HDU 5251 矩形面积(二维凸包旋转卡壳最小矩形覆盖问题) --2015百度之星题目
2016-05-19 22:02
731 查看
B - 矩形面积
Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u
Submit Status
Description
小度熊有一个桌面,小度熊剪了很多矩形放在桌面上,小度熊想知道能把这些矩形包围起来的面积最小的矩形的面积是多少。
Input
第一行一个正整数 T,代表测试数据组数(




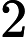

),接下来 T 组测试数据。
每组测试数据占若干行,第一行一个正整数

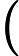



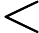





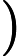
,代表矩形的数量。接下来 N 行,每行 8 个整数
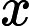


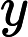


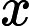


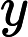


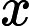
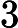

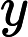
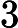

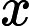
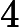

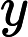
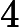
,代表矩形的四个点坐标,坐标绝对值不会超过10000。
Output
对于每组测试数据,输出两行:
第一行输出"Case #i:",i 代表第 i 组测试数据。
第二行包含1 个数字,代表面积最小的矩形的面积,结果保留到整数位。
Sample Input
2
2
5 10 5 8 3 10 3 8
8 8 8 6 7 8 7 6
1
0 0 2 2 2 0 0 2
Sample Output
Case #1:
17
Case #2:
4
题意:给出n个矩形,求能覆盖所有矩形的最小的矩形的面积。
题解:对所有点求凸包,然后旋转卡壳,对没一条边求该边的最左最右和最上的三个点。
利用叉积面积求高,利用点积的性质求最左右点和长度,更新面积最小值即可。
分析过程:

Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u
Submit Status
Description
小度熊有一个桌面,小度熊剪了很多矩形放在桌面上,小度熊想知道能把这些矩形包围起来的面积最小的矩形的面积是多少。
Input
第一行一个正整数 T,代表测试数据组数(




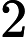

),接下来 T 组测试数据。
每组测试数据占若干行,第一行一个正整数

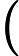









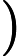
,代表矩形的数量。接下来 N 行,每行 8 个整数
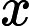


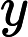


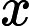


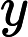


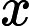
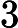

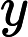
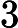

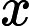
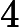

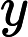
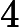
,代表矩形的四个点坐标,坐标绝对值不会超过10000。
Output
对于每组测试数据,输出两行:
第一行输出"Case #i:",i 代表第 i 组测试数据。
第二行包含1 个数字,代表面积最小的矩形的面积,结果保留到整数位。
Sample Input
2
2
5 10 5 8 3 10 3 8
8 8 8 6 7 8 7 6
1
0 0 2 2 2 0 0 2
Sample Output
Case #1:
17
Case #2:
4
题意:给出n个矩形,求能覆盖所有矩形的最小的矩形的面积。
题解:对所有点求凸包,然后旋转卡壳,对没一条边求该边的最左最右和最上的三个点。
利用叉积面积求高,利用点积的性质求最左右点和长度,更新面积最小值即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#define MAX 50010
using namespace std;
struct Point{
double x,y;
Point(double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y){}
};
Point P[MAX],ch[MAX];
typedef Point Vector;
typedef Point point;
Vector operator - (Point A,Point B)
{
return Vector(A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y);
}
bool operator <(const Point &a,const Point &b)
{
return a.x<b.x||(a.x==b.x&&a.y<b.y);
}
const double eps=1e-10;
int dcmp(double x)
{
if(fabs(x)<eps) return 0; else return x<0?-1:1;
}
bool operator ==(const Point &a,const Point &b)
{
return dcmp(a.x-b.x)==0&&dcmp(a.y-b.y)==0;
}
double Cross(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x;
}
double dot(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.x+A.y*B.y;
}
int ConvexHull(Point *p,int n)
{
sort(p,p+n);
n=unique(p,p+n)-p;
int m=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
while(m>1&&Cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2],p[i]-ch[m-2])<=0) m--;
ch[m++]=p[i];
}
int k=m;
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)
{
while(m>k&&Cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2],p[i]-ch[m-2])<=0) m--;
ch[m++]=p[i];
}
if(n>1) m--;
return m;
}
double Length(Vector A)
{
return dot(A,A);
}
double rotating_calipers(Point *p,int n)
{
int l=1,r=1,w;
double ans=1e30;
p
=p[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
//注意这里等于0一定要算上
//这里debug了整整一个小时 - -|||||
//找到至高点
while(dcmp(Cross(p[i+1]-p[i],p[w+1]-p[i])-Cross(p[i+1]-p[i],p[w]-p[i]))>=0) //因为边平行的时候面积相等 虽然如此但还是要继续找下一个 横着爬不动的意思
w=(w+1)%n;
//找到最右的点 不可能向左的
while(dcmp(dot(p[i+1]-p[i],p[r+1]-p[i])-dot(p[i+1]-p[i],p[r]-p[i]))>0) //凸包不可能凹进去 所以不需要等号 加深对凸包求解过程的理解
r=(r+1)%n;
if(i==0) l=r;
while(dcmp(dot(p[i+1]-p[i],p[l+1]-p[i])-dot(p[i+1]-p[i],p[l]-p[i]))<=0) //必须加等号 否则凸包遇到直边的时候拐不过来 上不去 第二组样例可以完美说明问题
l=(l+1)%n;
double d=Length(p[i+1]-p[i]);
double area=fabs(Cross(p[i+1]-p[i],p[w]-p[i]))
*fabs(dot(p[i+1]-p[i],p[r]-p[i])-dot(p[i+1]-p[i],p[l]-p[i]))/d;
//cout<<fabs(Cross(p[i+1]-p[i],p[w]-p[i]))<<" "; 这里灵活运用点积求底边长度 上面那一整行化简后就是底边长度
//cout<<"rrrrr "<<r<<" lll "<<l<<endl;
//cout<<dot(p[i+1]-p[i],p[r]-p[i])<<" "<<dot(p[i+1]-p[i],p[l]-p[i])<<endl;
ans=min(ans,area);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int t,n,cas=1;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
n*=4;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf",&P[i].x,&P[i].y);
int m=ConvexHull(P,n);
//for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
//cout<<ch[i].x<<" "<<ch[i].y<<endl;
double ans;
if(m<3) ans=0;
else ans=rotating_calipers(ch,m);
long long tmp = ans+0.5;
printf("Case #%d:\n%lld\n",cas++,tmp);
}
return 0;
}分析过程:

相关文章推荐
- Apache 禁止指定user_agent(防止爬虫扒取)
- Android studio Gradle icon error, Manifest Merger
- 渣渣表示很难
- android安卓触摸事件touchEvent分发的 核心精辟代码
- extends Thread 与 implements Runnable 的区别
- Linux面试题(2)
- 分布式环境下rabbitmq发布与订阅端
- 机器指令与微指令的关系
- 2016 ICPC World Finals -Ceiling Function
- php中final关键字
- SQL、HQL中left join、right join、inner join的区别
- JAVA设计模式(21):行为型-迭代器模式(Iterator)
- 04 替换空格
- 水题只会让自己更水,告别水题
- Apache访问控制
- poj 2653 线段与线段相交
- Extjs MVC架构 (官方文档翻译)【带源码】
- 创建tornado应用输出hello world
- Eclipse添加注释模板
- TensorFlow Machine Learning with Financial Data on Google Cloud Platform
