示求和的通道数;(2)通道内归一化时表示求和区间的边长;默认值为5;
alpha:缩放因子(详细见后面),默认值为1;
beta:指数项(详细见后面), 默认值为5;
局部响应归一化层完成一种“临近抑制”操作,对局部输入区域进行归一化。
在通道间归一化模式中,局部区域范围在相邻通道间,但没有空间扩展(即尺寸为 local_size x 1 x 1);
在通道内归一化模式中,局部区域在空间上扩展,但只针对独立通道进行(即尺寸为 1 x local_size x local_size);
每个输入值都将除以
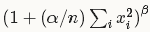
其中n为局部尺寸大小local_size,
alpha和beta前面已经定义。
求和将在当前值处于中间位置的局部区域内进行(如果有必要则进行补零)。
下面我们看Caffe代码如何实现。打开CAFFE_ROOT/include/caffe/vision_layers.hpp,从第242行开始看起:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?


// Forward declare PoolingLayer and SplitLayer for use in LRNLayer.
template <typename Dtype> class PoolingLayer;
template <typename Dtype> class SplitLayer;
/**
* @brief Normalize the input in a local region across or within feature maps.
*
* TODO(dox): thorough documentation for Forward, Backward, and proto params.
*/
template <typename Dtype>
class LRNLayer : public Layer<Dtype> {
public:
explicit LRNLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
: Layer<Dtype>(param) {}
virtual void LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual inline LayerParameter_LayerType type() const {
return LayerParameter_LayerType_LRN;
}
virtual inline int ExactNumBottomBlobs() const { return 1; }
virtual inline int ExactNumTopBlobs() const { return 1; }
protected:
virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
virtual void CrossChannelForward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void CrossChannelForward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void WithinChannelForward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void CrossChannelBackward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
virtual void CrossChannelBackward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
virtual void WithinChannelBackward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
int size_;
int pre_pad_;
Dtype alpha_;
Dtype beta_;
int num_;
int channels_;
int height_;
int width_;
// Fields used for normalization ACROSS_CHANNELS
// scale_ stores the intermediate summing results
Blob<Dtype> scale_;
// Fields used for normalization WITHIN_CHANNEL
shared_ptr<SplitLayer<Dtype> > split_layer_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> split_top_vec_;
shared_ptr<PowerLayer<Dtype> > square_layer_;
Blob<Dtype> square_input_;
Blob<Dtype> square_output_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> square_bottom_vec_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> square_top_vec_;
shared_ptr<PoolingLayer<Dtype> > pool_layer_;
Blob<Dtype> pool_output_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> pool_top_vec_;
shared_ptr<PowerLayer<Dtype> > power_layer_;
Blob<Dtype> power_output_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> power_top_vec_;
shared_ptr<EltwiseLayer<Dtype> > product_layer_;
Blob<Dtype> product_input_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> product_bottom_vec_;
};
内容较多,可能看一眼记不住所有的成员变量和函数,但记住一点,凡是Layer类型肯定都包含Forward()和Backward(),以及LayerSetUp()和Reshape(),这些在头文件中不必细看。关注的是以“_”结尾的成员变量,这些是和算法息息相关的。
很高兴看到了num_, height_, width_, channels_,这四个变量定义了该层输入图像的尺寸信息,是一个num_ x channels_ x height_ x width_的四维Blob矩阵(想不通?就当作视频流吧,前两维是宽高,第三维是颜色,第四维是时间)。
另外看到了alpha_, beta_, 这两个就是我们上面公式中的参数。
公式中的n(local_size)在类中用size_表示。
上面提到过需要补零,所以定义了pre_pad_变量。
在ACROSS_CHANNELS模式下,我们只需要用到scale_这个Blob矩阵,后面定义都可以忽略了~~好开森~~
读完了头文件中的声明,是不是觉得挺简单?我们接着看下实现细节,打开CAFFE_ROOT/src/caffe/layers/lrn_layer.cpp,从头看起,第一个实现函数为LayerSetUp(),代码如下:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?


template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) {
size_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().local_size();
CHECK_EQ(size_ % 2, 1) << "LRN only supports odd values for local_size";
pre_pad_ = (size_ - 1) / 2;
alpha_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().alpha();
beta_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().beta();
if (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region() ==
LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL) {
// Set up split_layer_ to use inputs in the numerator and denominator.
split_top_vec_.clear();
split_top_vec_.push_back(&product_input_);
split_top_vec_.push_back(&square_input_);
LayerParameter split_param;
split_layer_.reset(new SplitLayer<Dtype>(split_param));
split_layer_->SetUp(bottom, &split_top_vec_);
// Set up square_layer_ to square the inputs.
square_bottom_vec_.clear();
square_top_vec_.clear();
square_bottom_vec_.push_back(&square_input_);
square_top_vec_.push_back(&square_output_);
LayerParameter square_param;
square_param.mutable_power_param()->set_power(Dtype(2));
square_layer_.reset(new PowerLayer<Dtype>(square_param));
square_layer_->SetUp(square_bottom_vec_, &square_top_vec_);
// Set up pool_layer_ to sum over square neighborhoods of the input.
pool_top_vec_.clear();
pool_top_vec_.push_back(&pool_output_);
LayerParameter pool_param;
pool_param.mutable_pooling_param()->set_pool(
PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_AVE);
pool_param.mutable_pooling_param()->set_pad(pre_pad_);
pool_param.mutable_pooling_param()->set_kernel_size(size_);
pool_layer_.reset(new PoolingLayer<Dtype>(pool_param));
pool_layer_->SetUp(square_top_vec_, &pool_top_vec_);
// Set up power_layer_ to compute (1 + alpha_/N^2 s)^-beta_, where s is
// the sum of a squared neighborhood (the output of pool_layer_).
power_top_vec_.clear();
power_top_vec_.push_back(&power_output_);
LayerParameter power_param;
power_param.mutable_power_param()->set_power(-beta_);
power_param.mutable_power_param()->set_scale(alpha_);
power_param.mutable_power_param()->set_shift(Dtype(1));
power_layer_.reset(new PowerLayer<Dtype>(power_param));
power_layer_->SetUp(pool_top_vec_, &power_top_vec_);
// Set up a product_layer_ to compute outputs by multiplying inputs by the
// inverse demoninator computed by the power layer.
product_bottom_vec_.clear();
product_bottom_vec_.push_back(&product_input_);
product_bottom_vec_.push_back(&power_output_);
LayerParameter product_param;
EltwiseParameter* eltwise_param = product_param.mutable_eltwise_param();
eltwise_param->set_operation(EltwiseParameter_EltwiseOp_PROD);
product_layer_.reset(new EltwiseLayer<Dtype>(product_param));
product_layer_->SetUp(product_bottom_vec_, top);
}
}
这个函数实现了参数的初始化过程。首先从layer_param_对象中提取出size_的值,并检查是否为奇数,如果不是则报错;之后用size_计算pre_pad_的值,在前后各补一半0。接着alpha_和beta_也被初始化。如果是WITHIN_CHANNEL模式,那么还需要初始化一系列中间子层,这里我们不关心,因为我们用ACROSS_CHANNELS模式。这么简单,还是好开森~~
接下来看Reshape()函数的实现:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?


template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) {
num_ = bottom[0]->num();
channels_ = bottom[0]->channels();
height_ = bottom[0]->height();
width_ = bottom[0]->width();
switch (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region()) {
case LRNParameter_NormRegion_ACROSS_CHANNELS:
(*top)[0]->Reshape(num_, channels_, height_, width_);
scale_.Reshape(num_, channels_, height_, width_);
break;
case LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL:
split_layer_->Reshape(bottom, &split_top_vec_);
square_layer_->Reshape(square_bottom_vec_, &square_top_vec_);
pool_layer_->Reshape(square_top_vec_, &pool_top_vec_);
power_layer_->Reshape(pool_top_vec_, &power_top_vec_);
product_layer_->Reshape(product_bottom_vec_, top);
break;
}
}
首先根据bottom的尺寸初始化了num_, channels_, height_, width_这四个尺寸参数,之后根据归一化模式进行不同设置。在ACROSS_CHANNELS模式中,将top尺寸设置为和bottom一样大(num_,
channels_, height_, width_),然后将scale_的尺寸也设置为一样大,这样我们在进行归一化时,只要逐点将scale_值乘以bottom值,就得到相应的top值。scale_值需要根据文章开头的计算公式得到,我们进一步考察怎么实现。
看下一个函数:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?


template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) {
switch (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region()) {
case LRNParameter_NormRegion_ACROSS_CHANNELS:
CrossChannelForward_cpu(bottom, top);
break;
case LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL:
WithinChannelForward(bottom, top);
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown normalization region.";
}
}
很简单,根据归一化模式调用相应的Forward函数。我们这里看CrossChannelForward_cpu()这个函数,代码如下:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?


template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::CrossChannelForward_cpu(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = (*top)[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* scale_data = scale_.mutable_cpu_data();//用指针获取每个Blob对象的内存地址,便于后面操作
// start with the constant value
for (int i = 0; i < scale_.count(); ++i) {//初始化值为1.0
scale_data[i] = 1.;
}
Blob<Dtype> padded_square(1, channels_ + size_ - 1, height_, width_);//补零后的Blob,第三维尺寸比bottom大了size_ - 1;
Dtype* padded_square_data = padded_square.mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(padded_square.count(), Dtype(0), padded_square_data);//先清零
Dtype alpha_over_size = alpha_ / size_;//预先计算公式中的alpha/n
// go through the images
for (int n = 0; n < num_; ++n) {//bottom的第四维尺寸num_,需要分解为单个来做归一化
// compute the padded square
caffe_sqr(channels_ * height_ * width_,
bottom_data + bottom[0]->offset(n),
padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, pre_pad_));//计算bottom的平方,放入padded_square矩阵中,前pre_pad_个位置依旧0
// Create the first channel scale
for (int c = 0; c < size_; ++c) {//对n个通道平方求和并乘以预先算好的(alpha/n),累加至scale_中(实现计算 1 + sum_under_i(x_i^2))
caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, alpha_over_size,
padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, c),
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, 0));
}
for (int c = 1; c < channels_; ++c) {//这里使用了类似FIFO的形式计算其余scale_参数,每次向后移动一个单位,加头去尾,避免重复计算求和
// copy previous scale
caffe_copy<Dtype>(height_ * width_,
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c - 1),
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c));
// add head
caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, alpha_over_size,
padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, c + size_ - 1),
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c));
// subtract tail
caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, -alpha_over_size,
padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, c - 1),
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c));
}
}
// In the end, compute output
caffe_powx<Dtype>(scale_.count(), scale_data, -beta_, top_data);//计算求指数,由于将除法转换为乘法,故指数变负
caffe_mul<Dtype>(scale_.count(), top_data, bottom_data, top_data);//bottom .* scale_ -> top
}
可能你对caffe_axpy, caffe_sqr, caffe_powx, caffe_mul还不熟悉,其实都是很简单的数学计算,在CAFFE_ROOT/include/caffe/util/math_functions.hpp中有声明。
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?


template <typename Dtype>
void caffe_axpy(const int N, const Dtype alpha, const Dtype* X,
Dtype* Y);
实现如下操作:Y = alpha * X + Y;其中X, Y为N个元素的向量。
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?


template <typename Dtype>
void caffe_powx(const int n, const Dtype* a, const Dtype b, Dtype* y);
实现如下操作:y = a^b, 其中a, y为n个元素的向量,b为标量。
其余请自己推导。
LRN全称为Local Response Normalization,即局部响应归一化层,具体实现在CAFFE_ROOT/src/caffe/layers/lrn_layer.cpp和同一目录下lrn_layer.cu中。
该层需要参数有:
norm_region: 选择对相邻通道间归一化还是通道内空间区域归一化,默认为ACROSS_CHANNELS,即通道间归一化;
local_size:两种表示(1)通道间归一化时表示求和的通道数;(2)通道内归一化时表示求和区间的边长;默认值为5;
alpha:缩放因子(详细见后面),默认值为1;
beta:指数项(详细见后面), 默认值为5;
局部响应归一化层完成一种“临近抑制”操作,对局部输入区域进行归一化。
在通道间归一化模式中,局部区域范围在相邻通道间,但没有空间扩展(即尺寸为 local_size x 1 x 1);
在通道内归一化模式中,局部区域在空间上扩展,但只针对独立通道进行(即尺寸为 1 x local_size x local_size);
每个输入值都将除以
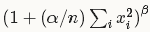
其中n为局部尺寸大小local_size,
alpha和beta前面已经定义。
求和将在当前值处于中间位置的局部区域内进行(如果有必要则进行补零)。
下面我们看Caffe代码如何实现。打开CAFFE_ROOT/include/caffe/vision_layers.hpp,从第242行开始看起:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?

// Forward declare PoolingLayer and SplitLayer for use in LRNLayer.
template <typename Dtype> class PoolingLayer;
template <typename Dtype> class SplitLayer;
/**
* @brief Normalize the input in a local region across or within feature maps.
*
* TODO(dox): thorough documentation for Forward, Backward, and proto params.
*/
template <typename Dtype>
class LRNLayer : public Layer<Dtype> {
public:
explicit LRNLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
: Layer<Dtype>(param) {}
virtual void LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual inline LayerParameter_LayerType type() const {
return LayerParameter_LayerType_LRN;
}
virtual inline int ExactNumBottomBlobs() const { return 1; }
virtual inline int ExactNumTopBlobs() const { return 1; }
protected:
virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
virtual void CrossChannelForward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void CrossChannelForward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void WithinChannelForward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top);
virtual void CrossChannelBackward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
virtual void CrossChannelBackward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
virtual void WithinChannelBackward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom);
int size_;
int pre_pad_;
Dtype alpha_;
Dtype beta_;
int num_;
int channels_;
int height_;
int width_;
// Fields used for normalization ACROSS_CHANNELS
// scale_ stores the intermediate summing results
Blob<Dtype> scale_;
// Fields used for normalization WITHIN_CHANNEL
shared_ptr<SplitLayer<Dtype> > split_layer_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> split_top_vec_;
shared_ptr<PowerLayer<Dtype> > square_layer_;
Blob<Dtype> square_input_;
Blob<Dtype> square_output_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> square_bottom_vec_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> square_top_vec_;
shared_ptr<PoolingLayer<Dtype> > pool_layer_;
Blob<Dtype> pool_output_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> pool_top_vec_;
shared_ptr<PowerLayer<Dtype> > power_layer_;
Blob<Dtype> power_output_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> power_top_vec_;
shared_ptr<EltwiseLayer<Dtype> > product_layer_;
Blob<Dtype> product_input_;
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> product_bottom_vec_;
};
内容较多,可能看一眼记不住所有的成员变量和函数,但记住一点,凡是Layer类型肯定都包含Forward()和Backward(),以及LayerSetUp()和Reshape(),这些在头文件中不必细看。关注的是以“_”结尾的成员变量,这些是和算法息息相关的。
很高兴看到了num_, height_, width_, channels_,这四个变量定义了该层输入图像的尺寸信息,是一个num_ x channels_ x height_ x width_的四维Blob矩阵(想不通?就当作视频流吧,前两维是宽高,第三维是颜色,第四维是时间)。
另外看到了alpha_, beta_, 这两个就是我们上面公式中的参数。
公式中的n(local_size)在类中用size_表示。
上面提到过需要补零,所以定义了pre_pad_变量。
在ACROSS_CHANNELS模式下,我们只需要用到scale_这个Blob矩阵,后面定义都可以忽略了~~好开森~~
读完了头文件中的声明,是不是觉得挺简单?我们接着看下实现细节,打开CAFFE_ROOT/src/caffe/layers/lrn_layer.cpp,从头看起,第一个实现函数为LayerSetUp(),代码如下:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?

template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) {
size_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().local_size();
CHECK_EQ(size_ % 2, 1) << "LRN only supports odd values for local_size";
pre_pad_ = (size_ - 1) / 2;
alpha_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().alpha();
beta_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().beta();
if (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region() ==
LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL) {
// Set up split_layer_ to use inputs in the numerator and denominator.
split_top_vec_.clear();
split_top_vec_.push_back(&product_input_);
split_top_vec_.push_back(&square_input_);
LayerParameter split_param;
split_layer_.reset(new SplitLayer<Dtype>(split_param));
split_layer_->SetUp(bottom, &split_top_vec_);
// Set up square_layer_ to square the inputs.
square_bottom_vec_.clear();
square_top_vec_.clear();
square_bottom_vec_.push_back(&square_input_);
square_top_vec_.push_back(&square_output_);
LayerParameter square_param;
square_param.mutable_power_param()->set_power(Dtype(2));
square_layer_.reset(new PowerLayer<Dtype>(square_param));
square_layer_->SetUp(square_bottom_vec_, &square_top_vec_);
// Set up pool_layer_ to sum over square neighborhoods of the input.
pool_top_vec_.clear();
pool_top_vec_.push_back(&pool_output_);
LayerParameter pool_param;
pool_param.mutable_pooling_param()->set_pool(
PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_AVE);
pool_param.mutable_pooling_param()->set_pad(pre_pad_);
pool_param.mutable_pooling_param()->set_kernel_size(size_);
pool_layer_.reset(new PoolingLayer<Dtype>(pool_param));
pool_layer_->SetUp(square_top_vec_, &pool_top_vec_);
// Set up power_layer_ to compute (1 + alpha_/N^2 s)^-beta_, where s is
// the sum of a squared neighborhood (the output of pool_layer_).
power_top_vec_.clear();
power_top_vec_.push_back(&power_output_);
LayerParameter power_param;
power_param.mutable_power_param()->set_power(-beta_);
power_param.mutable_power_param()->set_scale(alpha_);
power_param.mutable_power_param()->set_shift(Dtype(1));
power_layer_.reset(new PowerLayer<Dtype>(power_param));
power_layer_->SetUp(pool_top_vec_, &power_top_vec_);
// Set up a product_layer_ to compute outputs by multiplying inputs by the
// inverse demoninator computed by the power layer.
product_bottom_vec_.clear();
product_bottom_vec_.push_back(&product_input_);
product_bottom_vec_.push_back(&power_output_);
LayerParameter product_param;
EltwiseParameter* eltwise_param = product_param.mutable_eltwise_param();
eltwise_param->set_operation(EltwiseParameter_EltwiseOp_PROD);
product_layer_.reset(new EltwiseLayer<Dtype>(product_param));
product_layer_->SetUp(product_bottom_vec_, top);
}
}
这个函数实现了参数的初始化过程。首先从layer_param_对象中提取出size_的值,并检查是否为奇数,如果不是则报错;之后用size_计算pre_pad_的值,在前后各补一半0。接着alpha_和beta_也被初始化。如果是WITHIN_CHANNEL模式,那么还需要初始化一系列中间子层,这里我们不关心,因为我们用ACROSS_CHANNELS模式。这么简单,还是好开森~~
接下来看Reshape()函数的实现:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?

template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) {
num_ = bottom[0]->num();
channels_ = bottom[0]->channels();
height_ = bottom[0]->height();
width_ = bottom[0]->width();
switch (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region()) {
case LRNParameter_NormRegion_ACROSS_CHANNELS:
(*top)[0]->Reshape(num_, channels_, height_, width_);
scale_.Reshape(num_, channels_, height_, width_);
break;
case LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL:
split_layer_->Reshape(bottom, &split_top_vec_);
square_layer_->Reshape(square_bottom_vec_, &square_top_vec_);
pool_layer_->Reshape(square_top_vec_, &pool_top_vec_);
power_layer_->Reshape(pool_top_vec_, &power_top_vec_);
product_layer_->Reshape(product_bottom_vec_, top);
break;
}
}
首先根据bottom的尺寸初始化了num_, channels_, height_, width_这四个尺寸参数,之后根据归一化模式进行不同设置。在ACROSS_CHANNELS模式中,将top尺寸设置为和bottom一样大(num_,
channels_, height_, width_),然后将scale_的尺寸也设置为一样大,这样我们在进行归一化时,只要逐点将scale_值乘以bottom值,就得到相应的top值。scale_值需要根据文章开头的计算公式得到,我们进一步考察怎么实现。
看下一个函数:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?

template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) {
switch (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region()) {
case LRNParameter_NormRegion_ACROSS_CHANNELS:
CrossChannelForward_cpu(bottom, top);
break;
case LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL:
WithinChannelForward(bottom, top);
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown normalization region.";
}
}
很简单,根据归一化模式调用相应的Forward函数。我们这里看CrossChannelForward_cpu()这个函数,代码如下:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?

template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::CrossChannelForward_cpu(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = (*top)[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* scale_data = scale_.mutable_cpu_data();//用指针获取每个Blob对象的内存地址,便于后面操作
// start with the constant value
for (int i = 0; i < scale_.count(); ++i) {//初始化值为1.0
scale_data[i] = 1.;
}
Blob<Dtype> padded_square(1, channels_ + size_ - 1, height_, width_);//补零后的Blob,第三维尺寸比bottom大了size_ - 1;
Dtype* padded_square_data = padded_square.mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(padded_square.count(), Dtype(0), padded_square_data);//先清零
Dtype alpha_over_size = alpha_ / size_;//预先计算公式中的alpha/n
// go through the images
for (int n = 0; n < num_; ++n) {//bottom的第四维尺寸num_,需要分解为单个来做归一化
// compute the padded square
caffe_sqr(channels_ * height_ * width_,
bottom_data + bottom[0]->offset(n),
padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, pre_pad_));//计算bottom的平方,放入padded_square矩阵中,前pre_pad_个位置依旧0
// Create the first channel scale
for (int c = 0; c < size_; ++c) {//对n个通道平方求和并乘以预先算好的(alpha/n),累加至scale_中(实现计算 1 + sum_under_i(x_i^2))
caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, alpha_over_size,
padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, c),
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, 0));
}
for (int c = 1; c < channels_; ++c) {//这里使用了类似FIFO的形式计算其余scale_参数,每次向后移动一个单位,加头去尾,避免重复计算求和
// copy previous scale
caffe_copy<Dtype>(height_ * width_,
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c - 1),
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c));
// add head
caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, alpha_over_size,
padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, c + size_ - 1),
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c));
// subtract tail
caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, -alpha_over_size,
padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, c - 1),
scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c));
}
}
// In the end, compute output
caffe_powx<Dtype>(scale_.count(), scale_data, -beta_, top_data);//计算求指数,由于将除法转换为乘法,故指数变负
caffe_mul<Dtype>(scale_.count(), top_data, bottom_data, top_data);//bottom .* scale_ -> top
}
可能你对caffe_axpy, caffe_sqr, caffe_powx, caffe_mul还不熟悉,其实都是很简单的数学计算,在CAFFE_ROOT/include/caffe/util/math_functions.hpp中有声明。
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?

template <typename Dtype>
void caffe_axpy(const int N, const Dtype alpha, const Dtype* X,
Dtype* Y);
实现如下操作:Y = alpha * X + Y;其中X, Y为N个元素的向量。
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?

template <typename Dtype>
void caffe_powx(const int n, const Dtype* a, const Dtype b, Dtype* y);
实现如下操作:y = a^b, 其中a, y为n个元素的向量,b为标量。
其余请自己推导。
相关文章推荐
- javascript 判断是否是数组
- JS实现浏览器全屏和退出全屏
- caffe 中的损失函数分析
- Jquery 动态生成li标签以及单击事件的绑定
- json各种技术
- HTML常用符号
- jsp生成html
- SharedPreferences详解
- 微博登录界面的实现
- JavaScript数组的栈方法与队列方法详解
- H5页面实现一个Audio标签加载多个音频文件,并进行播放和展示音频长度
- 作为前端应当了解的Web缓存知识
- 详解JavaScript中this关键字的用法
- jquery form表单序列号
- jquery-$()参数详解
- 媒体查询常用样式表
- 【转载】jQuery手机移动端触屏日历日期选择
- 使用Bootstrap组件【下篇】
- angularJs控制器执行顺序
- js 使用总结
